Abstract
An innovative approach is presented for portable and sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria. A novel synthetic hybrid nanocomposite encapsulating platinum nanoparticles, as a highly efficient catalyst, catalyzes the hydrolysis of the ammonia–borane complex to generate hydrogen gas. The nanocomposites are used as a label for immunoassays. A portable hand-held hydrogen detector combined with nanocomposite-induced signal conversion was applied for point-of-care testing of pathogenic bacteria. A hand-held hydrogen detector was used as the transducer. Escherichia coli O157:H7 (E. coli O157: H7), as detection target, formed a sandwich structure with magnetic beads and hybrid nanocomposites. Magnetic beads were used for separation of the sandwich structure, and hybrid nanocomposites as catalysts to catalyze the generation of hydrogen from ammonia−borane. The generated hydrogen was detected by a hydrogen detector using an electrochemical method. E. coli O157:H7 has a detection limit of 10 CFU·mL−1. The immunosensor made the hand-held hydrogen detector a point-of-care meter to be used outdoors for the detection and quantification of targets beyond hydrogen.

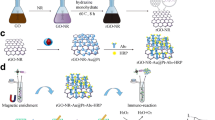
Schematic presentation of one-pot synthetic peptide–Cu3(PO4)2 hybrid nanocomposites embedded PtNPs (PPNs), encapsulating many Pt particles. The PPNs acts as an ideal immunoprobe for hand-held H2 detector signal readouts, by transforming pathogenic bacteria recognition events into H2 signals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao Y, Du D, Lin Y (2015) Glucose encapsulating liposome for signal amplification for quantitative detection of biomarkers with glucometer readout. Biosens Bioelectron 72:348–354
Zhang JJ, Shen Z, **ang Y, Lu Y (2016) Integration of solution-based assays onto lateral flow device for one-step quantitative point-of-care diagnostics using personal glucose meter. Acs Sensors 1(9):1091–1096
Alamer S, Eissa S, Chinnappan R, Zourob M (2018) A rapid colorimetric immunoassay for the detection of pathogenic bacteria on poultry processing plants using cotton swabs and nanobeads. Microchim Acta 185(3):164
Liu D, Tian T, Chen X, Lei Z, Song Y, Shi Y, Ji T, Zhu Z, Yang L, Yang C (2018) Gas-generating reactions for point-of-care testing. Analyst 143(6):1294–1304
Ye R, Zhu C, Song Y, Song J, Fu S, Lu Q, Yang X, Zhu MJ, Du D, Li H, Lin Y (2016) One-pot bioinspired synthesis of all-inclusive protein-protein nanoflowers for point-of-care bioassay: detection of E. coli O157:H7 from milk. Nanoscale 8(45):18980–18986
Bu SJ, Wang KY, Ju CJ, Han Y, Li ZY, Du P, Hao Z, Li CT, Liu WS, Wan JY (2018) A pregnancy test strip for detection of pathogenic bacteria by using concanavalin A-human chorionic gonadotropin-Cu-3(PO4)(2) hybrid nanoflowers, magnetic separation, and smartphone readout. Microchim Acta 185(10):464
Piro B, Reisberg S (2017) Recent advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Sensors 17(4):794
Das A, Cui XK, Chivukula V, Iyer SS (2018) Detection of enzymes, viruses, and bacteria using glucose meters. Anal Chem 90(19):11589–11598
Huang H, Zhao G, Dou W (2018) Portable and quantitative point-of-care monitoring of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using a personal glucose meter based on immunochromatographic assay. Biosens Bioelectron 107:266–271
Hong L, Zhou F, Shi DM, Zhang XJ, Wang GF (2017) Portable aptamer biosensor of platelet-derived growth factor-BB using a personal glucose meter with triply amplified. Biosens Bioelectron 95:152–159
Ye R, Zhu C, Song Y, Lu Q, Ge X, Yang X, Zhu MJ, Du D, Li H, Lin Y (2016) Bioinspired synthesis of all-in-one organic-inorganic hybrid Nanoflowers combined with a handheld pH meter for on-site detection of food pathogen. Small 12(23):3094–3100
Zhao M, Wang P, Guo Y, Wang L, Luo F, Qiu B, Guo L, Su X, Lin Z, Chen G (2018) Detection of aflatoxin B1 in food samples based on target-responsive aptamer-cross-linked hydrogel using a handheld pH meter as readout. Talanta 176:34–39
Zhang Y, Yang JN, Nie JF, Yang JH, Gao D, Zhang L, Li JP (2016) Enhanced ELISA using a handheld pH meter and enzyme-coated microparticles for the portable, sensitive detection of proteins. Chem Commun 52(17):3474–3477
Wang LX, Chen CQ, Huang HW, Huang D, Luo F, Qiu B, Guo LH, Lin ZY, Yang HH (2018) Sensitive detection of telomerase activity in cancer cells using portable pH meter as readout. Biosens Bioelectron 121:153–158
Zhang JJ, **ng H, Lu Y (2018) Translating molecular detections into a simple temperature test using a target-responsive smart thermometer. Chem Sci 9(16):3906–3910
Zhu Z, Guan ZC, Liu D, Jia SS, Li JX, Lei ZC, Lin SC, Ji TH, Tian ZQ, Yang CYJ (2015) Translating molecular recognition into a pressure signal to enable rapid, sensitive, and portable biomedical analysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(36):10448–10453
Zhang JJ, **ang Y, Wang M, Basu A, Lu Y (2016) Dose-dependent response of personal glucose meters to nicotinamide coenzymes: applications to point-of-care diagnostics of many non-glucose targets in a single step. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(2):732–736
Guo LT, Cai YY, Ge JM, Zhang YN, Gong LH, Li XH, Wang KX, Ren QZ, Su J, Chen JS (2015) Multifunctional Au-Co@CN Nanocatalyst for highly efficient hydrolysis of Ammonia borane. ACS Catal 5(1):388–392
Zhan WW, Zhu QL, Xu Q (2016) Dehydrogenation of Ammonia borane by metal nanoparticle catalysts. ACS Catal 6(10):6892–6905
Zhou QX, Xu CX (2017) Stratified nanoporous PtTi alloys for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J Colloid Interface Sci 496:235–242
Wang K-Y, Bu S-J, Ju C-J, Li C-T, Li Z-Y, Han Y, Ma C-Y, Wang C-Y, Hao Z, Liu W-S, Wan J-Y (2018) Hemin-incorporated nanoflowers as enzyme mimics for colorimetric detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28(23–24):3802–3807
Humblot V, Yala JF, Thebault P, Boukerma K, Hequet A, Berjeaud JM, Pradier CM (2009) The antibacterial activity of Magainin I immobilized onto mixed thiols self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials 30(21):3503–3512
Ge J, Lei J, Zare RN (2012) Protein-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers. Nat Nanotechnol 7(7):428–432
Hu R, Zhang X, Zhao Z, Zhu G, Chen T, Fu T, Tan W (2014) DNA nanoflowers for multiplexed cellular imaging and traceable targeted drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 53(23):5821–5826
Xu M, Wang R, Li Y (2016) An electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 with highly efficient bi-functional glucose oxidase-polydopamine nanocomposites and Prussian blue modified screen-printed interdigitated electrodes. Analyst 141(18):5441–5449
Li YX, Afrasiabi R, Fathi F, Wang N, **ang CL, Love R, She Z, Kraatz HB (2014) Impedance based detection of pathogenic E-coli O157:H7 using a ferrocene-antimicrobial peptide modified biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 58:193–199
Zhang H, Shi YP, Lan F, Pan Y, Lin YK, Lv JZ, Zhu ZH, Jiang Q, Yi C (2014) Detection of single-digit foodborne pathogens with the naked eye using carbon nanotube-based multiple cycle signal amplification. Chem Commun 50(15):1848–1850
Akanda MR, Tamilavan V, Park S, Jo K, Hyun MH, Yang H (2013) Hydroquinone diphosphate as a phosphatase substrate in enzymatic amplification combined with electrochemical-chemical-chemical redox cycling for the detection of E. coli O157:H7. Anal Chem 85(3):1631–1636
Dong ZM, Zhao GC (2015) Label-free detection of pathogenic bacteria via immobilized antimicrobial peptides. Talanta 137:55–61
Zhang Y, Tan C, Fei R, Liu X, Zhou Y, Chen J, Chen H, Zhou R, Hu Y (2014) Sensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay for E. coli O157:H7 detection with signal dual-amplification using glucose oxidase and laccase. Anal Chem 86(2):1115–1122
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFD0501001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2206 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, SJ., Wang, KY., Bai, HS. et al. Immunoassay for pathogenic bacteria using platinum nanoparticles and a hand-held hydrogen detector as transducer. Application to the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Microchim Acta 186, 296 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3409-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3409-6