Abstract
The authors describe the synthesis of spider-web-like chitosan/MIL-68(Al) composite nanofibers, their application to fast solid phase extraction (SPE) of trace levels of Pb(II) and Cd(II), and their quantitation by ICP-OES. The composite nanofibers were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, N2 adsorption-desorption experiments and FT-IR. The pH value of sample solutions, amount of sorbent, eluent concentration and type and volume of the eluting solvent were optimized using factorial experimental design. Under the optimum conditions, the detection limits are 0.16 μg L−1, and linear ranges extend from 0.5–50 μg L−1 for both Pb(II) and Cd(II). The intra-day relative standard deviations (RSDs) of <3.8% and inter-day RSDs of <4.3% are quite acceptable. The accuracy of the method was tested by the analysis of the certified reference material IAEA-407 and by recovery measurements on spiked real samples (phylum, gastropoda, Trochus erythraeus mollusks) which demonstrated the good performance of the method for SPE and determination of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions.

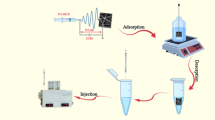
A novel spider-web-like chitosan/MIL-68(Al) composite nanofibers were synthesized via electrospining and applied for efficient solid phase extraction of the trace levels of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from a mollusk phylum, gastropoda, Trochus erythraeus following its combination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, **e J, Wu Y, Hu X (2014) A magnetic metal-organic framework as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of copper(II), and its determination by electrothermal AAS. Microchim Acta 181:949–956. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1183-z
Gu ZY, Yang CX, Chang N, Yan XP (2012) Metal–organic frameworks for analytical chemistry: from sample collection to chromatographic separation. Acc Chem Res 45:734–745. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar2002599
Asiabi M, Mehdinia A, Jabbari A (2015) Preparation of water stable methyl-modified metal–organic framework-5/polyacrylonitrile composite nanofibers via electrospinning and their application for solid-phase extraction of two estrogenic drugs in urine samples. J Chromatogr A 1426:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.11.036
Asiabi M, Mehdinia A, Jabbari A (2016) Electrospun biocompatible chitosan/MIL-101 (Fe) composite nanofibers for solid-phase extraction of 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in whole blood samples using Box-Behnken experimental design. J Chromatogr A 1479:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.024
Zhang S, Yao W, Ying J, Zhao H (2016) Polydopamine-reinforced magnetization of zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-7 for magnetic solid-phased extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the air-water environment. J Chromatogr A 1452:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.05.039
Wu Y, Xu G, Wei F, Song Q, Tang T, Wang X, Hu Q (2016) Determination of Hg (II) in tea and mushroom samples based on metal-organic frameworks as solid phase extraction sorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 235:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.08.010
Ghani M, Pic’o MFF, Salehinia SH, Cabello CP, Maya F, Berlier G, Saraji M, Cerd’a V, Palomino GT (2017) Metal-organic framework mixed-matrix disks: versatile supports for automated solid-phase extraction prior to chromatographic separation. J Chromatogr A 1488:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.01.069
Safari M, Yamini Y, Masoomi MY, Morsali A, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2017) Magnetic metal-organic frameworks for the extraction of trace amounts of heavy metal ions prior to their determination by ICP-AES. Microchim Acta 184:1555–1564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2133-3
Han T, **ao Y, Tong M, Huang H, Liu D, Wang L, Zhong CH (2015) Synthesis of CNT@MIL-68(Al) composites with improved adsorption capacity for phenol in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 275:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.005
Saghanejhad Tehrani M, Zare-Dorabei R (2016) Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of methylene blue and rhodamine B onto metal organic framework MIL-68(Al): central composite design optimization. RSC Adv 6:27416–27425. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA28052D
Ziaei E, Mehdinia A, Jabbari A (2014) A novel hierarchical nanobiocomposite of grapheme oxide–magnetic chitosan grafted with mercapto as a solid phase extraction sorbent for the determination of mercury ions in environmental water samples. Anal Chim Acta 850:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.08.048
Bozkurt SS, Erdogan D, Antep M, Tuzmen N, Merdivan M (2016) Use of ionic liquid based chitosan as sorbent for preconcentration of fluoroquinolones in milk, egg, fish, bovine and chicken meat samples by solid phase extraction before HPLC determination. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 39:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2015.1116010
Djerahov L, Vasileva P, Karadjova I, Kurakalva RM, Aradhi KK (2016) Chitosan film loaded with silver nanoparticles—sorbent for solid phase extraction of Al(III), Cd(II), Cu(II), Co(II), Fe(III), Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II). Carbohydr Polym 147:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.080
Guo H, Xue L, Yao SH, Cai X, Qian J (2017) Rhein functionalized magnetic chitosan as a selective solid phase extraction for determination isoflavones in soymilk. Carbohydr Polym 165:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.035
Sun K, Li ZH (2011) Preparations, properties and applications of chitosan based nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. Express Polym Lett 5:342–361. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2011.34
Qiu J, Yan Y, Chang H, Liu X, Kang X (2016) Preparation of a concentric layered structure of an electrospun nanofiber column for solid-phase extraction of mass viscous crude extracts. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:4425–4433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9547-3
Bagheri H, Rezvani O, Banihashemi S (2016) Core–shell electrospun polybutylene terephthalate/polypyrrole hollow nanofibers for micro-solid phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1434:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.12.082
Chu L, Zheng SH, Qu B, Geng SH, Kang X (2017) Detection of β-agonists in pork tissue with novel electrospun nanofibers-based solid-phase extraction followed ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 227:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.059
Chigome S, Torto N (2012) Electrospun nanofiber-based solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal Chem 38:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.04.011
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, de la Guardia M, Namieśnik J (2016) Modern trends in solid phase extraction: new sorbent media. Trends Anal Chem 77:23–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.10.010
Chen L, Zhu X, Shen J, Zhang W (2016) Selective solid-phase extraction of catecholamines from plasma using nanofibers doped with crown ether and their quantitation by HPLC with electrochemical detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:4987–4994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9596-7
Oh HJ, Pant HR, Kang YS, Jeon KS, Pant B, Kim CS, Kim HY (2012) Synthesis and characterization of spider-web-like electrospun mats of meta-aramid. Polym Int 61:1675–1682. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4260
Mehdinia A, Shoormeij Z, Jabbari A (2017) Trace determination of lead(II) ions by using a magnetic nanocomposite of the type Fe3O4/TiO2/PPy as a sorbent, and FAAS for quantitation. Microchim Acta 184:1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-2156-9
Mashhadizadeh MH, Karami Z (2011) Solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Ag, Cd, Cu, and Zn in environmental samples using magnetic nanoparticles coated by 3-(trimethoxysilyl)-1-propantiol and modified with 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole and their determination by ICP-OES. J Hazard Mater 190:1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.051
Beata Zawisza B, Baranik A, Malicka E, Talik E, Sitko R (2016) Preconcentration of Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) with ethylenediamine-modified graphene oxide. Michrochim Acta 183:231–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1629-y
Duysak Ö, Ersoy B (2014) A biomonitoring study: heavy metals in Monodonta Turbinata (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from Iskenderun Bay, north-eastern Mediterranean. Pakistan J Zool 46:1317–1322
Behbahani M, Bide Y, Bagheri S, Salarian M, Omidi F, Nabid MR (2016) A pH responsive nanogel composed of magnetite, silica and poly(4-vinylpyridine) for extraction of Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II). Microchim Acta 183:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1603-8
Ghorbani-Kalhor E (2016) A metal-organic framework nanocomposite made from functionalized magnetite nanoparticles and HKUST-1 (MOF-199) for preconcentration of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II). Microchim Acta 183:2639–2647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1896-2
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Saleh A, Rezaee M, Ghambarian M, Hassani R (2010) A nanoparticle-based solid-phase extraction procedure followed by flow injection inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry to determine some heavy metal ions in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 659:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.11.053
Karimi M, Haji Shabani AM, Dadfarnia S (2016) Deep eutectic solvent-mediated extraction for ligand-less preconcentration of lead and cadmium from environmental samples using magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:563–571. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1671-9
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this work by the Iran Delco Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 524 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asiabi, M., Mehdinia, A. & Jabbari, A. Spider-web-like chitosan/MIL-68(Al) composite nanofibers for high-efficient solid phase extraction of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Microchim Acta 184, 4495–4501 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2473-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2473-z