Abstract
Background
To identify novel miRNAs implicated in prostate cancer metastasis.
Methods
Sixty-five prostate cancer tissues and paired pan-cancer tissues were sequenced. Novel miRNAs were re-analyzed by MIREAP program. Biological functions of miR-N5 were transwell experiment and colony formation. Target genes of miR-N5 were analyzed by bioinformatic analysis. Downstream of target gene was analyzed by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) databases and confirmed by CHIP experiment.
Results
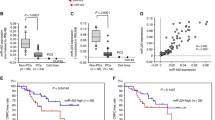
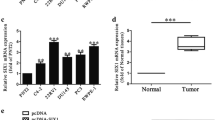
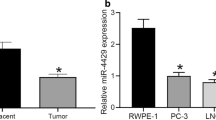
We identified a novel miRNA-miR-N5, which was downregulated in PCa cells, PCa tissue, and in the serum of patients with PCa. Knockout of miR-N5 enhanced migration and invasiveness in vitro. miR-N5 specified targeted CREBBP 3′-UTR and inhibited CREBBP expression, which mediated H3K56 acetylation at the promoter of EGFR, β-catenin and CDH1.
Conclusion
This study may shed the light on miR-N5 which influences metastasis via histone acetylation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data in this study were available for public.
Abbreviations
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- CREBBP:
-
CREB-binding protein
- H3K56ac:
-
Histone 3 lysine56 acetylation
- PCa:
-
Prostate cancer
- CRPC:
-
Castration-resistant prostate cancer cells
- 3′-UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated Regions
- MSKCC:
-
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- CHIP:
-
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
Bang YJ et al (1994) Terminal neuroendocrine differentiation of human prostate carcinoma cells in response to increased intracellular cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5330–5334. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.12.5330
Bhagirath D et al (2018) microRNA-1246 is an exosomal biomarker for aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res 78:1833–1844. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2069
Cerami E et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Chen W et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66:115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Das C et al (2014) Binding of the histone chaperone ASF1 to the CBP bromodomain promotes histone acetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E1072-1081. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319122111
Das R et al (2017) MicroRNA-194 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by inhibiting SOCS2. Cancer Res 77:1021–1034. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2529
Deng X, Liu H, Huang J, Cheng L, Keller ET, Parsons SJ, Hu CD (2008) Ionizing radiation induces prostate cancer neuroendocrine differentiation through interplay of CREB and ATF2: implications for disease progression. Cancer Res 68:9663–9670. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2229
Doldi V, Pennati M, Forte B, Gandellini P, Zaffaroni N (2016) Dissecting the role of microRNAs in prostate cancer metastasis: implications for the design of novel therapeutic approaches. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:2531–2542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2176-3
Gao J et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 6:pl1. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Gururajan M et al (2014) miR-154* and miR-379 in the DLK1-DIO3 microRNA mega-cluster regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition and bone metastasis of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20:6559–6569. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1784
Han J, Zhou H, Horazdovsky B, Zhang K, Xu RM, Zhang Z (2007) Rtt109 acetylates histone H3 lysine 56 and functions in DNA replication. Science 315:653–655. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133234
Hendrix D, Levine M, Shi W (2010) miRTRAP, a computational method for the systematic identification of miRNAs from high throughput sequencing data. Genome Biol 11:R39. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-4-r39
Hong BS et al (2019) Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p regulates growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodeling in breast cancer. Cancer Res 79:1520–1534. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0891
Hu Y et al (2018) A novel microRNA identified in hepatocellular carcinomas is responsive to LEF1 and facilitates proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting of NFIX. Oncogenesis 7:22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-017-0010-x
Ishteiwy RA, Ward TM, Dykxhoorn DM, Burnstein KL (2012) The microRNA -23b/-27b cluster suppresses the metastatic phenotype of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 7:e52106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052106
Josson S et al (2014) miR-409–3p/-5p promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20:4636–4646. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0305
Ma H, Nguyen C, Lee KS, Kahn M (2005) Differential roles for the coactivators CBP and p300 on TCF/beta-catenin-mediated survivin gene expression. Oncogene 24:3619–3631. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208433
Masumoto H, Hawke D, Kobayashi R, Verreault A (2005) A role for cell-cycle-regulated histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation in the DNA damage response. Nature 436:294–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03714
Mishra R, Haldar S, Suchanti S, Bhowmick NA (2019) Epigenetic changes in fibroblasts drive cancer metabolism and differentiation. Endocr Relat Cancer 26:R673–R688. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-19-0347
Puppo M, Taipaleenmaki H, Hesse E, Clezardin P (2019) Non-coding RNAs in bone remodelling and bone metastasis: Mechanisms of action and translational relevance. Br J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14836
Quiroz-Munoz M, Izadmehr S, Arumugam D, Wong B, Kirschenbaum A, Levine AC (2019) Mechanisms of osteoblastic bone metastasis in prostate cancer: role of prostatic acid phosphatase. J Endocr Soc 3:655–664. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2018-00425
Rice MA et al (2016) The microRNA-23b/-27b cluster suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related. Oncogene 35:4752–4761. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.6
Sakamoto KM, Frank DA (2009) CREB in the pathophysiology of cancer: implications for targeting transcription factors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:2583–2587. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1137
Sheffield NC et al (2017) DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma. Nat Med 23:386–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4273
Strub T et al (2018) SIRT6 haploinsufficiency induces BRAF(V600E) melanoma cell resistance to MAPK inhibitors via IGF signalling. Nat Commun 9:3440. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05966-z
Taylor BS et al (2010) Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 18:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026
Tuck MK et al (2009) Standard operating procedures for serum and plasma collection: early detection research network consensus statement standard operating procedure integration working group. J Proteome Res 8:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr800545q
Wang L et al (2015) MiR-573 inhibits prostate cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 6:35978–35990. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5427
Wang N et al (2016) miR-135b inhibits tumour metastasis in prostate cancer by targeting STAT6. Oncol Lett 11:543–550. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3970
Wu D et al (2007) cAMP-responsive element-binding protein regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression: implication in human prostate cancer bone metastasis. Oncogene 26:5070–5077. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210316
Xu F, Zhang K, Grunstein M (2005) Acetylation in histone H3 globular domain regulates gene expression in yeast. Cell 121:375–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.011
Zuniga KB et al (2019) Trends in complementary and alternative medicine use among patients with prostate cancer. J Urol 202:689–695. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000336
Funding
This study was funded by the grant of National Natural Science Foundation Youth Project (81702514, C.R.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.B.W. and Z.W. performed the experiments. C.R. and F.B.W. performed assistance for experiment design; Y.Y. performed the data analysis and drafted the manuscript; Z.J.S., M.Y.W., and H.X.W. provided clinical samples. All authors discussed and approved the manuscript; C.R. was responsible for research supervision and coordination.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All samples were collected from patients with prostate cancer. Leftover samples were sequenced. This study did not change the clinical treatment. All samples were anonymous. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Second Medical Military University.
Consent to participate
All patients in the study were from Changhai Hospital, Shanghai, China and informed consent following the principles of Changhai Hospital.
Consent for publication
All authors were agreed with publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhang, W., Song, Z. et al. A novel miRNA inhibits metastasis of prostate cancer via decreasing CREBBP-mediated histone acetylation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 469–480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03455-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03455-9