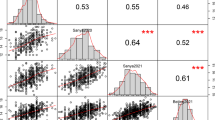
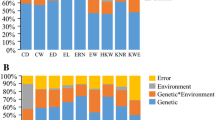
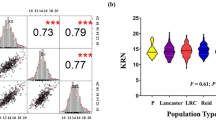
Abstract
Kernel weight in a unit volume is referred to as kernel test weight (KTW) that directly reflects maize (Zea mays L.) grain quality. In this study, an inter-mated B73 × Mo17 (IBM) Syn10 doubled haploid (DH) population and an association panel were used to identify loci responsible for KTW of maize across multiple environments. A total of 18 significant KTW-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified using genome-wide association study (GWAS); they were closely linked to 12 candidate genes. In the IBM Syn10 DH population, linkage analysis detected 19 common quantitative trait loci (QTL), five of which were repeatedly detected among multiple environments. Several verified genes that regulate maize seed development were found in the confidence intervals of the mapped QTL and the LD regions of GWAS, such as ZmYUC1, BAP2, ZmTCRR-1, dek36 and ZmSWEET4c. Combined QTL map** and GWAS identified one significant SNP that was co-identified in the both populations. Based on the co-localized SNP across the both populations, 17 candidate genes were identified. Of them, Zm00001d044075, Zm00001d044086, and Zm00001d044081 were further identified by candidate gene association study for KTW. Zm00001d044081 encodes homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-4, which has been demonstrated to control apical embryo development in Arabidopsis. Our findings provided insights into the mechanism underlying maize KTW and contributed to the application of molecular-assisted selection of high KTW breeding in maize.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JR, Schrag T, Melchinger AE, Zein I, Lübberstedt T (2005) Validation of Dwarf8 polymorphisms associated with flowering time in elite European inbred lines of maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:206–217
Bernardi J, Lanubile A, Li QB, Kumar D, Kladnik A, Cook SD, Ross JJ, Marocco A, Chourey PS (2012) Impaired auxin biosynthesis in the defective endosperm18 mutant is due to mutational loss of expression in the ZmYuc1 gene encoding endosperm-specific YUCCA1 protein in maize. Plant Physiol 160:1318–1328
Blandino M, Sacco D, Reyneri A (2013) Prediction of the dry-milling performance of maize hybrids through hardness-associated properties. J Sci Food Agric 93:1356–1364
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association map** of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Byung-Ho K, Yuqing X, Williams DS, Diego PR, Chourey PS (2009) Miniature1-encoded cell wall invertase is essential for assembly and function of wall-in-growth in the maize endosperm transfer cell. Plant Physiol 151:1366–1376
Cabral AL, Jordan MC, Larson G, Somers DJ, Humphreys DG, Mccartney CA (2018) Relationship between QTL for grain shape, grain weight, test weight, milling yield, and plant height in the spring wheat cross RL4452/’AC Domain’. PLoS ONE 13:e0190681
Debbie W, Ben V, Hardeep N, Ron A, Wilson GV, Provart NJ (2007) An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2:e718
Deng M, Li D, Luo J, **ao Y, Liu H, Pan Q, Zhang X, ** M, Zhao M, Yan J (2017) The genetic architecture of amino acids dissection by association and linkage analysis in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1250–1263
Depege-Fargeix N, Javelle M, Chambrier P, Frangne N, Gerentes D, Perez P, Rogowsky PM, Vernoud V (2010) Functional characterization of the HD-ZIP IV transcription factor OCL1 from maize. J Exp Bot 62:293–305
Ding J-Q, Ma J-L, Zhang C-R, Dong H-F, ** for test weight by using F 2: 3 population in maize. J Genet 90:75–80
Dorsey-Redding C, Hurburgh CR, Johnson LA, Fox SR (1991) Relationships among maize quality factors. Cereal Chem 68:602–605
Gao X, Starmer J, Martin ER (2008) A multiple testing correction method for genetic association studies using correlated single nucleotide polymorphisms. Genet Epidemiol 32:361–369
Gawel N, Jarret R (1991) A modified CTAB DNA extraction procedure for Musa and Ipomoea. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:262–266
Gutierrez-Marcos JF, Dal Pra M, Giulini A, Costa LM, Gavazzi G, Cordelier S, Sellam O, Tatout C, Paul W, Perez P, Dickinson HG, Consonni G (2007) Empty pericarp4 encodes a mitochondrion-targeted pentatricopeptide repeat protein necessary for seed development and plant growth in maize. Plant Cell 19:196–210
Holland JB, Munkvold GP (2001) Genetic relationships of crown rust resistance, grain yield, test weight, and seed weight in oat. Crop Sci 41:1041–1050
Hughes TA (2006) Regulation of gene expression by alternative untranslated regions. Trends Genet 22:119–122
Hussain T, Tausend P, Graham G, Ho J (2007) Registration of IBM2 SYN10 doubled haploid map** population of maize. J Plant Reg 1:81
Jiao Y, Zhao H, Ren L, Song W, Zeng B, Guo J, Wang B, Liu Z, Chen J, Li W, Zhang M, **e S, Lai J (2012) Genome-wide genetic changes during modern breeding of maize. Nat Genet 44:812–815
Kaler AS, Ray JD, Schapaugh WT, King CA, Purcell LC (2017) Genome-wide association map** of canopy wilting in diverse soybean genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 130:2203–2217
Khaled AS, Vernoud V, Ingram GC, Perez P, Sarda X, Rogowsky PM (2005) Engrailed-ZmOCL1 fusions cause a transient reduction of kernel size in maize. Plant Mol Biol 58:123–139
Knapp S, Stroup W, Ross W (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis 1. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Kristensen PS, Jahoor A, Andersen JR, Cericola F, Orabi J, Janss LL, Jensen J (2018) Genome-wide association studies and comparison of models and cross-validation strategies for genomic prediction of quality traits in advanced winter wheat breeding lines. Front Plant Sci 9:69
Larsson SJ, Lipka AE, Buckler ES (2013) Lessons from Dwarf8 on the strengths and weaknesses of structured association map**. PLoS Genet 9:e1003246
Li X, Zhou Z, Ding J, Wu Y, Zhou B, Wang R, Ma J, Wang S, Zhang X, ** reveals QTL and candidate genes for plant and ear height in maize. Front Plant Sci 7:833
Liu L, Du Y, Huo D, Wang M, Shen X, Yue B, Qiu F, Zheng Y, Yan J, Zhang Z (2015) Genetic architecture of maize kernel row number and whole genome prediction. Theor Appl Genet 128:2243–2254
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 12:e1005767
Liu H, Zhang L, Wang J, Li C, Zeng X, **e S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Hu S, Wang J, Lee M, Lubberstedt T, Zhao G (2017a) Quantitative trait locus analysis for deep-sowing germination ability in the maize IBM Syn10 DH population. Front Plant Sci 8:813
Liu J, Huang J, Guo H, Lan L, Wang H, Xu Y, Yang X, Li W, Tong H, **ao Y, Pan Q, Qiao F, Raihan MS, Liu H, Zhang X, Yang N, Wang X, Deng M, ** M, Zhao L, Luo X, Zhou Y, Li X, Zhan W, Liu N, Wang H, Chen G, Li Q, Yan J (2017b) The conserved and unique genetic architecture of kernel size and weight in maize and rice. Plant Physiol 175:774–785
Liu M, Tan X, Yang Y, Liu P, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang L, Hu Y, Ma L, Li Z, Zhang Y, Zou C, Lin H, Gao S, Lee M, Lübberstedt T, Pan G, Shen Y (2019) Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize kernel size traits by combined linkage and association map**. Plant Biotechnol J
Lu Y, Zhang S, Shah T, ** is a powerful approach to detecting quantitative trait loci underlying drought tolerance in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19585–19590
Ma L, Liu M, Yan Y, Qing C, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Long Y, Wang L, Pan L, Zou C, Li Z, Wang Y, Peng H, Pan G, Jiang Z, Shen Y (2018) Genetic dissection of maize embryonic callus regenerative capacity using multi-locus genome-wide association studies. Front Plant Sci 9:561
Mahuku G, Chen J, Shrestha R, Narro LA, Guerrero KV, Arcos AL, Xu Y (2016) Combined linkage and association map** identifies a major QTL (qRtsc8-1), conferring tar spot complex resistance in maize. Theor Appl Genet 129:1217–1229
Mdela L, Cldejr S, Dav B, Apde S, Carlinigarcia LA (2006) Map** QTL for grain yield and plant traits in a tropical maize population. Mol Breed 17:227–239
Mertz ET, Bates LS, Nelson OE (1964) Mutant gene that changes protein composition and increases lysine content of maize endosperm. Science 145(3629):279–280
Muniz LM, Royo J, Gomez E, Barrero C, Bergareche D, Hueros G (2006) The maize transfer cell-specific type-A response regulator ZmTCRR-1 appears to be involved in intercellular signalling. Plant J 48:17–27
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Zhang Y, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B (2011) QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet theoretische Und Angewandte Genetik 122:1305–1320
Pixley KV, Frey KJ (1991) Inheritance of test weight and its relationship with grain yield of oat. Crop Sci 31:36–40
Ribaut JeanMarcel, Hoisington David (1998) Marker-assisted selection: new tools and strategies. Trend Plant Sci 3:236–239
SAC (2003) National standards of the P. R. C, 3rd edn. Standardization Administration of the People Republic of China, Standards Press of China, Bei**g, P. R. China
Schulthess AW, Reif JC, Ling J, Plieske J, Kollers S, Ebmeyer E, Korzun V, Argillier O, Stiewe G, Ganal MW, Roder MS, Jiang Y (2017) The roles of pleiotropy and close linkage as revealed by association map** of yield and correlated traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Exp Bot 68:4089–4101
Sekhon RS, Lin H, Childs KL, Hansey CN, Buell CR, de Leon N, Kaeppler SM (2011) Genome-wide atlas of transcription during maize development. Plant J 66:553–563
Serna A, Maitz M, O’connell T, Santandrea G, Thevissen K, Tienens K, Hueros G, Faleri C, Cai G, Lottspeich F (2001) Maize endosperm secretes a novel antifungal protein into adjacent maternal tissue. Plant J 25:687–698
Sosso D, Luo D, Li QB, Sasse J, Yang J, Gendrot G, Suzuki M, Koch KE, McCarty DR, Chourey PS, Rogowsky PM, Ross-Ibarra J, Yang B, Frommer WB (2015) Seed filling in domesticated maize and rice depends on SWEET-mediated hexose transport. Nat Genet 47:1489–1493
Sun X-Y, Wu K, Zhao Y, Kong F-M, Han G-Z, Jiang H-M, Huang X-J, Li R-J, Wang H-G, Li S-S (2008) QTL analysis of kernel shape and weight using recombinant inbred lines in wheat. Euphytica 165:615–624
Tao Y, Jiang L, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Ingvardsen CR, Frei UK, Wang B, Lai J, Lübberstedt T (2013) Combined linkage and association map** reveals candidates for Scmv1, a major locus involved in resistance to sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV) in maize. BMC Plant Biol 13:162
Tian F, Bradbury PJ, Brown PJ, Hung H, Sun Q, Flint-Garcia S, Rocheford TR, McMullen MD, Holland JB, Buckler ES (2011) Genome-wide association study of leaf architecture in the maize nested association map** population. Nat Genet 43:159–162
Turchi L, Carabelli M, Ruzza V, Possenti M, Sassi M, Penalosa A, Sessa G, Salvi S, Forte V, Morelli G, Ruberti I (2013) Arabidopsis HD-Zip II transcription factors control apical embryo development and meristem function. Development 140:2118–2129
Visscher PM (2008) Sizing up human height variation. Nat Genet 40:489–490
Wang G, Zhong M, Shuai B, Song J, Zhang J, Han L, Ling H, Tang Y, Wang G, Song R (2017) E+ subgroup PPR protein defective kernel 36 is required for multiple mitochondrial transcripts editing and seed development in maize and Arabidopsis. New Phytol 214:1563–1578
Woffelman C (2004) DNAMAN for Windows, Version 5.2. 10. Lynon Biosoft, Institute of Molecular Plant Sci, Netherlands: Leiden University
Wu X, Li Y, Shi Y, Song Y, Zhang D, Li C, Buckler ES, Li Y, Zhang Z, Wang T (2016) Joint-linkage map** and GWAS reveal extensive genetic loci that regulate male inflorescence size in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1551–1562
Yu J, Buckler ES (2006) Genetic association map** and genome organization of maize. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:155–160
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S, Buckler ES (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association map** that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zhang Z, Ersoz E, Lai CQ, Todhunter RJ, Tiwari HK, Gore MA, Bradbury PJ, Yu J, Arnett DK, Ordovas JM, Buckler ES (2010) Mixed linear model approach adapted for genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 42:355–360
Zhang X, Zhang H, Li L, Lan H, Ren Z, Liu D, Wu L, Liu H, Jaqueth J, Li B, Pan G, Gao S (2016) Characterizing the population structure and genetic diversity of maize breeding germplasm in Southwest China using genome-wide SNP markers. BMC Genomics 17:697
Zhang C, Zhou Z, Yong H, Zhang X, Hao Z, Zhang F, Li M, Zhang D, Li X, Wang Z, Weng J (2017) Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association map**. Theor Appl Genet 130:1011–1029
Zhao X, Luo L, Cao Y, Liu Y, Li Y, Wu W, Lan Y, Jiang Y, Gao S, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Pan G, Lin H (2018) Genome-wide association analysis and QTL map** reveal the genetic control of cadmium accumulation in maize leaf. BMC Genomics 19:91
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Major Project of China on New Varieties of GMO Cultivation (2016ZX08003003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871637), and the Science and Technology Research Program of Sichuan Municipal Education Commission (2018JY0170).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z-RG, LW, JF, Y-CZ, Z-LL, L-LM, Y-LZ, ML, PL, C-YZ, and YCH participated in the management of the experiment and KTW measurements in this work. This study was conceived by Y-OS and Z-RG. Collections of all plant materials were performed by H-JL, G-SY, S-BG, and G-TP. X-XZ and PL conducted the data analysis. X-XZ wrote the initial manuscript, and Y-OS reviewed the manuscript and made significant editorial contributions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This study does not include human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Guan, Z., Wang, L. et al. Combined GWAS and QTL analysis for dissecting the genetic architecture of kernel test weight in maize. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 409–420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01631-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01631-2