Summary.
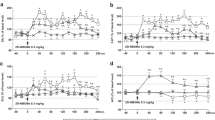
Acute GABA transporter inhibition can induce anxiolytic-like behaviors. The present analysis addressed whether chronic treatment (23 days via drinking water) with a GABA transporter inhibitor affects rat behavior similar to acute treatment and interferes with additional benzodiazepine-receptor agonistic treatment. Seventy-one rats divided into seven groups were acutely treated with either vehicle, diazepam (2 mg/kg), zolpidem (0.05 mg/kg), tiagabine (19 mg/kg) or chronically with tiagabine with or without acute diazepam or zolpidem. Animals were behaviorally characterized in an elevated plus-maze. None of the treatments induced changes in the activity of the animals. Acute and chronic treatment with tiagabine induced anxiolytic-like effects, similar to acute doses of diazepam. Acute diazepam did not enhance chronic tiagabine effects, whereas acute zolpidem attenuated the anxiolytic-like effects of chronic tiagabine. It is concluded that anxiolytic effects of acute GABA-uptake inhibition by tiagabine persist under chronic treatment and are sensitive to concomitant use of benzodiazepine receptor ligands.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 26, 2001; accepted January 30, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitt, U., Lüddens, H. & Hiemke, C. Anxiolytic-like effects of acute and chronic GABA transporter inhibition in rats. J Neural Transm 109, 871–880 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020200071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020200071