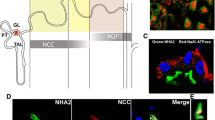
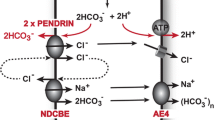
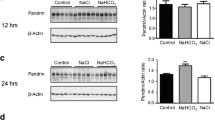
Abstract.
The aim of the present study was to determine the molecular responses of the main salt-reabsorbing systems in the distal nephron to changes of salt load of the organism. For this purpose we analysed messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) levels for the bumetanide-sensitive Na+K+2Cl– cotransporter (BSC1), the thiazide-sensitive Na+Cl– cotransporter (TSC), the kidney-specific inwards rectifier K+ channel (ROMK), the amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) and the kidney-specific Cl– channel ClC-K2, in the cortex and inner and outer medulla of kidneys from male Sprague-Dawley rats fed a high- (8% w/w), normal- (0.6%) or low- (0.02%) salt diet or treated chronically with subcutaneous infusions of furosemide (12 mg/kg per day). BSC1 and ROMK mRNA levels did not differ between the four treatment groups. TSC mRNA increased during furosemide treatment 1.75-fold versus control but was not affected by a high- or a low-salt diet. The mRNA for the α-subunit of ENaC increased with the low-salt diet (about 1.5-fold) and with furosemide (about 2.1-fold) in all kidney zones, but did not change with the high-salt diet. Dietary salt loading down-regulated ClC-K2 mRNA in the outer medulla 0.6-fold versus control whilst furosemide treatment, but not the low-salt diet, increased ClC-K2 mRNA in the outer (1.6-fold) and inner medulla (2.0-fold). These findings suggest that gene expression of Na+ and Cl– entry pathways in the distal nephron are at least partly regulated by the salt load of the organism, such that salt-reabsorbing systems are stimulated by salt deficiency and suppressed by salt overload.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 25 January 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, K., Castrop, H., Riegger, G.A. et al. Differential gene regulation of renal salt entry pathways by salt load in the distal nephron of the rat. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 498–504 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100544
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100544