Abstract
Purpose
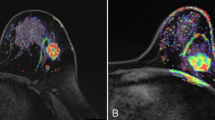
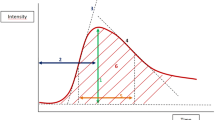
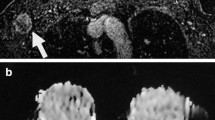
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) has emerged as a promising diagnostic modality in various breast cancer treatments. However, little is known about the correlation between the pattern of time to signal intensity curves (TIC) on the CE-MRI and clinicopathologic features. This study was designed to investigate these correlations and evaluate the predictive value of TIC on CE-MRI in order to identify high-risk patients.
Methods
Between 2001 and 2003, 101 lesions were evaluated to detect malignancy on CE-MRI in 101 women who were suspected of having breast tumors based on either clinical findings or conventional imaging studies. Moreover, the clinicopathologic findings were compared with the pattern of TIC for the 69 surgically treated malignant lesions.
Results
In detecting malignancy, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 78.7%, 88.5%, and 81.2%, respectively, in the 101 breast lesions. Especially for the 69 surgically treated malignant lesions, in comparison with breast cancer tumors with the benign pattern of TIC, the breast cancer tumors with a malignant pattern were found more frequently in lymphatic invasion (P < 0.01) and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.005), although no statistical correlation regarding the histological type, tumor size, vascular invasion, extensive intraductal component, hormone receptor status, or pathological stage was noted between the two groups. According to a logistic regression model, lymph node metastasis was found to be a significant independent variable.
Conclusion
The pattern of TIC could be used to predict lymphatic spreading associated with lymph node metastasis prior to surgery as well as to detect malignancy. Therefore, a more detailed evaluation should be made to identify the presence of lymphatic spreading in patients with a malignant pattern of TIC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L Nystrom LG Larsson LE Rutqvist A Lindgren M Lindqvist S Ryden et al. (1995) ArticleTitleDetermination of cause of death among breast cancer cases in the Swedish randomized mammography screening trials. A comparison between official statistics and validation by an endpoint committee Acta Oncol 34 145–52 Occurrence Handle7718250
SE Harms DP Flamig (1993) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the breast J Magn Reson Imaging 3 277–83 Occurrence Handle8428095
K Kinkel G Vlastos (2001) ArticleTitleMR imaging: breast cancer staging and screening Semin Surg Oncol 20 187–96 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ssu.1033 Occurrence Handle11523103
CK Kuhl RK Schmutzler CC Leutner A Kempe E Wardelmann A Hocke et al. (2000) ArticleTitleBreast MR imaging screening in 192 women proved or suspected to be carriers of a breast cancer susceptibility gene: preliminary results Radiology 215 267–79 Occurrence Handle10751498
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Japanese Breast Cancer Society (2000) General rules for clinical and pathological recording of breast cancer (in Japanese) EditionNumber14th ed. Kanehara Tokyo
SH Heywang A Wolf E Pruss T Hilbertz W Eiermann W Permanetter (1989) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the breast with Gd-DTPA: use and limitations Radiology 171 95–103 Occurrence Handle2648479
AW Kaiser E Zeitler (1989) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the breast: fast imaging sequences with and without Gd-DTPA Radiology 170 681–6 Occurrence Handle2916021
JP Stack OM Redmond MB Codd PA Dervan JT Ennis (1990) ArticleTitleBreast disease: tissue characterization with Gd-DTPA enhancement profiles Radiology 174 491–4 Occurrence Handle2296657
PC Stomper S Herman DL Klippenstein JS Winston SB Edge MA Arredondo et al. (1995) ArticleTitleSuspect breast lesions: finding at dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging correlated with mammographic and pathologic features Radiology 197 387–95 Occurrence Handle7480682
LD Buadu J Murakami S Murayama N Hashiguchi S Sakai K Masuda et al. (1996) ArticleTitleBreast lesions: correlation of contrast medium enhancement patterns on MR images with histopathologic findings and tumor angiogenesis Radiology 200 639–49 Occurrence Handle8756909
DL Buckley PJ Drew S Mussurakis JR Monson A Horsman (1997) ArticleTitleMicrovessel density of invasive breast cancer assessed by dynamic Gd-DTPA enhanced MRI J Magn Reson Imaging 7 461–4 Occurrence Handle9170027
CF van Dijke RC Brasch TP Roberts N Weidner A Mathur DM Shames et al. (1996) ArticleTitleMammary carcinoma model: correlation of macromolecular contrast-enhanced MR imaging characterizations of tumor microvasculature and histologic capillary density Radiology 198 813–8 Occurrence Handle8628876
E Furman-Haran R Margalit D Grobgeld H Degani (1996) ArticleTitleDynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging reveals stress-induced angiogenesis in MCF7 human breast tumors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93 6247–51 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.13.6247 Occurrence Handle8692800
H Degani E Furman S Fields (1994) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of MCF7 human breast cancer: pathophysiology and monitoring of treatment Clin Chim Acta 228 19–33 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0009-8981(94)90054-X Occurrence Handle7955426
JC Weinreb G Newstead (1995) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the breast Radiology 196 593–610 Occurrence Handle7644617
Y Ogawa YS Chung B Nakata S Takatsuka K Maeda T Sawada et al. (1995) ArticleTitleMicrovessel quantitation in invasive breast cancer by staining for factor VIII-related antigen Br J Cancer 71 1297–301 Occurrence Handle7779727
ME Van Hoef WF Knox SS Dhesi A Howell AM Schor (1993) ArticleTitleAssessment of tumor vascularity as a prognostic factor in lymph node negative invasive breast cancer Eur J Cancer 29 1141–5
SE Harms DP Flamig KL Hesley MD Meiches RA Jensen WP Evans et al. (1993) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the breast with rotating delivery of excitation off response: clinical experience with pathologic correlation Radiology 187 493–501 Occurrence Handle8475297
SG Orel MD Schnall VA LiVolsi RH Troupin (1994) ArticleTitleSuspicious breast lesions: MR imaging with radiologic-pathologic correlation Radiology 190 485–93 Occurrence Handle8284404
CK Kuhl HH Schild (2000) ArticleTitleDynamic image interpretation of MRI of the breast J Magn Reson Imaging 12 965–74 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1522-2586(200012)12:6<965::AID-JMRI23>3.0.CO;2-1 Occurrence Handle11105038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was presented at the 103rd Annual Congress of the Japan Surgical Society, Sapporo, Hokkaido, June 4–6, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komatsu, S., Lee, C., Ichikawa, D. et al. Predictive Value of the Time–Intensity Curves on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Lymphatic Spreading in Breast Cancer. Surg Today 35, 720–724 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-005-3032-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-005-3032-5