Abstract
The authors describe an electrochemical method for the determination of the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) oligonucleotide with a sequence derived from the genom of hepatitis B virus (HBV). It is making use of circular strand displacement (CSD) and rolling circle amplification (RCA) strategies mediated by a molecular beacon (MB). This ssDNA hybridizes with the loop portion of the MB immobilized on the surface of a gold electrode, while primer DNA also hybridizes with the rest of partial DNA sequences of MB. This triggers the MB-mediated CSD. The RCA is then initiated to produce a long DNA strand with multiple tandem-repeat sequences, and this results in a significant increase of the differential pulse voltammetric response of the electrochemical probe Methylene Blue at a rather low working potential of −0.24 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). Under optimal experimental conditions, the assay displays an ultrahigh sensitivity (with a 2.6 aM detection limit) and excellent selectivity. Response is linear in the 10 to 700 aM DNA concentration range.

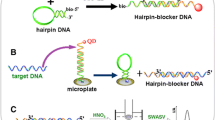
Schematic of a voltammetric method for the determination of attomolar levels of target DNA. It is based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification strategies. Under optimal experimental conditions, the assay displays an ultrahigh sensitivity with a 2.6 aM detection limit and excellent selectivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song LW, Wang YB, Fang LL, Wu Y, Yang L, Chen JY, Ge SX, Zhang J, **. Anal Chem 87:5173–5180. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504832c
Liu LL, Wang XY, Ma Q, Lin ZH, Chen SF, Li Y, Lu LH, Qu HP, Su XG (2016) Multiplex electrochemiluminescence DNA sensor for determination of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus based on multicolor quantum dots and Au nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 916:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.02.024
Wolford J, Blunt D, Ballecer C, Prochazka M (2000) High-throughput SNP detection by using DNA pooling and denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC). Hum Genet 107:483–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000396
Hige S, Yamamoto Y, Yoshida S, Kobayashi T, Horimoto H, Yamamoto K, Sho T, Natsuizaka M, Nakanishi M, Chuma M, Asaka M (2010) Sensitive assay for quantification of hepatitis B virus mutants by use of a minor groove binder probe and peptide nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol 48:4487–4494. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00731-10
Zhu H, Lu F, Wu XC, Zhu JJ (2015) An upconversion fluorescent resonant energy transfer biosensor for hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA hybridization detection. Analyst 140:7622–7628. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01634g
Hong SP, Kim NK, Hwang SG, Chung HJ, Kim S, Han JH, Kim HT, Rim KS, Kang MS, Yoo W, Kim SO (2004) Detection of hepatitis B virus YMDD variants using mass spectrometric analysis of oligonucleotide fragments. J Hepatol 40:837–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2004.01.006
Shi LJ, Yu YY, Chen ZG, Zhang L, He SJ, Shi QJ, Yang HZ (2015) A label-free hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme biosensor developed on electrochemically modified electrodes for detection of a HBV DNA segment. RSC Adv 5:11541–11548. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA09936B
Teng J, Ye YW, Yao L, Yan C, Cheng KW, Xue F, Pan DD, Li BG, Chen W (2017) Rolling circle amplification based amperometric aptamer/immuno hybrid biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184:3477–3485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2383-0
Yang JR, Tang M, Diao W, Cheng WB, Zhang Y, Yan YR (2016) Electrochemical strategy for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on MNAzyme-mediated rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 186:3061–3067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1958-5
Fan TT, Mao Y, Liu F, Zhang W, Yin JX, Jiang YY (2017) Dual signal amplification strategy for specific detection of circulating microRNAs based on Thioflavin T. Sensors Actuators B 249:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.079
Kim DM, Seo J, Jun BH, Kim DH, Jeong W, Hwang SH, Kim DE (2017) Fluorometric detection of influenza virus RNA by PCR-coupled rolling circle amplification generating G-quadruplex. Sensors Actuators B 251:894–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.101
Chen AY, Ma SY, Zhou Y, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2016) In situ electrochemical generation of electrochemiluminescent silver naonoclusters on target-cycling synchronized rolling circle amplification platform for microRNA detection. Anal Chem 88:3203–3210. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04578
Yin D, Tao YY, Tang L, Li W, Zhang Z, Li JL, **e GM (2017) Cascade toehold-mediated strand displacement along with non-enzymatic target recycling amplification for the electrochemical determination of the HIV-1 related gene. Microchim Acta 184:3721–3728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2368-z
Sun AL, Zhang YF, Wang XN (2015) Sensitive voltammetric determination of DNA via a target-induced strand-displacement reaction using quantum dot-labeled probe DNA. Microchim Acta 182:1403–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1467-y
Shen J, Wang HY, Li CX, Zhao YY, Yu XJ, Luo XL (2017) Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for adenosine detection based on cascade signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 90:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.009
Deng KQ, Li CX, Huang HW, Li XF (2017) Rolling circle amplification based on signal-enhanced electrochemical DNA sensor for ultrasensitive transcription factor detection. Sensors Actuators B 238:1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.107
Lee CY, Fan HT, Hsieh YZ (2018) Disposable aptasensor combining functional magnetic nanoparticles with rolling circle amplification for the detection of prostate-specific antigen. Sensors Actuators B 255:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.061
Dong HF, Zhang J, Ju HX, Lu HT, Wang SY, ** S, Hao KH, Du HW, Zhang XJ (2012) Highly sensitive multiple microRNA detection based on fluorescence quenching of graphene oxide and isothermal strand-displacement polymerase reaction. Anal Chem 84:4587–4593. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300721u
Zhou H, Liu J, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2011) Ultrasensitive DNA detection based on Au nanoparticles and isothermal circular double-assisted electrochemiluminescence signal amplification. Chem Commun 47:8358–8360. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CC12413G
Cheng W, Zhang W, Yan YR, Shen B, Zhu D, Lei PH, Ding SJ (2014) A novel electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive and specific detection of DNA based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 62:274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.056
Li XL, Guo J, Zhai Q, **a J, Yi G (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for specific detection of DNA based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement polymerization and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Anal Chim Acta 934:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.06.034
Huang S, Lu SY, Huang CS, Sheng JR, Zhang LX, Su W, **ao Q (2016) An electrochemical biosensor based on single-stranded DNA modified gold electrode for acrylamide determination. Sensors Actuators B 224:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.008
Huang L, Wu JJ, Zheng L, Qian HS, Xue F, Wu YC, Pan DD, Adeloju SB, Chen W (2013) Rolling chain amplification based signal-enhanced electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Anal Chem 85:10842–10849. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402228n
Das R, Goel AK, Sharma MK, Upadhyay S (2015) Electrochemical DNA sensor for anthrax toxin activator gene atxA-detection of PCR amplicons. Biosens Bioelectron 74:939–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.066
Huang YC, Ge BX, Sen D, Yu HZ (2008) Immobilized DNA switches as electronic sensors for picomolar detection of plasma proteins. J Am Chem Soc 130:8023–8029. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8011066
Wang S, Li L, ** HL, Yang T, Bao WW, Huang SM, Wang JC (2013) Electrochemical detection of hepatitis B and papilloma virus DNAs using SWCNT array coated with gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 41:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.08.021
Karastogianni S, Girousi S (2015) Detection of short oligonucleotide sequences of hepatitis B virus using electrochemical DNA hybridisation biosensor. Chem Pap 69:202–210. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0599-6
Chen JY, Weng SH, Chen QQ, Liu AL, Wang FQ, Chen J, Yi Q, liu QC, Lin XH (2014) Development of an electrochemical sensing technique for rapid genoty** of hepatitis B virus. Sensors 14:5611–5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140305611
Castro ACH, França EG, de Paula LF, Soares MMCN, Goulart LR, Madurro JM, Brito-Madurro AG (2014) Preparation of genosensor for detection of specific DNA sequence of the hepatitis B virus. Appl Surf Sci 314:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.06.084
Zheng J, Chen C, Wang XL, Zhang F, He PG (2014) A sequence-specific DNA sensor for hepatitis B virus diagnostics based on the host–guest recognition. Sensors Actuators B 199:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.03.110
Shakoori Z, Salimian S, Kharrazi S, Adabi M, Saber R (2015) Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on gold nanorods for detecting hepatitis B virus. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8303-9
Li FQ, Xu YM, Yu X, Yu ZG, He XJ, Ji HR, Dong JH, Song YB, Yan H, Zhang GL (2016) A “signal on” protection-displacement-hybridization-based electrochemical hepatitis B virus gene sequence sensor with high sensitivity and peculiar adjustable specificity. Biosens Bioelectron 82:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.014
Narang J, Singhal C, Malhotra N, Narang S, PN AK, Gupta R, Kansal R, Pundir CS (2016) Impedimetric genosensor for ultratrace detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in patient samples assisted by zeolites and MWCNT nano-composites. Biosens Bioelectron 86:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.013
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21403039, 21563006, 21763005), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2015GXNSFAA139033, 2016GXNSFBA380118, 2017GXNSFDA198034, 2017GXNSFFA198005), Guangxi Scientific and Technological Development Projects (AD17195081), High-Level-Innovation Team (guijiaoren[2017]38) and Outstanding Scholar Project of Guangxi Higher Education Institutes, and BAGUI Scholar Program of Guangxi Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 510 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Feng, M., Li, J. et al. Voltammetric determination of attomolar levels of a sequence derived from the genom of hepatitis B virus by using molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 185, 206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2744-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2744-3