Abstract
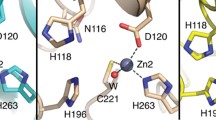
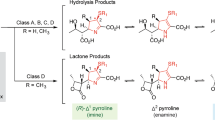
Metallo-β-lactamases are zinc-ion-dependent and are known to exist either as mononuclear or as dinuclear enzymes. The kinetics and mechanism of hydrolysis of the native zinc Bacillus cereus metallo-β-lactamase (BcII) have been investigated under pre-steady-state conditions at different pHs and zinc-ion concentrations. Biphasic kinetics are observed for the hydrolysis of cefuroxime and benzylpenicillin with submicromolar concentrations of enzyme and zinc. The initial burst of product formation far exceeds the concentration of enzyme and the subsequent slower rate of hydrolysis is attributed to a branched kinetic pathway. The pH and metal-ion dependence of the microscopic rate constants of this branching were determined, from which it is concluded that two enzyme species with different metal-to-enzyme stoichiometries are formed during catalytic turnover. The dizinc enzyme is responsible for the fast route but during the catalytic cycle it slowly loses the less tightly bound zinc ion via the branching route to give an inactive monozinc enzyme; the latter is only catalytic following the uptake of a second zinc ion. The rate constant for product formation from the dinuclear enzyme and the branching rate constant show a sigmoidal dependence on pH indicative of important ionizing groups with pK as of 9.0 ± 0.1 and 8.2 ± 0.1, respectively. The rate constant for the regeneration of enzyme activity depends on zinc-ion concentration. This unusual behaviour is attributed to an intrinsic property of metallo hydrolytic enzymes that depend on a metal bound water both as a ligand for the second metal ion and as the nucleophile which is consumed during hydrolysis of the substrate and so has to be replaced to maintain the catalytic cycle.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frère JM (1995) Mol Microbiol 16:385–395
Fisher JD, Meroueh SO, Mobashery S (2005) Chem Rev 105:395–424
Galleni M, Lamotte-Brasseur J, Rossolini GM, Spencer J, Dideberg O, Frère JM (2001) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:660–663
Fabiane SM, Sohi MK, Wan T, Payne DJ, Bateson JH, Mitchell T, Sutton BJ (1998) Biochemistry 37:12404–12411
Orellano EG, Girardini JE, Cricco JA, Ceccarelli EA, Vila AJ (1998) Biochemistry 37:10173–10180
Paul-Soto R, Bauer R, Frère JM, Galleni M, Meyer-Klaucke W, Nolting H, Rossolini GM, de Seny D, Hernandez-Valladares M, Zeppezauer M, Adolph HW (1999) J Biol Chem 274:13242–13249
Crowder MW, Walsh TR (1999) Recent Res Dev Antimicrob Agents Chemother 3:105–132
Fitzgerald PM, Wu JK, Toney JH (1998) Biochemistry 37:6791–6800
Concha NO, Rasmussen BA, Bush K, Herzberg O (1997) Protein Sci 6:2671–2676
Toney JH, Fitzgerald PM, Grover-Sharma N, Olson SH, May WJ, Sundelof JG, Vanderwall DE, Cleary KA, Grant SK, Wu JK, Kozarich JW, Pompliano DL, Hammond GG (1998) Chem Biol 5:185–196
Carfi A, Pares S, Duee E, Galleni M, Duez C, Frère JM, Dideberg O (1995) EMBO J 1995 14:4914–4921
Carfi A, Duee E, Galleni M, Frère JM, Dideberg O (1998) Acta Crystallogr Biol Crystallogr D54:313–323
Concha NO, Rasmussen BA, Bush K, Herzberg O (1996) Structure 4:823–836
Carfi A, Duee E, Paul-Soto R, Galleni M, Frère JM, Dideberg O (1998) Acta Crystallogr Biol Crystallogr D54:45–57
Paul-Soto R, Zeppezauer M, Adolph HW, Galleni M, Frère JM, Carfi A, Dideberg O, Wouter J, Hemmingsen L, Bauer R (1999) Biochemistry 38:16500–16506
Concha NO, Janson CA, Rowling P, Pearson S, Cheever CA, Clarke BP, Lewis C, Galleni M, Frère JM, Payne DJ, Bateson JH, Abdel-Meguid SS (2000) Biochemistry 39:4288–4298
de Seny D, Heinz U, Wommer S, Kiefer M, Meyer-Klaucke W, Galleni M, Frère JM, Bauer R, Adolph HW (2001) J Biol Chem 276:45065–45078
Wommer S, Rival S, Heinz U, Galleni M, Frère JM, Franceschini N, Amicosante G, Rasmussen B, Bauer R, Adolph HW (2002) J Biol Chem 277:24142–24147
Crowder MW, Wang Z, Franklin SL, Zovinka EP, Benkovic SJ (1996) Biochemistry 35:12126–12132
Fast W, Wang Z, Benkovic SJ (2001) Biochemistry 40:1640–1650
Badarau A, Page MI (2006) Biochemistry 45:11012–11020
Bicknell R, Waley SG (1985) Biochemistry 24:6876–6887
Rasia RM, Vila AJ (2002) Biochemistry 41:1853–1860
Bounaga S, Laws AP, Galleni M, Page MI (1998) Biochem J 331:703–711
Rasia RM, Vila AJ (2004) J Biol Chem 279:26046–26051
Davies AM, Rasia RM, Vila AJ, Sutton BJ, Fabiane SM (2005) Biochemistry 44:4841–4849
De Seny D, Prosperi-Meys C, Bebrone C, Rossolini GM, Page MI, Noel P, Frere JM, Galleni M (2002) Biochem J 363:687–696
Heinz U, Kiefer M, Tholey A, Adolph HW (2005) J Biol Chem 280:3197–3207
Llarrull LL, Tioni MF, Kowalski J, Bennett B, Vila AJ (2007) J Biol Chem 282:30586–30595
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the European Union research network on MBLs within the Training and Mobility of Researchers (TMR) Program, contract number HPRN-CT-2002-00264, and the University of Huddersfield.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badarau, A., Page, M.I. Loss of enzyme activity during turnover of the Bacillus cereus β-lactamase catalysed hydrolysis of β-lactams due to loss of zinc ion. J Biol Inorg Chem 13, 919–928 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-008-0379-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-008-0379-2