Abstract
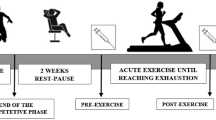
It is well known that exposure to extreme environments, such as in high-mountain expeditions, is associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species and related oxidative damage. However, there is little information concerning antioxidant recovery after this type of expedition. Thus, the aim of this study is to analyze the antioxidant recovery status at sea level of five expert alpinists 4 weeks after climbing Cho-Oyu (8,201 m). Body composition, cardiorespiratory capacity, and circulating parameters were almost similar to the values obtained at the beginning of the study. However, the alpinists presented high erythrocyte number, related hemogram values, and ferritin. Sodium, alkaline phosphatase, and γ-glutamyltransferase plasma levels were lower. Concerning oxidative stress, plasma uric acid levels were significantly increased, as well as malondialdehyde and protein carbonyls. Neutrophils displayed significantly higher levels of malondialdehyde and lower catalase activity. Therefore, these data indicate that the oxidative stress during a high mountain expedition is the most probable cause to explain an incomplete recovery in plasma and neutrophil antioxidant status.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Baillie JK, Bates MGD, Thompson AAR, Waring WS, Partridge RW, Simpson A, Maxwell SRJ (2007) Endogenous urate production augments plasma antioxidant capacity in healthy lowland subjects exposed to high altitude. Chest 131:1473–1478
Bärtsch P, Saltin B (2008) General introduction to altitude adaptation and mountain sickness. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18(Suppl 1):1–10
Bowers LD, Wong ET (1980) Kinetic serum creatinine assays. II. A critical evaluation and review. Clin Chem 26:555–561
Boyum A (1964) Separation of white blood cells. Nature 204:793–794
Bucolo G, David H (1973) Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem 19:476–482
Dosek A, Ohno H, Acs Z, Taylor AW, Radak Z (2007) High altitude and oxidative stress. Resp Physiol Neurobiol 158:128–131
Drust B, Waterhouse J (2010) Exercise and altitude. Scott Med J 55:31–34
Edwards NL (2009) The role of hyperuricemia in vascular disorders. Curr Opin Rheumatol 21:132–137
Faulkner JA (1968) Physiology of swimming and diving. In: Falls H (ed) Exercise physiology. Academic Press, Baltimore, pp 415–445
Flohé L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Fossati P, Prencipe L, Berti G (1980) Use of 3, 5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid/4-aminophenazone chromogenic system in direct enzymic assay of uric acid in serum and urine. Clin Chem 26:227–231
Goldberg DM, Spooner RJ (1983) Glutathione reductase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Basel, pp 258–265
Heinicke I, Boehler A, Rechsteiner T, Bogdanova A, Jelkmann W, Hofer M, Rawlings P, Araneda OF, Behn C, Gassmann M, Heinicke K (2009) Moderate altitude but not additional endurance training increases markers of oxidative stress in exhaled breath condensate. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:599–604
Hovind P, Rossing P, Johnson RJ, Parving HH (2011) Serum uric acid as a new player in the development of diabetic nephropathy. J Ren Nutr 21:124–127
Ilavazhagan G, Bansal A, Prasad D, Thomas P, Sharma SK, Kain AK, Kumar D, Selvamurthy W (2001) Effect of vitamin E supplementation on hypoxia-induced oxidative damage in male albino rats. Aviat Space Environ Med 72:899–903
Imai H, Kashiwazaki H, Suzuki T, Kabuto M, Himeno S, Watanabe C, Moji K, Kim SW, Rivera JO, Takemoto T (1995) Selenium levels and glutathione peroxidase activities in blood in an Andean high-altitude population. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 41:349–361
Itano M (1978) CAP comprehensive chemistry. Serum iron survey. Am J Clin Pathol 70:516–522
Joanny P, Steinberg J, Robach P, Richalet JP, Gortan C, Gardette B, Jammes Y (2001) Operation Everest III (Comex’97): the effect of simulated sever hypobaric hypoxia on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in human blood at rest and after maximal exercise. Resuscitation 49:307–314
Khan S, O’Brien PJ (1995) Modulating hypoxia-induced hepatocyte injury by affecting intracellular redox state. Biochim Biophys Acta 1269:153–161
Laporta O, Funes L, Garzon MT, Villalain J, Micol V (2007) Role of membranes on the antibacterial and anti-Inflammatory activities of the bioactive compounds from Hypoxis rooperi corm extract. Arch Biochem Biophys 467:119–131
Levine RL, Williams JA, Stadtman ER, Shacter E (1994) Carbonyl assays for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 233:346–357
Marfell-Jones M, Olds T, Steward A, Carter L (2006) International standards for anthropometric assessment. ISAK, Potchefstroom
Martarelli D, Cocchioni M, Scuri S, Spataro A, Pompei P (2011) Cold exposure increases exercise-induced oxidative stress. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 51:299–304
Martin AD, Daniel M, Clarys JP, Marfell-Jones MJ (2003) Cadaver-assessed validity of anthropometric indicators of adipose tissue distribution. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:1052–1058
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Mohanraj P, Merola AJ, Wright VP, Clanton TL (1998) Antioxidants protect rat diaphragmatic muscle function under hypoxic conditions. J Appl Physiol 84:1960–1966
Naito HK, David JA (1984) Laboratory considerations: determination of cholesterol, triglyceride, phospholipid, and other lipids in blood and tissues. Lab Res Methods Biol Med 10:1–76
Nakanishi K, Tajima F, Nakamura A, Yagura S, Ookawara T, Yamashita H, Suzuki K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H (1995) Antioxidant system in hypobaric-hypoxia. J Physiol 489:869–876
Nikolaidis MG, Jamurtas AZ (2009) Blood as a reactive species generator and redox status regulator during exercise. Arch Biochem Biophys 490:77–84
Olsen NV (1995) Effect of hypoxaemia on water and sodium homeostatic hormones and renal function. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl 107:165–170
Pialoux V, Mounier R, Brown AD, Steinback CD, Rawling JM, Poulin MJ (2009) Relationship between oxidative stress and HIF-1 alpha mRNA during sustained hypoxia in humans. Free Radic Biol Med 46:321–326
Pialoux V, Brugniaux JV, Rock E, Mazur A, Schmitt L, Richalet JP, Robach P, Clottes E, Coudert J, Fellmann N, Mounier R (2010) Antioxidant status of elite athletes remains impaired 2 weeks after a simulated altitude training camp. Eur J Nutr 49:285–292
Prentice AM, Jebb SA (2001) Beyond body mass index. Ob Rev 2:141–147
Radak Z, Lee K, Choi W, Sunoo S, Kizaki T, Oh-Ishi S, Suzuki K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H, Asano K (1994) Oxidative stress induced by intermittent exposure at a simulated altitude of 4000 m decreases mitochondrial superoxide dismutase content in soleus muscle of rats. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 69:392–395
Smith EU, Diaz-Tomé C, Pérez-Ruiz F, March LM (2010) Epidemiology of gout: an update. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 24:811–827
Tabacco A, Meiattini F, Moda E, Tarli P (1979) Simplified enzymic/colorimetric serum urea nitrogen determination. Clin Chem 25:336–337
Tauler P, Aguilo A, Gimeno I, Fuentespina E, Tur JA, Pons A (2003) Influence of vitamin C diet supplementation on endogenous antioxidant defences during exhaustive exercise. Pflugers Arch 446:658–664
Trinder P (1969) Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J Clin Pathol 22:158–161
Vij AG, Dutta R, Satija NK (2005) Acclimatization to oxidative stress at high altitude. High Alt Med Biol 6:301–310
Weisshaar D, Gossrau E, Faderl B (1975) Normal ranges of alpha-HBDH, LDH, AP, and LAP as measured with substrate-optimated test charges. Med Welt 26:387–392
Wozniak A, Drewa G, Chesy G, Rakowski A, Rozwodowska M, Olszewska D (2001) Effect of altitude training on the peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in sportmen. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1109–1113
Young DS, Friedman RB (2001) Effects of disease on clinical laboratory tests. AACC Press, Washington DC
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the valuable participation of the six climbers Juan Agullo, Jose Alejo, Jaime Anton, Francisco Marcos, Jose Tari, and Jose Trasobares. The authors also thank Jose Maria Adsuar for his technical assistance in blood analysis, Dolores Perez for her assistance in exercise test and Angel Sanchez for statistical analysis. This work was supported by grants from Spanish Science and Innovation Ministry/FEDER DPS08-07033-C03-03 to AP, AGL2007-60778 to VM and Fundacion Medica Mutua Madrileña, Instituto de Salud Carlos III-FEDER (PS09/01093) and Fundacion Salud 2000-Merck Serono to ER. LC-Q and LF have been recipients of CONACYT-Mexico (ref 197139) and FPI (Spanish Science Ministry) fellowships respectively.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflicting financial interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan A. Ward.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrera-Quintanar, L., Lopez-Fuertes, M., Climent, V. et al. Oxidative damage is present in plasma and circulating neutrophils 4 weeks after a high mountain expedition. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 2923–2932 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2272-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2272-x