Abstract
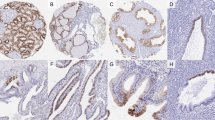
We aimed to detect truncated CCN3 protein variants in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of eight Wilms’ tumors using anti-K19M and novel domain-specific antibodies, anti-NH2, anti-NH3, anti-NH4, and anti-NH5 raised against C-terminal (CT) domain and modules 1, 2, 3, and 4 of the CCN3 protein, respectively. In Wilms’ tumors, all the domain antibodies except anti-NH4 exhibited both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in blastema as well as primitive tubules. NH4 was detected only in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. Normal fetal kidneys revealed mainly cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for all antibodies in tubules and glomeruli, except for K19 and NH5, which showed some nuclear staining. Our data suggest expression of a truncated nuclear CCN3 variant lacking the thrombospondin type-1-like domain and cytoplasmic full-length CCN3 protein in Wilms’ tumor cells. In addition, normal fetal kidneys express mainly full-length protein mostly localized to cytoplasm. Truncated CCN3 protein in Wilms’ tumor cells may provide evidence for its tumorigenic role in these tumors. Uniform NH5 staining compared to variable expression of K19M indicates that using NH5 is a better approach for detecting the CT domain of CCN3 protein in archival specimens. Thus, the domain-specific antibodies represent valuable tools for detecting CCN3 protein variants in normal and neoplastic kidneys.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NOV:
-
Nephroblastoma overexpressed gene
- MAV-1:
-
Myeloblastosis-associated virus type 1
- SIOP:
-
International Society of Pediatric Oncology
- CTGF:
-
Connective tissue growth factor
- IGFBP:
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein
- VWC:
-
Von Willebrand complex
- CT:
-
C-terminal domain
- TSP1:
-
Thrombospondin type 1 repeat
- WT1:
-
Wilms’ tumor gene 1
References
Benini S, Perbal B, Zambelli D, Colombo MP, Manara MC, Serra M, Parenza M, Martinez V, Picci P, Scotlandi K (2005) In Ewing’s sarcoma CCN3(NOV) inhibits proliferation while promoting migration and invasion of the same cell type. Oncogene 24:4349–4361
Bork P (1993) The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett 327:125–130
Breslow N, Beckwith JB, Ciol M, Sharples K (1988) Age distribution of Wilms’ tumor: report from the National Wilms’ Tumor Study. Cancer Res 48:1653–1657
Brigstock DR, Goldschmeding R, Katsube KI, Lam SC, Lau LF, Lyons K, Naus C, Perbal B, Riser B, Takigawa M, Yeger H (2003) Proposal for a unified CCN nomenclature. Mol Pathol 56:127–128
Cervello M, Giannitrapani L, Labbozzetta M, Notarbartolo M, D’Alessandro N, Lampiasi N, Azzolina A, Montalto G (2004) Expression of WISPs and of their novel alternative variants in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1028:432–439
Chevalier G, Yeger H, Martinerie C, Laurent M, Alami J, Schofield PN, Perbal B (1998) novH: differential expression in develo** kidney and Wilms’ tumors. Am J Pathol 152:1563–1575
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA (2002) Pathology and genetics of tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs. In: Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumors. IARC Press, Lyon
Ellis PD, Metcalfe JC, Hyvonen M, Kemp PR (2003) Adhesion of endothelial cells to NOV is mediated by the integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha5beta1. J Vasc Res 40:234–243
Gellhaus A, Dong X, Propson S, Maass K, Klein-Hitpass L, Kibschull M, Traub O, Willecke K, Perbal B, Lye SJ, Winterhager E (2004) Connexin43 interacts with NOV: a possible mechanism for negative regulation of cell growth in choriocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 279:36931–36942
Gupta N, Wang H, McLeod TL, Naus CC, Kyurkchiev S, Advani S, Yu J, Perbal B, Weichselbaum RR (2001) Inhibition of glioma cell growth and tumorigenic potential by CCN3 (NOV). Mol Pathol 54:293–299
Jiang WG, Watkins G, Fodstad O, Douglas-Jones A, Mokbel K, Mansel RE (2004) Differential expression of the CCN family members Cyr61, CTGF and Nov in human breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 11:781–791
Joliot V, Martinerie C, Dambrine G, Plassiart G, Brisac M, Crochet J, Perbal B (1992) Proviral rearrangements and overexpression of a new cellular gene (nov) in myeloblastosis-associated virus type 1-induced nephroblastomas. Mol Cell Biol 12:10–21
Kyurkchiev S, Yeger H, Bleau AM, Perbal B (2004) Potential cellular conformations of the CCN3 (NOV) protein. Cell Commun Signal 2:9–17
Leu SJ, Liu Y, Chen N, Chen CC, Lam SC, Lau LF (2003) Identification of a novel integrin alpha 6 beta 1 binding site in the angiogenic inducer CCN1 (CYR61). J Biol Chem 278:33801–33808
Lin CG, Leu SJ, Chen N, Tebeau CM, Lin SX, Yeung CY, Lau LF (2003) CCN3 (NOV) is a novel angiogenic regulator of the CCN protein family. J Biol Chem 278:24200–24208
Lin CG, Chen CC, Leu SJ, Grzeszkiewicz TM, Lau LF (2005) Integrin-dependent functions of the angiogenic inducer NOV (CCN3): implication in wound healing. J Biol Chem 280:8229–8237
Manara MC, Perbal B, Benini S, Strammiello R, Cerisano V, Perdichizzi S, Serra M, Astolfi A, Bertoni F, Alami J, Yeger H, Picci P, Scotlandi K (2002) The expression of ccn3 (nov) gene in musculoskeletal tumors. Am J Pathol 160:849–859
McCallum L, Price S, Planque N, Perbal B, Pierce A, Whetton AD, Irvine AE (2006) A novel mechanism for BCR-ABL action: stimulated secretion of CCN3 is involved in growth and differentiation regulation. Blood 108:1716–1723
Olsnes S, Klingenberg O, Wiedlocha A (2003) Transport of exogenous growth factors and cytokines to the cytosol and to the nucleus. Physiol Rev 83:163–182
Perbal B (1999) Nuclear localisation of NOVH protein: a potential role for NOV in the regulation of gene expression. Mol Pathol 52:84–91
Perbal B (2001) NOV (nephroblastoma overexpressed) and the CCN family of genes: structural and functional issues. Mol Pathol 54:57–79
Perbal B (2004) CCN proteins: multifunctional signalling regulators. Lancet 363:62–64
Perbal B (2006) The CCN3 protein and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 587:23–40
Planque N, Bleau AM, Perbal B (2005) The CCN3 protein: a multifunctional cell growth regulator. In: Perbal B, Takigawa M (eds) The CCN proteins: a new family of cell growth and differentiation regulators. Imperial College Press, London, pp 239–257
Planque N, Perbal B (2003) A structural approach to the role of CCN (CYR61/CTGF/NOV) proteins in tumourigenesis. Cancer Cell Int 3:1–15
Planque N, Perbal B (2003) The CCN Proteins, a new family of cell growth regulators. In: Pandalai SG (ed) Recent research developments in human pathology, vol 1. 2003 Part II. Transworld Research Network, Trivandrum, pp 333–369
Planque N, Long Li C, Saule S, Bleau AM, Perbal B (2006) Nuclear addressing provides a clue for the transforming activity of amino-truncated CCN3 proteins. J Cell Biochem 99:105–116
Wahab NA, Brinkman H, Mason RM (2001) Role of connective tissue growth factor in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Biochem J 359:77–87
**e D, Yin D, Wang HJ, Liu GT, Elashoff R, Black K, Koeffler HP (2004) Levels of expression of CYR61 and CTGF are prognostic for tumor progression and survival of individuals with gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 10:2072–2081
Yeger H, Chevalier G, Alami J, Perbal B (1998) Expression of novH in rhabdomyosarcoma. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 39 (Abstract 265)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a grant (PI-04/0822) from the FIS (Instituto Carlos-III, Madrid, Spain) and PROTHETS (Prognosis and therapeutic targets of Ewing’s family of tumors) FP6 contract number 503036. Manish Mani Subramaniam is a holder of a grant from the Hospital Clinic of University and the Spanish Association Against Cancer (AECC) of Valencia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manish Mani Subramaniam and Noureddine Lazar made an equal contribution to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramaniam, M.M., Lazar, N., Navarro, S. et al. Expression of CCN3 protein in human Wilms’ tumors: immunohistochemical detection of CCN3 variants using domain-specific antibodies. Virchows Arch 452, 33–39 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0523-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0523-3