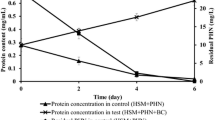
Abstract
Polycyclic aromatics hydrocarbons (PAHs) are ubiquitous and toxic pollutants that are dangerous to humans and living organism in aquatic environment. Normally, PAHs has lower molecular weight such as phenanthrene and naphthalene that are easy and efficient to degrade, but high-molecular-weight PAHs such as chrysene and pyrene are difficult to be biodegraded by common microorganism. This study investigated the isolation and characterization of a potential halophilic bacterium capable of utilizing two high-molecular-weight PAHs. At the end of the experiment (25–30 days of incubation), bacterial counts have reached a maximum level (over 40 × 1016 CFU/mL). The highest biodegradation rate of 77% of chrysene in 20 days and 92% of pyrene in 25 days was obtained at pH 7, temperature 25 °C, agitation of 150 rpm and Tween 80 surfactant showing to be the most impressive parameters for HMWPAHs biodegradation in this research. The metabolism of initial compounds revealed that Hortaea sp. B15 utilized pyrene to form phthalic acid while chrysene was metabolized to form 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. The result showed that Hortaea sp. B15 can be promoted for the study of in situ biodegradation of high molecular weight PAH.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhay A, Magnin JP, Gondrexon N, Baup S, Willison J (2008) Optimization and modeling of phenanthrene degradation by Mycobacterium sp. 6PY1 in a biphasic medium using response-surface methodology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:881–888
Lazim ZM, Hadibarata T, Puteh MH, Yusop Z (2015) Adsorption characteristics of Bisphenol A onto low cost modified phyto-waste material in aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:34
Harmsen J, Rietra RPJJ (2018) 25 years monitoring of PAHs and petroleum hydrocarbons biodegradation in soil. Chemosphere 207:229–238
Jiang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang X (2018) Co-biodegradation and pyrene and other PAHs by the bacterium Acinetobacter johnsonii. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:465–470
Hadibarata T, Chuang TZ, Rubiyatno A, Zubir MMFA, Khudhair AB, Yusoff ARM, Salim MR, Hidayat T (2013) Identification of naphthalene metabolism by white rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii. Bioprocrocess Biosyst Eng 36:1455–1461
Chauhan A, Fazlurrahman C, Oakeshott JG, Jain RK (2008) Bacterial metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: strategies for bioremediation. Ind J Microbiol 48:95–113
Kristanti RA, Hadibarata T, Al Farraj DA, Elshikh MS, Alkufeidy RM (2018) Biodegradation mechanism of phenanthrene by halophilic Hortaea sp. B15. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:324
Khudhair AB, Hadibarata T, Kamyab H, Kristanti RA (2017) Biotransformation of pyrene by Candida sp. S1 under high salinity conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:1411–1418
Singh K, Chandra S (2014) Treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon polluted environment through bioremediation: a review. Pak J Biol Sci 17:1–8
Zhou H, Wang H, Huang Y, Fang T (2016) Characterization of pyrene degradation by halophilic Thalassospira sp. strain TSL5-1 isolated from the coastal soil of Yellow Sea, China. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 107:62–69
Nzila A, Ramirez CA, Musa MM, Sankara S, Basheer C, Li QX (2018) Pyrene biodegradation and proteomic analysis in Achromobacter xylosoxidans, PY4 strain. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 130:40–47
Wang S, Li X, Liu W, Li P, Kong L, Ren W, Wu H, Tu Y (2012) Degradation of pyrene by immobilized microorganisms in saline-alkaline soil. J Environ Sci 24:1662–1669
Lu J, Guo C, Zhang M, Lu G, Dang Z (2014) Biodegradation of single pyrene and mixtures of pyrene by a fusant bacterial strain F14. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 87:75–80
Ghevariya CM, Bhatt JK, Bharti P (2011) Enhanced chrysene degradation by halotolerant Achromobacter xylosoxidans using Response Surface Methodology. Bioresour Technol 102:9668–9674
Vaidya S, Devpura N, Jain K, Madamwar D (2018) Degradation of chrysene by enriched bacterial consortium. Front Microbiol 9:1333
Dhote M, Juwarkar A, Kumar A, Kanade GS, Chakrabarti T (2010) Biodegradation of chrysene by the bacterial strains isolated from oily sludge Monika. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:329–335
Sawadogo A, Harmonie OC, Sawadogo JB, Kabore A (2014) Isolation and characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria from wastewaters in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J Environ Prot 5:1183–1196
Thapa B, Kumar A, Ghimire A (2012) A review on bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants on soil. Kathmandu Univ J Sci Eng Technol 8:167–170
Collina E, Bestetti G, Di Gennaro P, Franzetti A, Gugliersi F, Lasagni M, Pitea D (2005) Naphthalene biodegradation kinetics in an aerobic slurry-phase bioreactor. Environ Int 31:167–171
Hassan SED, Desouky SE, Fouda A, El-Gamal MS, Alemam A (2015) Biodegradation of phenanthrene by Klebsiella sp. Isolated from organic contaminated sediment. J Adv Biol Biotechnol 4:1–12
Adnan LA, Sathishkumar P, Yusoff ARM, Hadibarata T, Ameen F (2017) Rapid bioremediation of Alizarin Red S and Quinizarine Green SS dyes using Trichoderma lixii F21 mediated by biosorption and enzymatic processes. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:85–97
Hadibarata T, Kristanti RA (2014) Effect of surfactants and identification of metabolites on the biodegradation of fluoranthene by basidiomycetes fungal isolate Armillaria sp. F022. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:593–600
Kaczorek E, Olszanowski A (2011) Uptake of hydrocarbon by Pseudomonas fluorescens (P1) and Pseudomonas putida (K1) strains in the presence of surfactants: a cell surface modification. Water Air Soil Pollut 214:451–459
Hadibarata T, Tachibana S, Askari M (2011) Identification of metabolites from phenanthrene oxidation by phenoloxidases and dioxygenases of Polyporus sp. S133. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:299–304
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through research group no. RG1439-044, Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education through Fundamental Research Grant Scheme no. 5F244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Farraj, D.A., Hadibarata, T., Yuniarto, A. et al. Characterization of pyrene and chrysene degradation by halophilic Hortaea sp. B15. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42, 963–969 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02096-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02096-8