Abstract
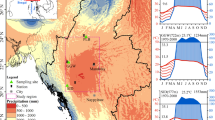
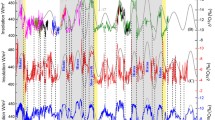
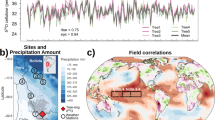
The trend of the Indian summer monsoon (ISM) intensity and its nature during the past 100 and 200 years still remain unclear. In this study we reconstructed the ISM intensity during the past 270 years from tree ring δ18O at Hongyuan, eastern edge of the Tibet Plateau. The monsoon failures inferred from δ18Otree ring correlate well with those recorded in ice cores, speleothem, and historical literature sources. 22.6, 59.0, and 110.9-years frequency components in the Hongyuan δ18Otree ring series, which may be the responses to solar activities, synchronize well with those recorded in other ISM indices. A notable feature of the reconstructed ISM intensity is the gradually decreasing trend from about 1860 to the present, which is inversely related to the increasing temperature trend contemporaneously. Such “decreasing ISM intensity–increasing temperature” tendency can also be supported by ice core records and meteorological records over a wide geographic extension. The decrease in sea surface temperature gradient between tropical and north Indian Ocean, and the decrease in land-sea thermal contrast between tropical Indian Ocean and “Indian sub-continent–western Himalaya” are possibly responsible for the observed decreasing ISM trend.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri R, Dutta K (2003) Centennial scale variations in monsoonal rainfall (Indian, east equatorial and Chinese monsoons): manifestations of solar variability. Curr Sci 85:459–463
Agnihotri R, Dutta K, Bhushan R, Somayajulu BLK (2002) Evidence for solar forcing on the Indian Monsoon during the last millennium. Earth Planet Sci Lett 198:521–527
Anderson DM, Overpeck JT, Gupta AK (2002) Increase in the Asian southwest monsoon during the past four centuries. Science 297:596–599
Borella S, Leuenberger M, Saurer M, Siegwolf R (1998) Reducing uncertainties in δ13C analysis of tree rings: pooling, milling, and cellulose extraction. J Geophys Res 103(D16):19519–19526. doi:10.1029/98JD01169
Burns SJ, Fleitmann D, Mudelsee M, Neff U, Matter A, Mangini A(2002)A 780-year annually resolved record of Indian Ocean monsoon precipitation from a speleothem from south Oman. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2001JD001281
Chung CE, Ramanathan V (2006) Weakening of North Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J Clim 19:2036–2045
Cole JE, Dunbar RB, McClanahan TR, Muthiga NA (2000) Tropical Pacific forcing of decadal SST variability in the Western Indian Ocean over the past two centuries. Science 287:617–619
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Douville H, Royer J-F, Polcher J, Cox P, Gedney N, Stephenson DB, Valdes PJ (2000) Impact of CO2 doubling on the Asian summer monsoon: robust versus model dependent responses. J Meteor Soc Jpn 78:421–439
Duan KQ, Wang NL, Li YF, Sun WZ (2000) Accumulation in Dasuopu ice core in Qinghai-Tibet plateau and solar activity. Chinese Sci Bull 45:1038–1042
Duan KQ, Yao TD, Thompson LG (2004) Low-frequency of southern Asian monsoon variability using a 295-year record from the Dasuopu ice core in the central Himalayas. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2004GL020015
Dykoski CA, Edwards RL, Cheng H, Yuan D, Cai Y, Zhang M, Lin Y, Qing J, An Z, Revenaugh J (2005) A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 233:71–86
Fleitmann D, Burns SJ, Mudelsee M, Neff U, Kramers J, Mangini A, Matter A (2003) Holocene forcing of the Indian Monsoon recorded in a stalagmite from Southern Oman. Science 300:1737–1739
Fleitmann D, Burns SJ, Mangini A, Mudelsee M, Kramers J, Villa I, Neff U, Al-Subbary AA, Buettner A, Hippler D, Matter A (2007) Holocene ITCZ and Indian monsoon dynamics recorded in stalagmites from Oman and Yemen (Socotra). Quat Sci Rev 26:170–188
Gadgil A, Dhorde A (2005) Temperature trends in twentieth century at Pune, India. Atmos Environ 39:6550–6556
Ganguly ND, Iyer KN (2009) Long-tern variations of surface air temperature during summer in India. Int J Climatol 29:735–746
Giannini A, Saravanan R, Chang P (2003) Oceanic forcing of Sahel rainfall on interannual to interdecadal time scales. Science 302:1027–1030
Grießinger J, Bräuning A, Helle G, Thomas A, Schleser G (2011) Late holocene Asian summer monsoon variability reflected by δ18O in tree-rings from Tibetan junipers. Geophys Res Let 38(L03701):1–5. doi:10.1029/2010GL045988
Hiremath KM, Mandi PI (2004) Influence of the solar activity on the Indian Monsoon rainfall. New Astron 9:651–662
Hong YT, Jiang HB, Liu TS, Zhou LP, Beer J, Li HD, Leng XT, Hong B, Qin XG (2000) Response of climate to solar forcing recorded in a 6000-year δ18O time-series of Chinese peat cellulose. Holocene 10(1):1–7
Kalnay E et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–470
Kumar KK, Rajagopalan B, Hoerling M, Bates G, Cane M (2006) Unraveling the mystery of Indian monsoon failure during El Niño. Science 314:115–119
Lean J (2000) Evolution of the sun’s spectral irradiance since the maunder minimum. Geophys Res Lett 27:2425–2428
Liang EY, Shao XM, Qin NS (2008) Tree-ring based summer temperature reconstruction for the source region of the Yangtze River on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob Planet Change 61:313–320
May W (2002) Simulated changes of the Indian summer monsoon under enhanced greenhouse gas conditions in a global timeslice experiment. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2001GL013808
Meehl GA, Washington WM (1993) South Asian summer monsoon variability in a model with doubled atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. Science 260:1101–1104
Miller DL, Mora CI, Grissino-Mayer HD, Mock CJ, Uhle ME, Sharp Z (2006) Tree-ring isotope records of tropical cyclone activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14294–14297
Naidu CV, Durgalakshmi K, Krishna KM, Rao SR, Satyanarayana GC, Lakshminarayana P, Rao LM(2009)Is summer monsoon rainfall decreasing over India in the global warming era? J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2008JD011288
Neff U, Burns SJ, Mangini A, Mudelsee M, Fleitmann D, Matter A (2001) Strong coherence between solar variability and themonsoon in Oman between 9 and 6 kyr ago. Nature 411:290–293
Pant GB, Rupa Kumar K (1997) Climates of South Asia. Wiley, Chichester
Parthasarathy B, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1995) Contributions from Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology. Research Report RR-065, Pune. Data from IRI Climate Data Library. http://ingrid.ldeo.columbia.edu/SOURCES/Indices/india/rainfall
Ramanathan V, Chung C, Kim D, Bettge T, Buja L, Kiehl JT, Washington WM, Fu Q, Sikka DR, Wild M (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: impacts on South Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5326–5333
Roden JS, Lin G, Ehleringer JR (2000) A mechanistic model for the interpretation of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in tree ring cellulose. Cosmochim Acta 64:21–35
Sachs JP, Sachse D, Smittenberg RH, Zhang Z, Battisti DS, Golubic S (2009) Southward movement of the Pacific intertropical convergence zone AD 1400–1850. Nat Geosci 2:519–525
Sano M, Sheshshayee MS, Managave S, Ramesh R, Sukumar R, Sweda T (2010) Climatic potential of δ18O of Abies spectabilis from the Nepal Himalaya. Dendrochronologia 28:93–98
Stokes MA, Smiley TL (1968) An introduction to tree-ring dating. University of Arizona Press, Tucson. (Reprinted 1995), pp xi–xiii, xv–xvii, 3–20
Thompson LG, Yao T, Mosley-Thompson E, Davis ME, Henderson KA, Lin PN (2000) A high-resolution millennial record of the South Asian monsoon from Himalayan ice cores. Science 289:1916–1919
von Rad U (1999) A 5000-yr record of climate change in varved sediments from the oxygen minimum zone off Pakistan, northern Arabian Sea. Quat Res 51:39–53
Wang Y, Cheng H, Kong X, Edwards RL, An Z, Wu J, Dykoski CA, He Y, Kelly MJ, Li X (2005) The holocene Asian Monsoon: links to solar changes and north. Science 308:854–857
Wilson R, Tudhope A, Brohan P, Briffa K, Osborn T, Tett S (2006) Two-hundred-fifty years of reconstructed and modeled tropical temperatures. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2005JC003188
**ang LY, Chen X, Li CH, Zheng JH (2007) The regional features of abrupt precipitation change in China in recent 55 years. Torre Rain Disasters 26:149–153 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xu H, Hong YT, Lin QH, Zhu YX, Hong B, Jiang HB (2006) Temperature responses to quasi-100-yr solar variability during the past 6000 years based on δ18O of peat cellulose in Hongyuan, eastern Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 230:155–164
Xu H, Hong YT, Hong B, Zhu YX, Wang Y (2010) Influence of ENSO on multi annual temperature variations at Hongyuan, NE Qinghai-Tibet plateau: evidence from δ13C of spruce tree rings. Int J Clim 30:120–126
Yadav RR, Singh J (2002) Tree-ring-based spring temperature patterns over the past four centuries in Western Himalaya. Q Res 57:299–305
Yadav RR, Park WK, Singh J, Dubey B (2004) Do the western Himalayas defy global warming? Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2004GL020201
Yan Z, Ji J, Ye D (1990) Northern hemispheric summer climatic jump in the 1960s, part I—rainfall and temperature. Sci China Ser B 33:1092–1101
Yuan D, Cheng H, Edwards RL, Dykoski CA, Kelly MJ, Zhang M, Qing J, Lin Y, Wang Y, Wu J, Dorale JA, An Z, Cai Y (2004) Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon. Science 304:575–578
Zhang DE, Li XQ, Liang YY (2003) Complement of the Chinese drought/flood index during 1993–2000. J Appl Meteorol Sci 14:379–383 (in Chinese)
Zhang DQ, Qin DH, Hou SG, Kang SC, Ren JW (2004) Net accumulation rate of the east Rongbuk Glacier and Indian summer monsoon rainfall. J Glaciol Geocry 2:129–134 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang P, Cheng H, Edwards RL, Chen F, Wang Y, Yang X, Liu J, Tan M, Wang X, Liu J, An C, Dai Z, Zhou J, Zhang D, Jia J, ** L, Johnson KR (2008) A test of climate, sun, and culture relationships from an 1810-year Chinese cave record. Science 322:940–942
Zhao H, Moore GWK (2006) Reduction in Himalayan snow accumulation and weakening of the trade winds over the Pacific since the 1840s. Geophys Res Lett 33:L17709. doi:10.1029/2006GL027339
Acknowledgments
We thank Thompson LG, Duan KQ, Zhang DQ, and Liang EY for providing Dasuopu dust concentration data, Dasuopu ice accumulation data, Rongbuk ice accumulation data, and Yushu tree ring widths, respectively. This work was supported by the projects (41073103; 41173122) funded by natural science foundation of China, and the project (KZCX2-EW-QN103) founded by Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Hong, Y. & Hong, B. Decreasing Asian summer monsoon intensity after 1860 AD in the global warming epoch. Clim Dyn 39, 2079–2088 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1378-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1378-0