Abstract.
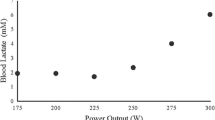
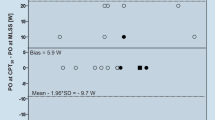
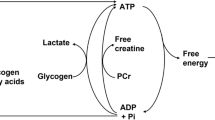
We hypothesised that: (1) the maximal lactate steady state (MLSS), critical power (CP) and electromyographic fatigue threshold (EMGFT) occur at the same power output in cycling exercise, and (2) exercise above the power output at MLSS (P-MLSS) results in continued increases in oxygen uptake (V˙O2), blood lactate concentration ([La]) and integrated electromyogram (iEMG) with time. Eight healthy subjects [mean (SD) age 25 (3) years, body mass 72.1 (8.2) kg] performed a series of laboratory tests for the determination of MLSS, CP and EMGFT. The CP was determined from four exhaustive trials of between 2 and 15 min duration. The MLSS was determined as the highest power output at which the increase in blood [La] was less than 1.0 mM across the last 20 min of a series of 30-min trials. The EMGFT was determined from four trials of 2 min duration at different power outputs. The surface electromyogram was recorded continuously from the vastus lateralis muscle. The CP was significantly higher than the P-MLSS [242 (25) vs. 222 (23) W; P<0.05], although the two variables were strongly correlated (r=0.95; P<0.01). The EMGFT could not be determined in 50% of the subjects. Blood [La], V˙O2 and minute ventilation all increased significantly with time for exercise at power outputs above the P-MLSS. In conclusion, the P-MLSS, and not the CP, represents the upper limit of the heavy exercise domain in cycling. During exercise above the P-MLSS, there is no association between changes in iEMG and increases in V˙O2 and blood [La] with time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pringle, J.S., Jones, A.M. Maximal lactate steady state, critical power and EMG during cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 88, 214–226 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0703-4
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0703-4