Abstract
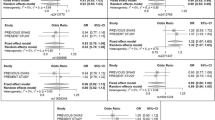
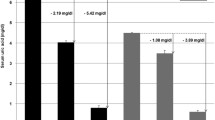
Taiwanese aborigines have a high prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout. Uric acid levels and urate excretion have correlated with dopamine-induced glomerular filtration response. MAOs represent one of the major renal dopamine metabolic pathways. We aimed to identify the monoamine oxidase A (MAOA, Xp11.3) gene variants and MAO-A enzyme activity associated with gout risk. This study was to investigate the association between gout and the MAOA single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs5953210, rs2283725, and rs1137070 as well as between gout and the COMT SNPs rs4680 Val158Met for 374 gout cases and 604 controls. MAO-A activity was also measured. All three MAOA SNPs were significantly associated with gout. A synonymous MAOA SNP, rs1137070 Asp470Asp, located in exon 14, was associated with the risk of having gout (P = 4.0 × 10−5, adjusted odds ratio 1.46, 95% confidence intervals [CI]: 1.11–1.91). We also showed that, when compared to individuals with the MAOA GAT haplotype, carriers of the AGC haplotype had a 1.67-fold (95% CI: 1.28–2.17) higher risk of gout. Moreover, we found that MAOA enzyme activity correlated positively with hyperuricemia and gout (P for trend = 2.00 × 10−3 vs. normal control). We also found that MAOA enzyme activity by rs1137070 allele was associated with hyperuricemia and gout (P for trend = 1.53 × 10−6 vs. wild-type allele). Thus, our results show that some MAOA alleles, which have a higher enzyme activity, predispose to the development of gout.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzai N, Ichida K, Jutabha P, Kimura T, Babu E, ** CJ, Srivastava S, Kitamura K, Hisatome I, Endou H, Sakurai H (2008) Plasma urate level is directly regulated by a voltage-driven urate efflux transporter URATv1 (SLC2A9) in humans. J Biol Chem 283:26834–26838
Bianchi P, Seguelas MH, Parini A, Cambon C (2003) Activation of pro-apoptotic cascade by dopamine in renal epithelial cells is fully dependent on hydrogen peroxide generation by monoamine oxidases. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:855–862
Cappuccio FP, Strazzullo P, Farinaro E, Trevisan M (1993) Uric acid metabolism and tubular sodium handling. Results from a population-based study. JAMA 270:354–359
Cases O, Seif I, Grimsby J, Gaspar P, Chen K, Pournin S, Muller U, Aguet M, Babinet C, Shih JC et al (1995) Aggressive behavior and altered amounts of brain serotonin and norepinephrine in mice lacking MAOA. Science 268:1763–1766
Chang SJ, Ko YC, Wang TN, Chang FT, Cinkotai FF, Chen CJ (1997) High prevalence of gout and related risk factors in Taiwan’s Aborigines. J Rheumatol 24:1364–1369
Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM (2005) Pathogenesis of gout. Ann Intern Med 143:499–516
Dalbeth N, Merriman T (2009) Crystal ball gazing: new therapeutic targets for hyperuricaemia and gout. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:222–226
Emmerson BT (1996) The management of gout. N Engl J Med 334:445–451
Feig DI, Kang DH, Johnson RJ (2008) Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 359:1811–1821
Fernandes MH, Soares-da-Silva P (1994) Role of monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyltransferase in the metabolism of renal dopamine. J Neural Transm Suppl 41:101–105
Gilad Y, Rosenberg S, Przeworski M, Lancet D, Skorecki K (2002) Evidence for positive selection and population structure at the human MAO-A gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:862–867
Guimaraes JT, Soares-da-Silva P (1998) The activity of MAO A and B in rat renal cells and tubules. Life Sci 62:727–737
Hediger MA, Johnson RJ, Miyazaki H, Endou H (2005) Molecular physiology of urate transport. Physiology (Bethesda) 20:125–133
Johnson RJ, Gaucher EA, Sautin YY, Henderson GN, Angerhofer AJ, Benner SA (2008) The planetary biology of ascorbate and uric acid and their relationship with the epidemic of obesity and cardiovascular disease. Med Hypotheses 71:22–31
Jose PA, Raymond JR, Bates MD, Aperia A, Felder RA, Carey RM (1992) The renal dopamine receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 2:1265–1278
Kunduzova OR, Bianchi P, Pizzinat N, Escourrou G, Seguelas MH, Parini A, Cambon C (2002) Regulation of JNK/ERK activation, cell apoptosis, and tissue regeneration by monoamine oxidases after renal ischemia-reperfusion. FASEB J 16:1129–1131
Monteiro HP, Stern A (1996) Redox modulation of tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent signal transduction pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 21:323–333
Pascual E, Perdiguero M (2006) Gout, diuretics and the kidney. Ann Rheum Dis 65:981–982
Pestana M, Jardim H, Correia F, Vieira-Coelho MA, Soares-da-Silva P (2001) Renal dopaminergic mechanisms in renal parenchymal diseases and hypertension. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16(Suppl 1):53–59
Pizzinat N, Copin N, Vindis C, Parini A, Cambon C (1999) Reactive oxygen species production by monoamine oxidases in intact cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 359:428–431
Sulikowska B, Manitius J, Odrowaz-Sypniewska G, Lysiak-Szydlowska W, Rutkowski B (2008) Uric acid excretion and dopamine-induced glomerular filtration response in patients with IgA glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol 28:391–396
Taniguchi A, Kamatani N (2008) Control of renal uric acid excretion and gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol 20:192–197
Terkeltaub RA (2003) Clinical practice. Gout. N Engl J Med 349:1647–1655
Vindis C, Seguelas MH, Lanier S, Parini A, Cambon C (2001) Dopamine induces ERK activation in renal epithelial cells through H2O2 produced by monoamine oxidase. Kidney Int 59:76–86
Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker JL, McCarty DJ, Yu TF (1977) Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum 20:895–900
Wang WH, Chang SJ, Wang TN, Cheng LS, Feng YP, Chen CJ, Huang CH, Ko YC (2004) Complex segregation and linkage analysis of familial gout in Taiwanese aborigines. Arthritis Rheum 50:242–246
Zeng C, Zhang M, Asico LD, Eisner GM, Jose PA (2007) The dopaminergic system in hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 112:583–597
Acknowledgments
We thank the medical staffs and primary care doctors at Jianshih and Wufong health center for the precise clinical phenotypes. We thank the study staff (Chun-Lan Hsu, Yu Tai and Chih-Shan Liu) from Division of Environmental Health and Occupational Medicine, National Health Research Institutes for data handling. This study was supported by grants from the National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-98A1-PDCO-0307101), Center of Excellence for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University (KMU-EM-98-1-1), and the National Science Council (NSC97-2314-B-037-007 and NSC97-3112-B-400-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, HP., Ko, A.MS., Wang, SJ. et al. Monoamine oxidase A gene polymorphisms and enzyme activity associated with risk of gout in Taiwan aborigines. Hum Genet 127, 223–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0765-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0765-z