Abstract
Background
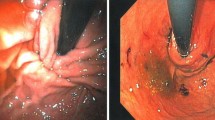
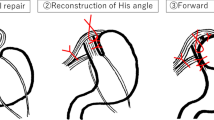
EsophyX is an endolumenal approach to the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This report describes one of the earliest and largest North American experiences with this device.
Methods
Prospective data were gathered on consecutive patients undergoing EsophyX fundoplication for a 1-year period between September 2007 and March 2009. During this time, the procedure evolved to the current technique. A P value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
The study enrolled 26 patients with a mean age of 45 years. The patients included 16 women (62%) with a mean body mass index (BMI) of 28 and an American Society Anesthesiology (ASA) classification of 2. These patients included 11 with associated small hiatal hernias, 3 with Barrett’s esophagus, and 5 with esophageal dysmotility. The procedure time was 65 min (range, 29–137 min), and the length of hospital stay was 1 day (range, 0–6 days). The postoperative valve circumference was 217º, and the valve length was 2.7 cm. Two complications of postoperative bleed occurred, requiring transfusion. The mean follow-up period was 10 months. Comparison of pre- and postoperative Anvari scores (34–17; P = 0.002) and Velanovich scores (22–10; P = 0.0007) showed significant decreases. Although 68% of the patients were still taking antireflux medications, 21% had reduced their dose by half. Three patients had persistent symptoms requiring Nissen fundoplication, and there was one late death unrelated to the procedure.
Conclusion
This study represents an initial single-institution experience with EsophyX. According to the findings, 53% of the patients had either discontinued their antireflux medication (32%) or had decreased their dose by half (21%). Both symptoms and health-related quality-of-life (HRQL) scores significantly improved after treatment. Further follow-up evaluation and objective testing are required.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locke GR III, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ III (1997) Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 112:1448–1456
El-Serag HB (2007) Time trends of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:17–26
Triadafilopoulos G (2007) Endotherapy and surgery for GERD. J Clin Gastroenterol 41(Suppl 2):S87–S96
Cadière GB, Rajan A, Germay O, Himpens J (2008) Endolumenal fundoplication by a transoral device for the treatment of GERD: a feasibility study. Surg Endosc 22:333–342
Dallemagne B, Weerts J, Markiewicz S, Dewandre JM, Wahlen C, Monami B, Jehaes C (2006) Clinical results of laparoscopic fundoplication at ten years after surgery. Surg Endosc 20:159–165
Papasavas PK, Keenan RJ, Yeaney WW, Caushaj PF, Gagne DJ, Landreneau RJ (2003) Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy. Surg Endosc 17:1200–1205
Cadière GB, Buset M, Muls V, Rajan A, Rosch T, Eckardt AJ, Weerts J, Bastens B, Costamagna G, Marchese M, Louis H, Mana F, Sermon F, Gawlicka AK, Daniel MA, Deviere J (2008) Antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX: 12-month results of a prospective multicenter study. World J Surg 32:1676–1688
Bergman S, Mikami DJ, Hazey JW, Roland JC, Dettorre R, Melvin WS (2008) Endolumenal fundoplication with EsophyX: the initial North American experience. Surg Innov 15:166–170
Cadière GB, Rajan A, Rqibate M, Germay O, Dapri G, Himpens J, Gawlicka AK (2006) Endolumenal fundoplication (ELF): evolution of EsophyX, a new surgical device for transoral surgery. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 15:348–355
Allen CJ, Parameswaran K, Belda J, Anvari M (2000) Reproducibility, validity, and responsiveness of a disease-specific symptom questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus 13:265–270
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality-of-life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183:217–224
Pearl JP, Marks JM (2007) Endolumenal therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they dead? Surg Endosc 21:1–4
Schiefke I, Zabel-Langhennig A, Neumann S, Feisthammel J, Moessner J, Caca K (2005) Long-term failure of endoscopic gastroplication (EndoCinch). Gut 54:752–758
Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Kozarek R, Haber G, Gostout C, Lembo A (2007) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: long-term multicenter results. Surg Endosc 21:439–444
Rothstein R, Filipi C, Caca K, Pruitt R, Mergener K, Torquati A, Haber G, Chen Y, Chang K, Wong D, Deviere J, Pleskow D, Lightdale C, Ades A, Kozarek R, Richards W, Lembo A (2006) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 131:704–712
Corley DA, Katz P, Wo JM, Stefan A, Patti M, Rothstein R, Edmundowicz S, Kline M, Mason R, Wolfe MM (2003) Improvement of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms after radiofrequency energy: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 125:668–676
Cadière GB, Van Sante N, Graves JE, Gawlicka AK, Rajan A (2009) Two-year results of a feasibility study on antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX. Surg Endosc 23:957–964
Hogan WJ (2006) Clinical trials evaluating endoscopic GERD treatments: is it time for a moratorium on the clinical use of these procedures? Am J Gastroenterol 101:437–439
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demyttenaere, S.V., Bergman, S., Pham, T. et al. Transoral incisionless fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease in an unselected patient population. Surg Endosc 24, 854–858 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0676-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0676-z