Abstract
A magnetic β-cyclodextrin (MCD) surface molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based on deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as cross-linker and functional monomer (MCD@DES-MIP) was successfully synthesized for the specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin (BHb). The adsorption behavior of MCD@DES-MIP for BHb was investigated by adsorption thermodynamics, adsorption kinetics, and pH control experiments. The maximum adsorption capacity of MCD@DES-MIP for BHb under the optimized conditions was 195.94 mg g−1 and the imprinting factor was 4.68. In addition, the competitive adsorption experiments demonstrated that MCD@DES-MIP showed excellent selective extraction ability for BHb in the binary mixture of BHb and bovine serum albumin (BSA). The actual sample analysis manifested that MCD@DES-MIP effectively separated BHb from complex samples. The results of circular dichroism spectra proved that the secondary structure of BHb did not change during elution. The result indicated that MCD@DES-MIP can be used as a new imprinting material for the separation and purification of BHb.
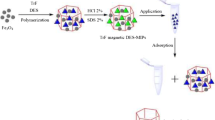
Graphical abstract

Magnetic imprinted microspheres (MCD@DES-MIP) were prepared by free radical polymerization using magnetic β-cyclodextrin (MCD) as carrier, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as functional monomer and cross-linker. MCD@DES-MIP show high adsorption capacity and excellent selectivity for BHb.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guan HY, Wang JD, Tan SY, Liang QL (2020) A facile method to synthesize magnetic nanoparticles chelated with copper (II) for selective adsorption of bovine hemoglobin. Korean J Chem Eng 37:1097–1106
Kishore KRT, Katarzyna S, Mark L, Dimitrios FS (2013) A metal ion charged mixed matrix membrane for selective adsorption of hemoglobin. Sep Purif Technol 115:20–26
Duan HM, Wang XJ, Wang YH, Li JB, Luo CN (2015) Bioreceptor multi-walled carbon nanotubes@Fe3O4@SiO2-surface molecular imprinted polymer in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescent biosensor for bovine hemoglobin. RSC Adv 5:88492–88499
Thayyath SA, Sheeba A (2017) A potentiometric sensor for the trace level determination of hemoglobin in real samples using multiwalled carbon nanotube based molecular imprinted polymer. Eur Polym J 97:84–93
Wang JD, Tan SY, Liang QL, Guan HY (2019) Selective separation of bovine hemoglobin using magnetic mesoporous rare-earth silicate microspheres. Talanta 204:792–801
Poma A, Guerreiro A, Whitcombe MJ, Piletska EV (2013) Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles with a reusable template-“plastic antibodies”. Adv Funct Mater 23:2821–2827
Shi W, Zhang SQ, Li KB, Jia WP, Han DM (2018) Integration of mixed-mode chromatography and molecular imprinting technology for double recognition and selective separation of proteins. Sep Purif Technol 202:165–173
Wang JD, Tan SY, Liang QL (2018) Preparation of magnetic microspheres functionalized by lanthanide oxides for selective isolation of bovine hemoglobin. Talanta 190:210–218
Shen R, Tang JJ, Zhang ZY (2009) New magnetic beads-based enzyme linked aptamer colorimetric assay for trace amount protein detection. Chem Res Chin Univ 4:701–705
Moein MM (2021) Advancements of chiral molecularly imprinted polymers in separation and sensor fields: a review of the last decade. Talanta 224:121794
Yuan XC, Gao X, **ong ZL, Zhao LS (2021) Fe3O4/graphene molecularly imprinted composite for selective separation of catecholamine neurotransmitters and their analysis in rat brain tissues. Talanta 224:121843
Bagheri AR, Arabi M, Ghaedi M, Chen LX (2019) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on a green synthesis strategy for magnetic solid-phase extraction of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 195:390–400
Han WY, Han X, Ou LL, Fu GQ (2020) Facile modification of protein-imprinted polydopamine coatings over nanoparticles with enhanced binding selectivity. Chem Eng J 385:123463
Xu W, Dai QZ, Wang YZ, Hu XJ (2018) Creating magnetic ionic liquid-molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of lysozyme. RSC Adv 8:21850–21856
Chrzanowska AM, Díaz-Álvarez M, Wieczorek PP, Poliwoda A (2019) The application of the supported liquid membrane and molecularly imprinted polymers as solid acceptor phase for selective extraction of biochanin a from urine. J Chromatogr A 1599:9–16
Yao J, Chen M, Li NN, Liu CH (2019) Experimental and theoretical studies of a novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and B, N, F-CQDs/AgNPs for enhanced specific identification and dual signal amplification in highly selective and ultra-trace bisphenol S determination in plastic products. Anal Chim Acta 1066:36–48
Liu LT, Chen MJ, Yang HL, Gong CB (2020) An NIR-light-responsive surface molecularly imprinted polymer for photoregulated drug release in aqueous solution through porcine tissue. Mater Sci Eng C 106:110253
Ansari S, Masoum S (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers for capturing and sensing proteins: current progress and future implications. TrAC-Trends in Anal Chem 114:29–47
Iskierko Z, Sharma PS, Noworyta KR (2019) Selective PQQPFPQQ gluten epitope chemical sensor with a molecularly imprinted polymer recognition unit and an extended-gate field-effect transistor transduction unit. Anal Chem 91:4537–4543
Yang ZT, Chen JJ, Wang JQ, Zhang BL (2020) Self-driven BSA surface imprinted magnetic tubular carbon nanofibers: fabrication and adsorption performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:3241–3252
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Niu MC, Pham-Huy C, He H (2016) Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Microchim Acta 183:2677–2695
Liu ZW, Wang YZ, Xu FT, Wei XX (2020) A new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on deep eutectic solvents as functional monomer and cross-linker for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Anal Chim Acta 1129:49–59
Liu YJ, Wang YZ, Dai QZ, Zhou YG (2016) Magnetic deep eutectic solvents molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition and separation of protein. Anal Chim Acta 936:168–178
Xu W, Wang YZ, Wei XX, Chen J (2019) Fabrication of magnetic polymers based on deep eutectic solvent for separation of bovine hemoglobin via molecular imprinting technology. Anal Chim Acta 1048:1–11
Xu KJ, Wang YZ, Wei XX, Chen J (2018) Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on a deep eutectic solvent as the functional monomer for specific recognition of lysozyme. Microchim Acta 185:1–8
Perna FM, Vitale P, Capriati V (2020) Deep eutectic solvents and their applications as green solvents. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 21:27–33
Liu DS, Huang Z, Li MN, Sun P (2019) Novel porous magnetic nanospheres functionalized by β-cyclodextrin polymer and its application in organic pollutants from aqueous solution. Environ Pollut 250:639–649
Xu KJ, Wang YZ, Li YX, Zhang HB (2016) A novel poly (deep eutectic solvent)-based magnetic silica composite for solid-phase extraction of trypsin. Anal Chim Acta 946:64–72
Gao RX, Mu XR, Hao Y, Zhang LL (2014) Combination of surface imprinting and immobilized template techniques for preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers based on directly amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. J Mater Chem B 2:1733–1741
Zhang YD, Cao HW, Huang QW, Zhang HX (2018) Isolation of transferrin by imprinted nanoparticles with magnetic deep eutectic solvents as monomer. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:6237–6245
Guo T, Deng QL, Fang GZ, Wang S (2016) Upconversion fluorescence metal-organic frameworks thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer for enrichment and sensing protein. Biosens Bioelectron 79:341–346
Wang P, Tang X, Hu LQ, Yin YK, Chen SH (2020) Preparation of bovine hemoglobin surface molecularly imprinted cotton for selective protein recognition. Process Biochem 88:31–37
Sun YH, Yao C, **e ZX, Zhang YG (2021) Lotus seedpod-like molecularly imprinted polymers fabricated by MOF-808 stabilized Pickering emulsion and their specific recognition of hemoglobin. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 197:111446
**e XY, Hu Q, Ke RF, Wang SC (2019) Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Eng J 371:130–137
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21675048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2325 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Wang, Y., Li, H. et al. Specific recognition of protein by deep eutectic solvent–based magnetic β-cyclodextrin molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 188, 232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04887-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04887-x