Abstract
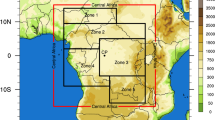
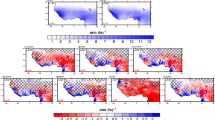
Regional climate model (RCM) is a valuable scientific tool to address the mechanisms of regional atmospheric systems such as the West African monsoon (WAM). This study aims to improve our understanding of the impact of some physical schemes of RCM on the WAM representation. The weather research and forecasting model has been used by performing six simulations of the 2006 summer WAM season. These simulations use all combinations of three convective parameterization schemes (CPSs) and two planetary boundary layer schemes (PBLSs). By comparing the simulations to a large set of observations and analysis products, we have evaluated the ability of these RCM parameterizations to reproduce different aspects of the regional atmospheric circulation of the WAM. This study focuses in particular on the WAM onset and the rainfall variability simulated over this domain. According to the different parameterizations tested, the PBLSs seem to have the strongest effect on temperature, humidity vertical distribution and rainfall amount. On the other hand, dynamics and precipitation variability are strongly influenced by CPSs. In particular, the Mellor–Yamada–Janjic PBLS attributes more realistic values of humidity and temperature. Combined with the Kain–Fritsch CPS, the WAM onset is well represented. The different schemes combination tested also reveal the role of different regional climate features on WAM dynamics, namely the low level circulation, the land–atmosphere interactions and the meridional temperature gradient between the Guinean coast and the Sahel.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa A (2004) The cumulus parameterization problem: past, present, and future. J Clim 17:2493–2525
Bock O et al (2008) West African monsoon observed with ground-based GPS receivers during African Monsoon Multidisciplinary Analysis (AMMA). J Geophys Res 113:D21105. doi:10.1029/2008JD010327
Bolton D (1980) The computation of equivalent potential temperature. Mon Weather Rev 108:1046–1053
Bright DR, Mullen SL (2002) The sensitivity of the numerical simulation of the southwest monsoon boundary layer to the choice of PBL turbulence parameterization in MM5. Weather Forecast 17:99–114
Challa VS, Indracanti J, Rabarison MK, Patrick C, Baham JM, Young J, Hughes R, Hardy MG, Swanier SJ, Anjaneyulu Y (2009a) A simulation study of mesoscale coastal circulations in Mississippi Gulf coast. Atmos Res 91:9–25
Challa VS, Indracanti J, Rabarison MK, Patrick C, Baham JM, Young J, Hughes R, Hardy MG, Swanier SJ, Yerramilli A (2009b) A simulation study of mesoscale coastal circulations in Mississippi Gulf coast. Atmos Res 91:9–25. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2008.05.004
Cook KH (1999) Generation of the African Easterly Jet and its role in determining West African precipitation. J Clim 12:1165–1184
Diedhiou A, Janicot S, Viltard A, de Felice P, Laurent H (1999) Easterly wave regimes and associated convection over West Africa and tropical Atlantic: results from NCEP/NCAR and ECMWF reanalysis. Clim Dyn 15:795–822
Douville H (2002) Influence of soil moisture on the Asian and African monsoons. Part II: interanual variability. J Clim 16:701–720
Douville H, Chauvin F, Broqua H (2001) Influence of soil moisture on the Asian and African monsoons. Part I: mean monsoon and daily precipitation. J Clim 15:2381–2403
Duvel JP (1990) Convection over tropical Africa and the Atlantic ocean during northern summer. Part II: modulation by easterly waves. Mon Weather Rev 118:1855–1868
Folland CK, Palmer TN, Parker DE (1986) Sahel rainfall and worldwide sea temperature 1901–1985. Nature 320:602–607
Fontaine B, Philippon N (2000) Seasonal evolution of boundary layer heat content in the West African monsoon from the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis (1968–1998). Int J Climatol 20:1777–1790
Fontaine B, Janicot S, Moron V (1995) Rainfall anomaly patterns and wind field signals over West Africa in August (1958–1989). J Clim 8:1503–1510
Fontaine B, Louvet S, Roucou P (2008) Definition and predictability of an OLR-based West African monsoon onset. Int J Climatol 28:1787–1798
Gallee H, Moufouma-Okia W, Bechtold P, Brasseur O, Dupays I, Marbaix P, Messager C, Ramel R, Lebel T (2004) A high-resolution simulation of a West African rainy season using a regional climate model. J Geophys Res 109. doi:10.1029/2003JD004020
Giannini A, Saravanan R, Chang P (2003) Oceanic forcing of Sahel rainfall on interannual to interdecadal time scales. Science 302:1027–1030. doi:10.1126/science.1089357
Gochis DJ, Shuttleworth WJ, Yang ZL (2002) Sensitivity of the modeled North American monsoon regional climate to convective parameterization. Mon Weather Rev 130:1282–1298
Grell GA (1993) Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon Weather Rev 121:764–787
Grell GA, Devenyi D (2002) A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys Res Lett 29, 38-1-4
Grist JP, Nicholson SA (2001) A study of the dynamic factors influencing the rainfall variability in the West African Sahel. J Clim 14:1337–1359
Hagos SM, Cook KH (2007) Dynamics of the West African monsoon jump. J Clim 20(21):5264–5284
Hagos SM, Cook KH (2009) Development of a coupled regional model and its application to the study of interactions between the West African monsoon and the eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean. J Clim 22:2591–2604
Hodges KI, Thorncroft CD (1997) Distribution and statistics of African mesoscale convective weather systems based on the ISCCP Meteosat imagery. Mon Weather Rev 125:2821–2837
Hong SY, Pan HL (1996) Non-local boundary layer vertical diffusion in medium-range forecast model. Mon Weather Rev 124:1215–1238
Hong SY, Noh Y, Dudhia J (2006) A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon Weather Rev 134:2318–2341
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Morrissey MM, Curtis S, Joyce R, McGavock B, Susskind J (2000) Global precipitation at 1 degree daily resolution from multi-satellite observations. J Hydrometeorol 2(1):36–50
Janicot S, Sultan B (2001) Intra-seasonal modulation of convection in the West African monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 28:523–526
Janicot S, Trzaska S, Poccard I (2001) Summer Sahel-ENSO teleconnection and decadal time scale SST variations. Clim Dyn 18:303–320
Janicot S, Thorncroft C et al (2008) Large scale overview of the summer monsoon over the summer monsoon in West Africa during the AMMA field experiment in 2006. Ann Geophys 26:2569–2595
Janicot S, Mounier F, Hall NM, Leroux S, Sultan B, Kiladis G (2009) The dynamics of the West African monsoon. Part IV: analysis of 25–90-day variability of convection and the role of the Indian monsoon. J Clim 22:1541–1565
Kain JS (2004) The Kain–Fritsch convective parameterization: an update. J Appl Meteorol 43:170–181
Kain JS Fritsch JM (1993) Convective parameterization for mesoscale models: the Kain–Fritsch scheme. The representation of cumulus convection in numerical models. Meteor. Monogr. No. 46. Amer. Meteor. Soc., pp 165–170
Koster and the GLACE Team (2004) Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 305:1138–1140
Kummerow C, Barnes W, Kozu T, Shiue J, Simpson J (1998) The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J Atmos Ocean Technol 15:809–817
Lavaysse C, Flamant C, Janicot S, Parker D, Lafore JP, Sultan B, Pelon J (2009) Seasonal cycle of the West African heat low: a climatological perspective. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0553-4
Le Barbé L, Lebel T, Tabsoba D (2002) Rainfall variability in West Africa during the years 1950–1990. J Clim 15:187–202
Lebel T, Diedhiou A, Laurent H (2003) Seasonal cycle and interannual variability of the Sahelian rainfall at hydrological scales. J Geophys Res 108. doi:10.1029/2001JD001580
Liebmann B, Smith CA (1996) Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull Am Meteor Soc 77:1275–1277
Lothon M, Saïd F, Lohou F, Campistron B (2008) Observation of the diurnal cycle in the low troposphere of West Africa. Mon Weather Rev 136:3477–3500
Mathon V, Laurent H (2001) Life cycle of Sahelian mesoscale convective cloud systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 127:377–406
Mathon V, Laurent H, Lebel T (2002) Mesoscale convective systems rainfall in the Sahel. J Appl Meteorol 41:1081–1092
Matthews AJ (2004) Intraseasonal variability over tropical Africa during northern summer. J Clim 17:2427–2440
Mellor GL, Yamada T (1982) Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev Geophys 20:851–875
Messager C, Gallee H, Brasseur O (2004) Precipitation sensitivity to regional SST in a regional climate simulation during the West African monsoon for two dry years. Clim Dyn 22:249–266
Mounier FS, Janicot S, Kiladis G (2008) The West African monsoon dynamics. Part III: the quasi-biweekly zonal dipole. J Clim 21:1911–1928
Nicholson SE, Webster PJ (2007) A physical basis for the interannual variability of rainfall in the Sahel. Q J R Meteorol Soc 133:2065–2084
Okumura Y, **e SP, Numaguti A, Tanimoto Y (2001) Tropical Atlantic air–sea interaction and its influence on NAO. Geophys Res Lett 28:1507–1510
Pagowski M (2004) Some comments on PBL parameterizations in WRF. In: Joint 5th WRF/14th MM5 users’ workshop, Boulder, CO, NCAR, pp 43–46 (Preprints). http://www.mmm.ucar.edu/mm5/workshop/workshop-papers_ws04.html
Philippon N, Fontaine B (2002) The relationship between the Sahelian and previous second Guinean rainy seasons: a monsoon regulation by soil wetness? Ann Geophys 20:575–582
Ramel R, Gallee H, Messager C (2006) On the northward shift of the West African monsoon. Clim Dyn 26(4). doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0093-5
Redelsperger JL, Thorncroft C, Diedhiou A, Lebel T, Parker D, Polcher J (2006) African monsoon multidisciplinary analysis (AMMA): an international research project and field campaign. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 87:1739–1746
Reed RJ, Norquist DC, Recker EE (1977) The structure and properties of African wave disturbances as observed during Phase III of GATE. Mon Weather Rev 105:317–333
Rowell DP (2001) Teleconnections between the Tropical Pacific and the Sahel. Q J R Meteorol Soc 127:1683–1706
Sijikumar S, Roucou P, Fontaine B (2006) Monsoon onset over Sudan-Sahel: simulation by the regional scale model MM5. Geophys Res Lett 33:L03814. doi: 10.1029/2005GL024819
Skamarock WC, Klemp JB, Dudhia J, Gill DO, Barker M, Duda MG, Huang XY, Wang W, Powers JG (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF version 3. NCAR technical note, NCAR/TN\u2013475+STR, 123 pp. http://www.mmm.ucar.edu/wrf/users/docs/arw_v3.pdf
Steiner AL, Pal JS, Rauscher SA, Bell JL, Diffenbaugh NS, Sloan LC, Giorgi F (2008) Land surface coupling in regional climate simulations of the West African monsoon. Clim Dyn Obs Theor Comput Res Clim Syst. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0543-6
Sultan B, Janicot S (2000) Abrupt shift of the ITCZ over West Africa and intra-seasonal variability. Geophys Res Lett 27:3353–3356
Sultan B, Janicot S (2003) The West African monsoon dynamics. Part II: the “preonset” and “onset” of the summer monsoon. J Clim 16:3389–3406
Sultan B, Janicot S, Diedhiou A (2003) The West African monsoon dynamics. Part I: documentation of intraseasonal variability. J Clim 16:3407–3427
Sylla MB, Coppola E, Mariotti L, Giorgi F, Ruti PM, Dell’Aquila A, Bi X (2009) Multiyear simulation of the African climate using a regional climate model (RegCM3) with the high resolution ERA-interim reanalysis. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0613-9
Taylor C (2009) Intraseasonal land-atmosphere coupling in the West African monsoon. J Clim 21:6636–6648
Thorncroft CD, Blackburn M (1999) Maintenance of the African easterly jet. Q J R Meteorol Soc 125:763–786
Troen I, Mahrt L (1986) A simple model of the atmospheric boundary layer: sensitivity to surface evaporation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 37:129–148
Vaidya SS (2006) The performance of two convective parameterization schemes in a mesoscale model over the India region. Meteorol Atmos Phys 92(3–4):175–190
Vigaud N, Roucou P, Fontaine B, Sijikumar S, Tyteca S (2009) WRF/ARPEGE-CLIMAT simulated climate trends over West Africa. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0707-4
Vizy EK, Cook KH (2002) Development and application of a mesoscale climate model for the tropics: influence of sea surface temperature anomalies on the West African monsoon. J Geophys Res 107(D3):40223. doi:10.1029/2001JD000686
Wang W, Seaman NL (1997) A comparison study of convective parameterization schemes in a mesoscale model. Mon Weather Rev 125:252–278
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the help of Philippe Weill to install the model on the IPSL servers. We are also thankful to the Climate Diagnostics Center (NOAA, Boulder, CO) and to the NCEP for the OLR and Final Analyses (FNL) data. Finally, we would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their fruitful comments. Based on French initiative, AMMA was built by an international scientific group and is currently funded by a large number of agencies, especially from France, UK, US and Africa. It has been the beneficiary of a major financial contribution from the European Community’s Sixth Framework Research Programme. Detailed information on scientific coordination and funding is available on the AMMA International website http://www.amma-international.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flaounas, E., Bastin, S. & Janicot, S. Regional climate modelling of the 2006 West African monsoon: sensitivity to convection and planetary boundary layer parameterisation using WRF. Clim Dyn 36, 1083–1105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0785-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0785-3