Abstract
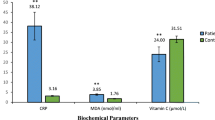
The exact etiology and pathogenesis of eczema are not yet fully understood, although different factors are considered as pathogenic mechanisms in the development of eczema. Our study was designed to determine extent of serum lipid peroxidation, antioxidants, macro minerals and trace elements in patients with eczema, and thereby, find any pathophysiological correlation. The study was conducted as a case–control study with 65 eczema patients as cases and 65 normal healthy individuals as controls. Lipid peroxidation was assessed by measuring the serum level of malondialdehyde (MDA). Antioxidants- vitamin A and E concentration was determined by RP-HPLC method whereas vitamin C was evaluated for serum ascorbic acid by UV spectrophotometric method. Serum macro minerals (Na, K, Ca) and trace elements (Zn, Fe) were determined by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS). This study found significantly higher level of MDA (p < 0.001) and lower level of antioxidants (p < 0.05) in patients in comparison to the control subjects. Analysis of serum macro minerals (Na, K and Ca) and trace elements (Zn, Fe) found that the mean values of Na, K, Ca, Zn and Fe were 2771.60 ± 75.64, 66.33 ± 3.03, 48.41 ± 2.50, 0.30 ± 0.02 and 0.29 ± 0.009 mg/L for the patient group and 3284.81 ± 34.51, 162.18 ± 3.72, 87.66 ± 2.10, 0.75 ± 0.06 and 0.87 ± 0.06 mg/L for the control group, accordingly. There was a significant difference for all the minerals between the patients and controls (p < 0.001). This study suggests a strong association between the pathogenesis of eczema with the elevated level of MDA and depleted level of antioxidants, macro minerals, and trace elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrogue HJ, Madias NE (2007) Sodium and potassium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. N Engl J Med 356(19):1966–1978
Afridi HI, Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Kazi GH, Shar GQ (2006) The status of trace and toxic elements in biological samples (scalp hair) of skin-disease patients and normal subjects. Turk J Med Sci 36(4):223–230
Arredondo M, Nunez MT (2005) Iron and copper metabolism. Mol Aspects Med 26(4–5):313–327
Ayala A, Munoz MF, Arguelles S (2014) Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:360438
Barragán-Meijueiro MM, Morfín-Maciel B, Nava-Ocampo AA (2006) A Mexican population based study on exposure to paracetamol and the risk of wheezing, rhinitis, and eczema in childhood. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 16(4):247–252
Bieri JG, Tolliver TG, Contingent GL (1979) Simultaneous determination of α-tocopherol and retinol in plasma or red cells by HPLC. Am J Clin Nutr 32(10):2143–2149
Catalá A (2009) Lipid peroxidation of membrane phospholipids generates hydroxy-alkenals and oxidized phospholipids active in physiological and/or pathological conditions. Chem Phys Lipids 157(1):1–11
Civelek E, Sahiner UM, Yuksel H, Boz AB, Orhan F, Uner A, Cakir B, Sekerel BE (2011) Prevalence, burden, and risk factors of atopic eczema in school children aged 10–11 years: a national multicenter study. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 21(4):270–277
Dewan SMR, Amin MN, Adnan T, Uddin SMN, Shahid-Ud-Daula AFM, Sarwar G, Hossain MS (2013) Investigation of analgesic potential and in vitro antioxidant activity of two plants of Asteraceae family growing in Bangladesh. J Pharm Res 6(6):599–603
Dursen P, Demirtas E, Bayrak A, HakenYarli (2006) De-creased serum paraoxonase 1 (PON1) activity: an addi-tional risk factor for atherosclerotic heart disease in patients with PCOS. Hum Reprod 21(1):104–108
Finch J, Munhutu MN, Whitaker-Worth DL (2010) Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol 28(6):605–614
Fukada T, Yamasaki S, Nishida K, Murakami M, Hirano I (2011) Zinc homeostasis and signaling in health and diseases: zinc signaling. J Biol Inorg Chem 16(7):1123–1134
Gu D, He J, Wu X, Duan X, Whelton PK (2001) Effect of potassium supplementationon BP in Chinese: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Hypertens 19(7):1325–1331
Gutteridge JM (1995) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin Chem 41(12):1819–1828
Halliwell B (1994) Free radicals and antioxidants: a personal view. Nutr Rev 52(8):253–265
Halliwell B, Murcia MA, Chirico S, Aruoma OI (1995) Free radicals and antioxidantsin food and in vivo: what they do and how they work. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 35(1–2):7–20
Harris JM, Cullinan P, Williams HC, Mills P, Moffat S, White C, Yaylor AJN (2001) Environmental associations with eczema in early life. Br J Dermatol 144(4):795–802
He FJ, MacGregor GA (2001) Fortnightly review: beneficial effects of potassium. Br Med J 323(7311):497–501
Islam SKN, Hossain KJ, Ahsan M (2001) Serum vitamin E, C and A status of the drug addicts undergoing detoxification: influence of drug habit, sexual practice and lifestyle factors. Eur J Clin Nutr 55(11):1022–1027
Kaur G, Mishra S, Sehgal A, Prasad R (2008) Alterations in lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in pregnancy with preeclampsia. Mol Cell Biochem 313(1–2):37–44
Kulkarni N, Kalele K, Kulkarni M, Kathariya R (2014) Trace elements in oral health and disease: an updated review. J Dent Res Rev 1(2):100–104
Kurt E, Metintas S, Basyigit I, Bulut I, CoskunE DabakS, Deveci F, Fidan F, Kaynar H, Kunt Uzaslan E, Onbasi K, Ozkurt S, Pasaoglu Karakis G, Sahan S, Sahin U, Oguzulgen K, Yildiz F, Mungan D, Yorgancioglu A, Gemicioglu B, Fuat Kalyoncu A (2009) Prevalence and risk factors of allergies in Turkey (PARFAIT): results of a multicentre crosssectional study in adults. Eur Respir J 33(4):724–733
Lee SM, Ahn JS, Noh CS, Lee SW (2011) Prevalence of allergic diseases and risk factors of wheezing in Korean military personnel. J Korean Med Sci 26(2):201–206
Maddrey WC (2005) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity: 2005. J Clin Gastroenterol 39(4 Suppl 2):S83–S89
Maret W, Sandstead HH (2006) Zinc requirements and the risks and benefits of zinc supplementation. J Trace Elem Med Biol 20(1):3–18
Mohamad NS (2013) Trace elements homeostatic imbalance in mild and severe psoriasis: a new insight in biomarker diagnostic value for psoriasis. Our Dermatol Online 4(4):449–452
Mohrenschlager M, Schafer T, Marp JH, Eberlein-Konig B, Weidinger S, Ring J, Behrendt H, Kramer U (2006) The course of eczema in children aged 5–7 years and its relation to atopy: differences between boys and girls. Br J Dermatol 154(3):505–513
Muralidhar LH (2004) Serum trace element levels and the complexity of inter element relations in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18(2):163–171
Nahar Z, Sarwar MS, Islam MS, Rahman A, Islam SN, Islam MS, Hasnat A (2013) Determination of serum antioxidant vitamins, glutathione and MDA levels in panic disorder patients. Drug Res 63(8):424–428
Peterlik M, Kállay E, Cross HS (2013) Calcium nutrition and extracellular calcium sensing: relevance for the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients 5(1):302–327
Polla BS, Ezekowitz RA, Leung DY (1992) Monocytes from patients with atopic dermatitis are primed for superoxide production. J Allergy Clin Immunol 89(2):545–551
Ronmark EP, Ekerljung L, Lotvall J, Wennergren G, Ronmark E, Toren K, Lundback B (2012) Eczema among adults: prevalence, risk factors and relation to airway diseases. Results from a large-scale population survey in Sweden. Br J Dermatol 166(6):1301–1308
Saleh BO, Anbar ZNH, Majid AY (2013) Role of some trace elements in pathogenesis and severity of acne vulgaris in Iraqi male patients. J Clin Exp Dermatol Res 4(1):169
Santoro D, Marsella R (2014) Animal models of allergic diseases. Vet Sci 1(3):192–212
Sarwar MS, Ahmed S, Ullah MS, Kabir H, Rahman GKMM, Hasnat A, Islam MS (2013) Comparative study of serum zinc, copper, manganese, and iron in preeclamptic pregnant women. Biol Trace Elem Res 154(1):14–20
Sivaranjani N, Rao SV, Rajeev G (2013) Role of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Diagn Res 7(12):2683–2685
Soetan KO, Olaiya CO, Oyewole OE (2010) The importance of mineral elements for humans, domestic animals and plants: a review. Afr J Food Sci 4(5):200–222
Sole D, Camelo-Nunes IC, Wandalsen GF, Mallozi MC, Naspitz CK, Brazilian ISAAC Group (2006) Prevalence of atopic eczema and related symptoms in Brazilian schoolchildren: results from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase 3. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 16(6):367–376
Toyran M, Kaymak M, Vezir E, Harmancı K, Kaya A, Ginis T, Kose G, Kocabas CN (2012) Trace element levels in children with atopic dermatitis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 22(5):341–344
Tsukahara H, Shibata R, Ohshima Y, Todoroki Y, Sato S, Ohta N, Hiraoka M, Mayumi M (2003) Oxidative stress and altered antioxidant defenses in children with acute exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. Life Sci 72(22):2509–2516
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT (2009) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(1):65–74
Vaskonen T (2003) Dietary minerals and modification of cardiovascular risk factors. J Nutr Biochem 14(9):492–506
Wang IJ, Guo YL, Weng HJ, Hsieh WS, Chuang YL, Lin SJ, Chen PC (2007) Environmental risk factors for early infantile atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 18(5):441–447
Whelton PK, He J, Cutler JA, Brancati FL, Appel IJ, Follmann D, Klag MJ (1997) Effects of oral potassium on blood pressure. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Am Med Assoc 277(20):1624–1632
Wintergerst ES, Maggini S, Hornig DH (2007) Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune function. Ann Nutr Metab 51(4):301–323
Yemaneberhan H, Flohr C, Lewis SA, Bekele Z, Parry E, Williams HC, Britton J, Venn A (2004) Prevalence and associated factors of atopic dermatitis symptoms in rural and urban Ethiopia. Clin Exp Allergy 34(5):779–785
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to all the staffs, nurses and physicians of Department of Dermatology, Noakhali Medical College Hospital (NMCH), Bangladesh and the participants of the research. The authors are also grateful to the Department of Pharmacy, Noakhali Science and Technology University, Bangladesh for providing the laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. N. Amin, K. F. Liza and M. S. Sarwar contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, M.N., Liza, K.F., Sarwar, M.S. et al. Effect of lipid peroxidation, antioxidants, macro minerals and trace elements on eczema. Arch Dermatol Res 307, 617–623 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-015-1570-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-015-1570-2