Abstract
Aim
To compare the relative effects of different dosages of sodium-glucose cotransport inhibitors (SGLT2i) for renoprotection in Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
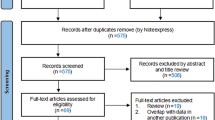
The study searched different databases (PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science) for studies comparing dose-dependent renoprotective efficacy defined as a decline in eGFR with the different “-flozins namely Empagliflozin, Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, Ertugliflozin, Ipragliflozin, Luseogliflozin, Remogliflozin and Sotagliflozin. The studies were compared with the Bayesian approach of network meta-analysis coupled with the random-effect model using the Cochrane risk of bias tool (RoB 2.0), and the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) score was allotted to each dosage of different SGLT-2i.
Results
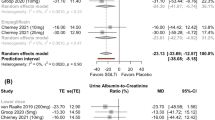
A total of 43,434 citations were identified, out of which forty-five randomized trials with 48,067 patients, mentioning the flozin dose and eGFR as an endpoint, were found to be eligible for further analysis. The median duration of the follow-up in the trials was 12 months (IQR 5.5–16 months). Canagliflozin 100 mg demonstrated distinct eGFR benefit with an odds ratio of 2.3 (CI 0.72–3.9) compared to placebo. A statistically non-significant eGFR benefit was observed with all other “-flozins.” Canagliflozin 100 mg drug dose category showed the highest sucra rank probability score of 93%, followed by the Canagliflozin 300 mg and Dapagliflozin 5 mg with sucra rank probability scores of 69% and 65%, respectively. The Flozin-dose assessment against eGFR was similar to the albumin-creatinine ratios as the secondary endpoint in the SUCRA ranking.
Conclusion
The renoprotective efficacy of SGLT2i is independent of the incremental doses suggesting lower doses may suffice for renal outcomes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reed J, Bain S, Kanamarlapudi V (2021) A review of current trends with type 2 diabetes epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, treatments and future perspectives. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther 14:3567–3602
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, et al (2022) 11. Chronic kidney disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 45(Suppl 1):S175–S184. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc22-S011
Hsia DS, Grove O, Cefalu WT (2017) An update on SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 24(1):73–79
Scheerer MF, Rist R, Proske O, Meng A, Kostev K (2016) Changes in HbA1c, body weight, and systolic blood pressure in type 2 diabetes patients initiating dapagliflozin therapy: a primary care database study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther 9:337–345
**ang B, Zhao X, Zhou X (2021) Cardiovascular benefits of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol 20:78
Giorgino F, Vora J, Fenici P, Solini A (2020) Renoprotection with SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes over a spectrum of cardiovascular and renal risk. Cardiovasc Diabetol 19:196
Bailey CJ, Day C, Bellary S (2022) Renal protection with SGLT2 inhibitors: effects in acute and chronic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep 22(1):39–52
Li N, Lv D, Zhu X, Wei P, Gui Y, Liu S et al (2021) Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. Front Med 8:728089
Pinto LC, Rados DV, Remonti LR, Viana MV, Leitão CB, Gross JL (2022) Dose-ranging effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Endocrinol Metab 66(1):68–76
Jiang Y, Yang P, Fu L, Sun L, Shen W, Wu Q (2022) Comparative cardiovascular outcomes of SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol 13:802992
Ferrannini E, Ramos SJ, Salsali A, Tang W, List JF (2010) Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Care 33(10):2217–2224
Bailey CJ, Iqbal N, T’joen C, List JF (2012) Dapagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with diabetes: a randomized-controlled trial of low-dose range. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(10):951–959
Wilding JPH, Woo V, Soler NG, Pahor A, Sugg J, Rohwedder K et al (2012) Long-term efficacy of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving high doses of insulin: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 156(6):405–415
Yang T, Lu M, Ma L, Zhou Y, Cui Y (2015) Efficacy and tolerability of canagliflozin as add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 71(11):1325–1332
Wilding JPH, Charpentier G, Hollander P et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sulphonylurea: a randomised trial. Int J Clin Pract 67(12):1267–1282
Forst T, Guthrie R, Goldenberg R et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes on background metformin and pioglitazone. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(5):467–477
Rodbard HW, Seufert J, Aggarwal N et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of titrated canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin and sitagliptin. Diabetes Obes Metab 18(8):812–819
Roden M, Weng J, Eilbracht J et al (2013) Empagliflozin monotherapy with sitagliptin as an active comparator in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 1(3):208–219
Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E et al (2013) Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 36(11):3396–3404
Søfteland E, Meier JJ, Vangen B, Toorawa R, Maldonado-Lutomirsky M, Broedl UC (2017) Empagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with linagliptin and metformin: a 24-week randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Diabetes Care 40(2):201–209
Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E et al (2014) Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 37(6):1650–1659
Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Swallow R et al (2014) EMPA-REG PIO™ trial investigators. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(2):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12188
Terauchi Y, Utsunomiya K, Yasui A, Seki T, Cheng G, Shiki K, Lee J (2019) Safety and efficacy of empagliflozin as add-on therapy to GLP-1 receptor agonist (Liraglutide) in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group phase 4 study. Diabetes Ther 10(3):951–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-019-0604-8
Zhou Y, Wu W (2017) The sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 41(6):2503–2512. https://doi.org/10.1159/000475942
Bhansali A (2017) SGLT2 inhibitors through the windows of EMPA-REG and CANVAS trials: a review. Diabetes Ther 8:1245–1251
Palmer SC, Tendal B, Mustafa RA et al (2021) Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 372:m4573
McGuire DK, Shih WJ, Cosentino F et al (2021) Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA Cardiol 6(2):1–11
Bae JH, Park EG, Kim S, Kim SG, Hahn S, Kim NH (2019) Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci Rep 9(1):13009
Mearns ES, Sobieraj DM, White CM et al (2015) Comparative efficacy and safety of antidiabetic drug regimens added to metformin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0125879
Zaccardi F, Webb DR, Htike ZZ, Youssef D, Khunti K, Davies MJ (2016) Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 18(8):783–794
Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJL et al (2019) SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(11):845–854
Cao H, Liu Y, Tian Z et al (2021) Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors benefit to kidney and cardiovascular outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease 3b–4: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 180:109033
Tsai WC, Hsu SP, Chiu YL et al (2022) Cardiovascular and renal efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open 12(10):e060655
Wang C, Zhou Y, Kong Z et al (2019) The renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without prevalent kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 21(4):1018–1026
Kluger AY, Tecson KM, Lee AY, Lerma EV, Rangaswami J, Lepor NE, Cobble ME, McCullough PA (2019) Class effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 18(1):99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-019-0903-4
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR and ANP contributed equally to study selection, manuscript writing, review and approval to the manuscript, data extraction and manuscript writing and important intellectual content. SB and NG contributed to data analysis. NH, AK, KSK contributed to the literature search and study selection; data analysis. ANP and NG contributed to risk of bias, manuscript writing and important intellectual content. AR helped in conception, data check, important intellectual content, literature review and final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical approval
The present article is a systematic review of prior studies, hence informed consent and human, animal rights disclosure is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Naveen C Hegde and Ankit Kumar are co-first authors.
This article belongs to the topical collection diabetic nephropathy, managed by Giuseppe Pugliese.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hegde, N.C., Kumar, A., Patil, A.N. et al. Dose-dependent renoprotection efficacy of sglt2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol 60, 1311–1331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-023-02126-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-023-02126-8