Abstract
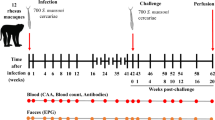
The present study tested the hypothesis that prenatal exposure of neonate Outbred albino mice to Schistosoma mansoni antigens (Ags) or antibodies (Abs) modulates their immunity against postnatal responses to infection. Persistence of maternal S. mansoni Abs and/or Ags in mice born to S. mansoni-infected mothers (IF-IMs) and noninfected mothers (IF-NMs) for up to 8 weeks after delivery was investigated. A higher level of anti-S. mansoni IgG Ab was detected in sera of 1-week-old mice born to IF-IM compared to controls. Then, immunoglobulin (Ig)G gradually decreased to the eight week. No anti-S. mansoni IgM Ab was detected in sera of these offspring at any week after delivery. Schistosoma Ags were detected in liver and kidney tissues of mice born to infected mothers. However, Ags decreased markedly till the sixth week in the liver but increased significantly at the sixth week in the kidney. Eight-week-old mice born to infected and noninfected mothers were infected with 200 S. mansoni ceracriae. Their sera and livers were collected for testing IgG and granuloma formation 6 weeks postinfection. Worms were collected via portal perfusion and counted. Anti-S. mansoni IgG level, size and number of liver granuloma, and worm burden were significantly reduced in the offspring of infected mothers. These data suggest that in utero exposure of Outbred albino mice to S. mansoni may attenuate the pathogenesis of S. mansoni in subsequent challenge.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aase JM, Noren GR, Reddy DV, Gemer JW Jr (1972) Mumps-virus infection in pregnant women and the immunologic response of their offspring. N Engl J Med 286:1379–1382
Abrahamson D, Rodewald R (1981) Evidence for sorting of endocytic vesicles during the receptor mediated transport of IgG across the newborn rat intestine. J Cell Biol 91:270–275
Amano T, Freeman GL Jr, Colley DG (1990) Reduced reproductive efficiency in mice with schistosomiasis mansoni and in uninfected pregnant mice injected with antibodies against Schistosoma mansoni soluble egg antigens. Am J Trop Med Hyg 43:180–185
Barrios C, Brawand P, Berney M, Brandt C, Lambert PH, Siegrist CA (1996) Neonatal and early life immune responses to various forms of vaccine antigens qualitatively differ from adult responses: predominance of a Th2-biased pattern which persists after adult boosting. Eur J Immunol 26:1489–1496
Billingham R, Brent L, Medawar PB (1953) Actively acquired tolerance of foreign cells. Nature (Lond) 172:603–605
Bina JC, Prata A (1984) A evolucoa natural da esquistossomose mansonica em uma area endemica, aspectos peculiares da infeccao par Schistosoma mansoni. Centro editorial e Didatico da UFBA, Salvador, pp 13–33
Bittencourt AL, Mott K (1969) Placental schistosomiasis. Gaz Med Bahia 69:113–118
Boros DL, Warren KS (1971) Specific granulomatous hyper-sensitivity elicited by bentonite particles coated with soluble antigens from Schistosoma eggs and tubercle bacilli. Nature (Lond) 229:200–201
Boros DV, Warren KS (1970) Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med 132:488–507
Borthistle BK, Kubo RT, Brom WR, Grey HM (1977) Studies on receptors for IgG on epithelial cells of rat intestine. J Immunol 19:471–475
Brambell FWR (1970) Transmission of passive immunity from mother to young. Front Biol 18:102–141
Bruce JI, Radke MG, Davis GM (1971) Culturing Biomphalaria and Oncomelania (Gastropoda) for large scale study of schistosomiasis: I. Cultivation of Biomphalaria glabrata and maintenance of S. mansoni in the laboratory. Biomedical Report No. 19, 406th Medical Laboratory, US Army, Tokyo
Camus D, Carliere Y, Bina JC, Borojevic R, Prata A, Capron A (1976) Sensitization to Schistosoma mansoni antigen in uninfected children born to infected mothers. J Infect Dis 134:405–408
Carlier Y, Bina JC, Camus D, Figuiredo MFJ, Capron A (1975) Immunological studies in human schistosomiasis: I. Parasitic antigen in urine. Am J Trop Med Hyg 24:949–953
Carlier Y, Nzeyimana H, Bout D, Capron A (1980) Evaluation of circulating antigens by a sandwich radioimmunoassay, and of antibodies and immune complexes, in Schistosoma mansoni-infected African parturients and their newborn children. Am J Trop Med Hyg 29:74–81
Cramer DV, Kunz HW, Gill TJ (1974) Immunologic sensitization prior to birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 120:431–439
Dunn MA, Kamel RK (1981) Hepatic schistosomiasis. Hepatology 1:653–661
Eissa AM, Saad MA, Abd-Elghaffar AK, El-Sharkaway IM, Kamal KA (1989) Transmission of lymphocyte responsiveness to schistosomal antigens by breast feeding. Trop Geogr Med 41:208–212
Eloi-Santos SM, Novata-Silva E, Maselli VM, Gazzinelli G, Colley DG, Correa-Oliveira R (1989) Idiotypic sensitization in utero of children born to mothers with schistosomiasis or Chagas’ disease. J Clin Invest 84:1028–1031
Engvall E, Perlmann P (1971) Enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry 8:871–874
Gill TJ, Kunz HW, Bernard CF (1971) Maternal–fetal interaction and immunological memory. Science 172:1346–1348
Hang LM, Boros DL, Warren KS (1974) Induction of immunological hyporesponsiveness to granulomatous hypersensitivity in Schistosoma mansoni infection. J Inf Dis 130:515–522
Hesse M, Piccirillo CA, Belkaid Y, Prufer J, Mentink-Kane M, Leusink M, Cheever AW, Shevach EM, Wynn TA (2004) The pathogenesis of schistosomiasis is controlled by cooperating IL-10-producing innate effector and regulatory T cells. J Immunol 172:3157–3166
Jones EA, Waldman TA (1972) The mechanism of intestinal uptake and transcellular transport of IgG in the neonatal rat. J Clin Invest 51:2916–2977
King CL, Nutman TB (1991) Regulation of the immune response in lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis. Immunol Today 12:A54–A58
King CL, Medhat A, Malhotra I, Nafeh M, Helmy A, Khaudary J, Ibrahim S, El-Sherbiny M, Zaky S, Stupi RJ, Brustoski K, Shehata M, Shata MT (1996) Cytokine control of parasite parasite-specific anergy in human urinary schistosomiasis: IL-10 modulates lymphocyte reactivity. J Immunol 156:4715–4721
Klei TR, Blanchard DP, Coleman SU (1986) Development of Brugia pahangi infections and lymphatic lesions in male offspring of female jirds with homologous infections. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:214–216
Laing YS, Bruce JI, Boyd DA (1987) Laboratory cultivation of schistosome vector snails and maintenance of schistosome life cycle. Proceedings of the first Sin, Amer Symposium, pp 1134–1138
Lambert AC (1911) Fevers with urticaria and esosinophila and their relation to infection with Schistosoma japonicum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 5:38–45
Lenzi JA, Sobral ACL, Araripe JR, Grimald FOG, Lenzi HL (1987) Congenital and nursing effects on the evolution of Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 82:257–267
Lewert RM (1970) Schistosomiasis, vol 2. Appleton Century Crofts, New York, pp 981–1008
Lewert RM, Mandlowitz S (1969) Schistosomiasis: prenatal induction of tolerance to antigens. Nature (Lond) 224:1029–1030
Malhotra I, Ouma J, Wamachi A, Kioko J, Mungai P, Omollo A, Elson L, Koech D, Kazura JW, King CL (1997) In utero exposure to helminth and mycobacterial antigens generates cytokine responses similar to that observed in adults. J Clin Invest 99:1759–1766
Morris B, Morris R (1976) Quantitative assessment of transmission of labeled protein by proximal and distal regions of the small intestine of young rats. J Physiol 255:619–634
Nash TE, Prescott B, Neva FA (1974) The characteristics of a circulating antigen in schistosomiasis. J Immunol 4:1500–1507
Newport GR, Colley DG (1993) Schistosomiasis. In: Warren KS (ed) Immunology and molecular biology of parasitic infections. Blackwell, Oxford
Peppard JV, Jackson LE, Hall JG, Robertson D (1984) The transfer of immune complexes from the lumen of the small intestine to the blood stream in suckling rat. Immunology 53:385–393
Phillips SM, Fox EF (1982) The immunopathology of parasitic disease. Clin Immunol Allergy 24:183–186
Raghavan NGS (1958) Congenital filariasis. Bull Nat Soc Indian Mal Mosz Dis 6:147–154
Ridge JP, Fuchs EJ, Matzinger P (1996) Neonatal tolerance revisited: turning on newborn T cells with dendritic cells. Science 271:1723–1726
Roitt IM (1988) Essential immunology, 6th edn. Blackwell, Oxford, p 116
Santoro F, Borojevic R, Bout D, Tachon P, Bina JC, Capron A (1977) Mother–child relationship in human schistosomiasis mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg 26:1164–1168
Smithers SR, Terry RJ (1965) The infection of laboratory hosts with cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni and the recovery of adult worms. Parasitology 55:695–700
Stastsy P (1965) Accelerated graft rejection in the offspring of immunized mothers. J Immunol 95:929–936
Steel C, Guinea A, McCarthy JS, Ottesen EA (1994) Long-term effect of prenatal exposure to maternal microfilaremia on immune responsiveness to filarial parasite antigens. Lancet 343:890–893
Sutherland JC, Berry A, Hynd M, Proctor NSF (1965) Placental bilhariziasis. Report of a case. S Afr J Obstet Gynecol 3:76–80
Tachon P, Borojevic R (1978) Mother–child relation in human schistosomiasis mansoni: skin test and cord blood reactivity to schistosomal antigens. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 72:605–609
Uhr JW, Slavin SB, Pappenheimer AM (1957) Delayed hypersensitivity induction of hypersensitivity in guinea pigs by means of antigen. Antibody complexes. J Exp Med 105:11–24
Warren KS (1982) The effect of immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis: in vivo models. Immunol Rev 61:189–192
Weil GJ, Hussain R, Kumaraswami V, Tripathy SP, Phillips KS, Ottesen EA (1983) Prenatal allergic sensitization to helminth antigens in offspring of parasite-infected mothers. J Clin Invest 71:1124–1129
Weir DM, Stewart J (1993) Immunology. Churchill Livingston, Edinburgh, pp 68–69
World Health Organization (1986) Scientific activities: the chemotherapy of schistosomiasis control. Bull WHO 64:23–24
World Health Organization (1991) Tropical diseases. Progress in research 1989–1990. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 41–51
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Benjamin M. Rosenthal from the Animal Parasitic Diseases Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture for the critical review of the manuscript. This work was conducted in compliance with Egyptian laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attallah, A.M., Abbas, A.T., Dessouky, M.I. et al. Susceptibility of neonate mice born to Schistosoma mansoni-infected and noninfected mothers to subsequent S. mansoni infection. Parasitol Res 99, 137–145 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0127-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0127-x