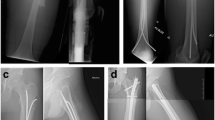
Abstract
The main objective of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of displaced tibia shaft fractures in children weighing 50 kg (110 lb) or more treated by elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN). Translation, sagittal and coronal angulations were assessed on plain radiographs in all the patients. Twenty-six out of 106 patients met the inclusion criteria. The average patient age at the time of injury was 13.5 ± 1.3 years (range 11.3–16.1). The mean patient weight was 57 ± 8 kg (range 50–80). This study demonstrates that the use of ESIN for displaced tibia shaft fractures in children and adolescents weighing 50 kg (110 lb) or more, or older than 13 years of age, is not contraindicated. In contrast to data in femoral shaft fractures, we did not find poorer outcomes in older or heavier patients. No correlation between nail size/medullary canal diameter ratio and outcome was observed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ligier JN, Métaizeau JP, Prévot J (1983) Closed flexible medullary nailing in pediatric traumatololgy. Chir Pediatr 24:383–385
Ligier JN, Métaizeau JP, Prévot J, Lascombes P (1988) Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:74–77
Métaizeau JP (1988) Ostéosynthèse chez l’enfant: embrochage centromédullaire élastique, stable. Sauramps Médical, Montpellier
Swindells MG, Rajan RA (2010) Elastic intramedullary nailing in unstable fractures of the paediatric tibial diaphysis: a systematic review. J Child Orthop 4:45–51
Goodwin RC, Gaynor T, Mahar A, Oka R, Lalond FD (2005) Intramedullary flexible nail fixation of unstable pediatric tibial diaphyseal fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 25:570–576
Vallamshetla VPR, De Silva U, Bache CE, Gibbons PJ (2006) Flexible intramedullary nails for unstable fractures of the tibia in children. An eight-year experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:536–540
Srivastava AK, Mehlman CT, Wall EJ, Do TT (2008) Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop 28:152–158
Karladani AH, Granhed H, Edshage B, Jerre R, Styf J (2000) Displaced tibial shaft fractures: a prospective randomized study of closed intramedullary nailing versus cast treatment in 53 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 71:160–167
Kubiak EN, Egol KA, Scher D, Wasserman B, Feldman D, Kovac KJ (2005) Operative treatment of tibial fractures in children: are elastic stable intramedullary nails an improvement over external fixation? J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:1761–1768
Ramseier LE, Janicki JA, Weir S, Narayanan UG (2010) Femoral fractures in adolescents: a comparison of four methods of fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:1122–1129
Marengo L, Canavese F, Cravino M, De Rosa V, Rousset M, Samba A, Andreacchio A (2014) Outcome of displaced distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in children between 6 and 15 years of age treated by elastic stable intramedullary nails. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24:1603–1608
Canavese F, Botnari A, Andreacchio A, Marengo L, Samba A, Dimeglio A, Rousset M (2015) Displaced tibial shaft fractures with intact fibula in children: nonoperative management versus operative treatment with elastic stable intramedullary nailing. J Pediatr Orthop (Epub ahead of print)
Deakin DE, Winter H, Jain P, Bache CE (2010) Malunion following flexible intramedullary nails for tibial and femoral fractures in adolescents. J Child Orthop 4:571–577
Sankar WN, Jones KJ, Horn RD, Wells L (2010) Titanium elastic nails for pediatric tibial shaft fractures. J Child Orthop 1:281–286
Lascombes P, Nespola A, Poircuitte JM, Popkov D, de Gheldere A, Haumont T, Journeau P (2012) Early complications with flexible intramedullary nailing in childhood fractures: 100 cases managed with precurved tip and shaft nails. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98:369–375
Moroz LA, Launay F, Kocher MS, Newton PO, Rick S, Sponseller PD, Flynn JM (2006) Titanium elastic nailing of fractures of the femur in children. Predictors of complications and poor outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:1361–1366
Flynn JM, Hresko T, Reynolds RA, Blasier RD, Davidson R, Kasser J (2001) Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: a multicenter study of early results with analysis of complications. J Pediatr Orthop 21:4–8
Luhmann SJ, Schootman M, Schoenecker PL, Dobbs MB, Gordon JE (2003) Complications of titanium elastic nails for pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 23:443–447
Muller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J (1990) The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. Springer, Berlin
Gordon JE, Gregush RV, Shoenecker PL, Dobbs MB, Luhmann SJ (2007) Complications after titanium elastic nailing of pediatric tibial fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 27:442–446
Griffet J, Leroux J, Boudjouraf N, Abou-Daher A, el Hayek T (2011) Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures in children. J Child Orthop 5:297–304
Zarad AL (2014) Flexible intramedullary nails for unstable fractures of the tibia in children: a retrospective evaluation effectiveness. Egypt Orthop J 49:281–285
Weiss JM, Choi P, Ghatan C, Skaggs DL, Kay RM (2009) Complications with flexible nailing of femur fractures more than double with child obesity and weight >50 kg. J Child Orthop 3:53–58
Leet AI, Pichard CP, Ain MC (2005) Surgical treatment of femoral fractures in obese children: does excessive body weight increase the rate of complications? J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:2609–2613
Ho CA, Skaggs DL, Tang CV, Kay RM (2006) Use of flexible intramedullary nails in pediatric femur fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 26:497–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
No patients were involved. This is a retrospective study of patient’s data, and an IRB approval was obtained.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marengo, L., Paonessa, M., Andreacchio, A. et al. Displaced tibia shaft fractures in children treated by elastic stable intramedullary nailing: results and complications in children weighing 50 kg (110 lb) or more. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 26, 311–317 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1729-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1729-8