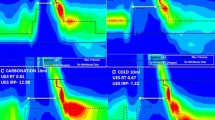
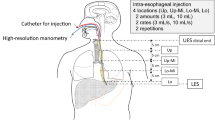
Abstract
UES opening occurs following cricopharyngeus deactivation and submental muscle contraction causing hyolaryngeal elevation and UES distraction. During impedance manometry, the inverse of impedance (admittance) can be used to measure bolus presence and infer UES opening. We hypothesized that the temporal relationship between UES relaxation, opening and hyolaryngeal elevation would change with increasing bolus volume. Simultaneous intramuscular cricopharyngeal (CP) electromyography (EMG), surface submental EMG (SM-EMG), and high-resolution impedance manometry were recorded in eight (aged 27 ± 7 years, 5 M) healthy volunteers, while swallowing 0.9 % saline boluses of 2, 5, 10, and 20 ml. Data were exported and analyzed via Matlab. Statistical analysis comprised repeated measures one-way ANOVA and Pearson correlation. A P value of <0.05 was considered significant. Duration of CP deactivation increased at 20 ml volume (P < 0.001). UES relaxation and opening increased with increasing bolus volume (P < 0.001); however, overall duration of SM activation did not change. As UES opening occurs progressively earlier with increasing volumes, peak SM-EMG activity occurs relatively later (P < 0.001) and shifts from occurring before to following peak UES distention. During healthy swallowing, there is sensory modulation of cricopharyngeal and submental muscle activity. Intrabolus pressures, transmitted from the tongue base and pharynx, play a progressively more important role in sphincter opening with increasing volume. The findings may explain why some healthy elderly and patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia have difficulty swallowing larger while tolerating smaller bolus volumes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asoh R, Goyal RK. Manometry and electromyography of the upper esophageal sphincter in the opossum. Gastroenterol. 1978;74:514–20.
Sivarao DV, Goyal RK. Functional anatomy and physiology of the upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Med. 2000;108(4A):27S–37S.
Miller AJ. Deglutition. Physiol Rev. 1982;62:129–84.
Samuel E, Shaker R. Deglutitive pharyngeal and UES pressure phenomena. In: Shaker R, Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Easterling C, editors. Principles of deglutition. New York: Springer; 2013.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114:2226–44.
Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Logemann J, Shaker R. Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterol. 1988;95:52–62.
Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, et al. Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1989;257:G748–59.
Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Lagemann JA, Shah V, Ha T. Upper esophageal sphinicter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterol. 1989;97:1469–78.
Shaker R, Ren J, Kern M, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ, Li Q. Mechanisms of airway protection and upper esophageal sphincter opening during belching. Am J Physiol. 1992;25:G621–8.
Lang IM, Dana N, Medda BK, Shaker R. Mechanisms of airway protection during retching, vomiting and swallowing. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G529–36.
Crary MA, Carnaby GD, Groher ME. Biomechanical correlates of surface electromyography signals obtained during swallowing by healthy adults. JSLHR. 2006;49:186–93.
Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, et al. Timing of video fluoroscopic, manometric events, and bolus transit during the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1989;4:8–15.
Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, Dodds WJ, Kahrilas PJ, Brasseur JG, Cook IJ, Lang IM. Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1990;258:G675–81.
Ertekin C, Pehlivan M, Aydogdu I, et al. An electrophysiological investigation of deglutition in man. Muscle Nerv. 1995;18:1177–86.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Electromyography of human cripharyngeal muscle of the upper esophageal sphincter—a review. Muscle Nerv. 2002;26:729–39.
Dodds WJ, Man KM, Cook IJ, Kahrilas PJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK. Influence of bolus volume of swallow-induced hyoid movement in normal subjects. AJR. 1988;150:1307–9.
Lang IM, Dantas RO, Cook IJ, Dodds WJ. Videoradiographic, manometric and electromyographic assessment of the canine upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1991;260:G911–9.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yűceyar N. Piecemeal deglutition and dysphagia limit in normal subjects and in patients with swallowing disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996;6:491–6.
Aydogdu I, Kiylioglu N, Tarlaci S, Tanriverdi Z, Alpaydin S, Acarer A, Baysal L, Arpaci E, Yuceyar N, Secil Y, Ozdemirkiran T, Ertekin C. Diagnostic value of “dysphagia limit” for neurogenic dysphagia: 17 years of experience in 1278 adults. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126:634–43.
Hammer MJ, Jones CA, Mielens JD, Kim CH, McCulloch TM. Evaluating the tongue-hold maneuver using high-resolution manometry and electromyography. Dysphagia. 2014;29:564–70.
Jones CA, Hammer MJ, Hoffman MR, McCulloch TM. Quantifying contributions of the cricopharyngeus to upper esophageal sphincter pressure changes by means of intramuscular electromyography and high-resolution manometry. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2014;123:174–82.
Jones CA, Cuicci MR, Hammer MJ, McCulloch TM. A mutisensor approach to improve manometric analysis of the upper esophageal sphincter. Laryngoscope. 2015. doi:10.1002/lary.25506.
Ghosh SK, Pandolfino JE, Zhang Q, Jarosz A, Kahrilas PJ. Degluttitive upper esophageal sphincter relaxation: a study of 75 volunteer subjects using solid-state high-resolution manometry. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291:G525–31.
Omari TI, Jones CA, Hammer MJ, Cock C, Dinning PG, Wiklendt L, Costa MC, McCulloch TM. Predicting the activation states of the muscles governing upper esophageal sphincter relaxation and opening. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00388.2015.
Omari TI, Wiklendt L, Dinning P, Costa M, Rommel N, Cock C. Upper esophageal sphincter mechanical states analysis: a novel methodology to describe UES relaxation and opening. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015;8:241. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2014.00241 eCollection 2014.
Kim HJ, Mittal RK, Patel N, Ledgerwood M, Bhargava V. Esophageal distention during bolus transport: can it be detected by intraluminal impedance recordings? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26:1122–30.
Cock C, Besanko L, Kritas S, et al. Maximum upper esophageal sphincter (UES) admittance: a non-specific marker of UES dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. doi:10.1111/nmo.12714.
Omari TI, Dejeager E, Van Beckevoort D, Goeleven A, De Cock P, Hoffmen I, Smet MH, Davidson GP, Tack J, Rommel N. A novel method for the nonradiological assessment of ineffective swallowing. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1796–802.
Omari TI, Savilampi J, Kokkinn K, Schar M, Lamvik K, Doeltgen S, Cock C. The reliability of pharyngeal high-resolution manometry with impedance and derivation of measures of swallowing function. Int J Otolaryngol. 2016. doi:10.1155/2016/2718482.
Weijenborg PW, Kessing BF, Smout AJPM, Bredenoord AJ. Normal values for solid-state esophageal high-resolution manometry in a European population; an overview of all current metrics. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26:654–9.
Nagai T. The occurrence and ultrastructure of a mechanoreceptor in the human cricopharyngeus muscle. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1991;248:144–6.
Shaker R, Ren J, Podvrsan B, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ, Kern M, Hoffmann R, Hintz J. Effect of aging and bolus variables on pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter motor function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1993;264:G427–32.
Jean A, Dellaporta M. Brainstem control of deglutition: swallowing pattern generator. In: Shaker R, Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Easterling C, editors. Principles of deglutition. New York: Springer; 2013.
Gokyigit MC, Pazarci NK, Ercan I, Seker S, Turgut S, Ertekin C. Identification of distinct swallowing patterns for different bolus volumes. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120:1750–4.
Acknowledgments
C Cock supported by a grant from the Repat foundation. TM McCulloch and CA Jones supported by NIH Grants DC011130/T32 GM007507. MJ Hammer supported by NIH Grants DC010900/DC014519. TI Omari supported by an NHMRI fellowship. TI Omari has a patent on AIMplot analysis software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author TO owns a patent on AIMplot software. Other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cock, C., Jones, C.A., Hammer, M.J. et al. Modulation of Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) Relaxation and Opening During Volume Swallowing. Dysphagia 32, 216–224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9744-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9744-4