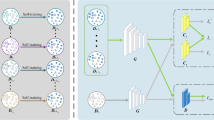
Abstract
Multi-source domain adaptation (MSDA) dedicates to establishing knowledge transfer from multiple labeled source domains to an unlabeled target domain. Although data from multiple source domains can provide rich information, it also brings two problems. First, it is not easy to directly align multiple source domains and target domain, because there are complex interactions among multiple source domains with different distributions. Second, some of the source samples may contribute negatively to domain adaptation. Thus, how to select the appropriate source domain samples is worth exploring. To solve these problems, we propose a novel framework of weighted progressive alignment (WPA), in which we develop a two-stage alignment with two distinct domain classifiers, as well as a dedicated classifier to judge the importance of source domain samples. Our proposed method progressively achieves multi-source domain adaptation through domain-adversarial training and coarse-to-fine alignment. We evaluate our framework on four public benchmark datasets. The extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves great performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baktashmotlagh, M., Harandi, M., Salzmann, M.: Distribution-matching embedding for visual domain adaptation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17, Article–number (2016)
Ben-David, S., Blitzer, J., Crammer, K., Kulesza, A., Pereira, F., Vaughan, J.W.: A theory of learning from different domains. Mach. Learn. 79(1), 151–175 (2010)
Cui, S., Wang, S., Zhuo, J., Su, C., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Gradually vanishing bridge for adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12455–12464 (2020)
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., Marchand, M., Lempitsky, V.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2030–2096 (2016)
Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: International conference on machine learning, pp. 1180–1189. PMLR (2015)
Goodfellow, I.J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 2, NIPS’14, p. 2672–2680. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hull, J.J.: A database for handwritten text recognition research. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 16(5), 550–554 (1994)
Ishii, M., Sugiyama, M.: Source-free domain adaptation via distributional alignment by matching batch normalization statistics. ar**v preprint ar**v:2101.10842 (2021)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Lee, S., Kim, D., Kim, N., Jeong, S.G.: Drop to adapt: Learning discriminative features for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 91–100 (2019)
Li, Y., Yuan, L., Chen, Y., Wang, P., Vasconcelos, N.: Dynamic transfer for multi-source domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10998–11007 (2021)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Do we really need to access the source data? source hypothesis transfer for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: ICML 2020: 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 1, pp. 6028–6039 (2020)
Liu, H., Shao, M., Fu, Y.: Structure-preserved multi-source domain adaptation. In: 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 1059–1064. IEEE (2016)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International conference on machine learning, pp. 97–105. PMLR (2015)
Long, M., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Conditional adversarial domain adaptation. ar**v preprint ar**v:1705.10667 (2017)
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Sun, J., Yu, P.S.: Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2200–2207 (2013)
Müller, R., Kornblith, S., Hinton, G.: When does label smoothing help? ar**v preprint ar**v:1906.02629 (2019)
Netzer, Y., Wang, T., Coates, A., Bissacco, A., Wu, B., Ng, A.Y.: Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning (2011)
Nguyen, T., Le, T., Zhao, H., Tran, Q.H., Nguyen, T., Phung, D.: Most: Multi-source domain adaptation via optimal transport for student-teacher learning. In: Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 225–235. PMLR (2021)
Nguyen, V.A., Nguyen, T., Le, T., Tran, Q.H., Phung, D.: Stem: An approach to multi-source domain adaptation with guarantees. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9352–9363 (2021)
Peng, X., Bai, Q., **a, X., Huang, Z., Saenko, K., Wang, B.: Moment matching for multi-source domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1406–1415 (2019)
Quionero-Candela, J., Sugiyama, M., Schwaighofer, A., Lawrence, N.D.: Dataset shift in machine learning. The MIT Press (2009)
Saenko, K., Kulis, B., Fritz, M., Darrell, T.: Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 213–226. Springer (2010)
Saito, K., Watanabe, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3723–3732 (2018)
Sun, B., Saenko, K.: Deep coral: Correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 443–450. Springer (2016)
Tang, H., Jia, K.: Discriminative adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 5940–5947 (2020)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7167–7176 (2017)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Zhang, N., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance. ar**v preprint ar**v:1412.3474 (2014)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-sne. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11) (2008)
Venkat, N., Kundu, J.N., Singh, D.K., Revanur, A., et al.: Your classifier can secretly suffice multi-source domain adaptation. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Venkateswara, H., Eusebio, J., Chakraborty, S., Panchanathan, S.: Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 5018–5027 (2017)
Wang, H., Xu, M., Ni, B., Zhang, W.: Learning to combine: Knowledge aggregation for multi-source domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 727–744. Springer (2020)
Wen, J., Greiner, R., Schuurmans, D.: Domain aggregation networks for multi-source domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10214–10224. PMLR (2020)
Xu, M., Wang, H., Ni, B.: Graphical modeling for multi-source domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2022)
Xu, M., Zhang, J., Ni, B., Li, T., Wang, C., Tian, Q., Zhang, W.: Adversarial domain adaptation with domain mixup. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 6502–6509 (2020)
Xu, R., Chen, Z., Zuo, W., Yan, J., Lin, L.: Deep cocktail network: Multi-source unsupervised domain adaptation with category shift. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3964–3973 (2018)
Yang, L., Balaji, Y., Lim, S.N., Shrivastava, A.: Curriculum manager for source selection in multi-source domain adaptation. In: ECCV (14), pp. 608–624 (2020)
Yosinski, J., Clune, J., Bengio, Y., Lipson, H.: How transferable are features in deep neural networks? ar**v preprint ar**v:1411.1792 (2014)
Yuan, J., Hou, F., Du, Y., Shi, Z., Geng, X., Fan, J., Rui, Y.: Self-supervised graph neural network for multi-source domain adaptation. ar**v preprint ar**v:2204.05104 (2022)
Zhang, J., Ding, Z., Li, W., Ogunbona, P.: Importance weighted adversarial nets for partial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 8156–8164 (2018)
Zhao, H., Zhang, S., Wu, G., Moura, J.M., Costeira, J.P., Gordon, G.J.: Adversarial multiple source domain adaptation. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 31, 8559–8570 (2018)
Zhao, S., Wang, G., Zhang, S., Gu, Y., Li, Y., Song, Z., Xu, P., Hu, R., Chai, H., Keutzer, K.: Multi-source distilling domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 12975–12983 (2020)
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Qiao, Y., **ang, T.: Domain adaptive ensemble learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 8008–8018 (2021)
Zhu, Y., Zhuang, F., Wang, D.: Aligning domain-specific distribution and classifier for cross-domain classification from multiple sources. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 5989–5996 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B-K Bao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Li, L. & Han, Y. Weighted progressive alignment for multi-source domain adaptation. Multimedia Systems 29, 117–128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00987-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00987-7