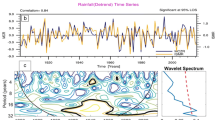
Summary
The present study examines the long term trend in sea surface temperatures (SSTs) of the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal and Equatorial South India Ocean in the context of global warming for the period 1901–2002 and for a subset period 1971–2002. An attempt has also been made to identify the relationship between SST variations over three different ocean areas, and All-India and homogeneous region summer monsoon rainfall variability, including the role of El-Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Annual sea surface temperatures of the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal and Equatorial South India Ocean show a significant warming trend of 0.7 °C, 0.6 °C and 0.5 °C per hundred years, respectively, and a relatively accelerated warming of 0.16 °C, 0.14 °C and 0.14 °C per decade during the 1971–2002 period.
There is a positive and statistically significant relationship between SSTs over the Arabian Sea from the preceding November to the current February, and Indian monsoon rainfall during the period 1901–2002. The correlation coefficient increases from October and peaks in December, decreasing from February to September. This significant relationship is also found in the recent period 1971–2002, whereas, during 1901–70, the relationship is not significant. On the seasonal scale, Arabian Sea winter SSTs are positively and significantly correlated with Indian monsoon rainfall, while spring SSTs have no significant positive relationship. Nino3 spring SSTs have a negative significant relationship with Indian monsoon rainfall and it is postulated that there is a combined effect of Nino3 and Arabian Sea SSTs on Indian monsoon. If the Nino3 SST effect is removed, the spring SSTs over the Arabian Sea also have a significant relationship with monsoon rainfall. Similarly, the Bay of Bengal and Equatorial South Indian Ocean spring SSTs are significantly and positively correlated with Indian monsoon rainfall after removing the Nino3 effect, and correlation values are more pronounced than for the Arabian Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CO Clark JE Cole PJ Webster (2000) ArticleTitleIndian Ocean SST and Indian summer rainfall: predictive relationships and their decadal variability J Climate 13 2503–2519 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<2503:IOSAIS>2.0.CO;2
SK Dash MS Shekher GP Sigh (2002) ArticleTitleRelationship between surface fields over: 1. Indian ocean and monsoon rainfall over homogeneous zones of India Mausam 53 133–144
MS Halpert CF Ropelewski (1992) ArticleTitleSurface temperature patterns associated with the Southern Oscillation J Climate 5 557–593 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(1992)005<0577:STPAWT>2.0.CO;2
IPCC (2001) Climate Change 2001: The scientific basis, Contribution of Working Group-I to the Third Assessment Report of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 881 pp
Kothawale DR (2005) Surface and Upper-Air temperature variability over India and its influence on the summer monsoon rainfall, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pune, Pune, 212 pp
KM Lau S Yang (1996) ArticleTitleThe Asian monsoon and predictability of the tropical Ocean-atmosphere system Quart J Roy Meteor Soc 122 945–957
T Nitta S Yamada (1989) ArticleTitleRecent warming of tropical sea surface temperatures and its relationship to the Northern Hemisphere circulation J Meteor Soc Japan 67 375–383
GB Pant K Rupa Kumar (1997) Climate of South Asia John Wiley and Sons Chichester 320
B Parthasarathy K Rupa Kumar DR Kothawale (1992) ArticleTitleIndian summer monsoon indices: 1871–1990 Meteorol Mag 121 IssueID1441 174–186
Parthasarathy B, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1995) Monthly and seasonal rainfall series for All-India homogeneous regions and meteorological subdivisions: 1871–1994, I. I. T. M. research report No. RR-65
M Rajeevan US De RK Prasad (2000) ArticleTitleDecadal variation of sea surface temperatures, cloudiness and monsoon depression in the north Indian ocean, current Science 79 IssueID3 283–285
KG Rao BN Goswami (1988) ArticleTitleInterannual variations of sea surface temperature over the Arabian Sea and the Indian monsoon: a new perspective Mon Wea Rev 116 558–568 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1988)116<0558:IVOSST>2.0.CO;2
J Shukla (1975) ArticleTitleEffect of Arabian Sea surface temperature anomaly on Indian summer monsoon: a numerical experiment with the GFDL Model J Atmos Sci 32 503–511 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0469(1975)032<0503:EOASST>2.0.CO;2
J Shukla DA Mooley (1987) ArticleTitleEmpirical prediction of the summer monsoon rainfall over India Mon Wea Rev 115 695–703 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<0695:EPOTSM>2.0.CO;2
OP Singh (2000) ArticleTitleRecent trends in summer temperatures over the North Indian Ocean Indian J Marine Sci 29 7–11
V Thapliyal M Rajeevan SR Patil (1998) ArticleTitleRelationship between Indian summer monsoon rainfall and sea surface temperature anomalies over equatorial central and eastern Pacific Mausam 2 229–234
Tim Li Zhang Yongsheng CP Chang Bin Wang (2001) ArticleTitleOn the relationship between Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature and Asian summer monsoon Geophys Res Lett 28 IssueID14 2843–2846 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2000GL011847
GT Walker (1918) ArticleTitleCorrelation in seasonal variation of weather Quart J Roy Meteor Soc 44 223–234
**n Wang Li Chongyin Wen Zhou (2006) ArticleTitleInterdecadal variation of the relationship between Indian rainfall and SSTA modes in the Indian Ocean Int J Climatol 26 595–606 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1283
PJ Webster VO Magana TN Palmer J Shukla M Tomas M Yanni T Yasunari (1998) ArticleTitleMonsoon Process, predictability, and the prospect for predication J Geophys Res 103-C7 14451–14510 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97JC02719
TML Wigley PD Jones (1981) ArticleTitleDetecting CO2 induced climatic change Nature 292 205–208 Occurrence Handle10.1038/292205a0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Authors’ address: Dr. D. R. Kothawale, A. A. Munot, H. P. Borgaonkar, Climatology and Hydrometeorology divisions, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune 411008, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kothawale, D., Munot, A. & Borgaonkar, H. Temperature variability over the Indian Ocean and its relationship with Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Theor Appl Climatol 92, 31–45 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-006-0291-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-006-0291-z