Abstract
Objective
Children with type 1 diabetes are usually associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. The present study explored the influence of physical activity on their autonomic nervous function by measuring the heart rate variability (HRV).
Materials and methods
A total of 93 type 1 diabetic children and 107 healthy control subjects were enrolled. The Physical Activity Questionnaire for Children (PAQ-C) was adopted to determine the physical activity level as low, moderate, or high activity. HRV was determined by frequency analysis and measured in both resting and active states.
Results
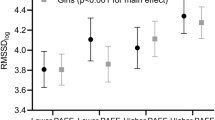
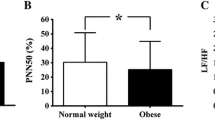
Children with type 1 diabetes had significantly lower HRV than that of healthy control subjects in resting state but not in active state. The decreased HRV in diabetic children was observed only in subjects with low physical activity. The HRV in diabetic children with moderate to high physical activity, however, was not different from that of their healthy controls.
Conclusions
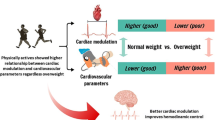
Diabetic children should be encouraged to engage in physical activity with more intensity, which can benefit their autonomic nervous function. Nevertheless, the potential risk of vigorous activity still needs our concern.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci A, Celiker A, Baykal E, Tezic T (1993) Heart rate variability in diabetic children, sensitivity of the time-and frequency-domain methods. Pediatr Cardiol 14:140–146
Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Berger AC, Cohen RJ (1981) Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science 213:220–222
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15:539–553
American Diabetes Association (2006) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2006. Diabetes Care 29:S4–S42
Bellavere F, Balzani I, De Masi G, Carraro M, Carenza P, Cobelli C, Thomasseth K (1992) Power spectral analysis if heart-rate variation improves assessment of diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 41:633–640
Chessa M, Butera G, Lanza GA, Bossone E, Delogu A, Rosa GD, Marietti G, Rosti L, Carminati M (2002) Role of heart rate variability in the early diagnosis of diabetic autonomic neuropathy in children. Herz 27:785–790
Colhoun HM, Francis DP, Rubens MB, Underwood SR, Fuller JH (2001) The association of heart-rate variability with cardiovascular risk factors and coronary artery calcification: a study in type 1 diabetic patients and the general population. Diabetes Care 24:1108–1114.
Crocker PR, Bailey DA, Faulkner RA, Kowalski KC, McGrath R (1997) Measuring general level of physical activity: preliminary evidence for the Physical Activity Questionnaire for older children. Med Sci Sports Exer 29:1344–1349
Ewing DJ, Boland O, Neilson JM, Cho CG, Clarke BF (1991) Autonomic neuropathy, QT interval lengthening, and unexpected deaths in male diabetic patients. Diabetologia 34:182–185
Ewing DJ, Campbell IW, Clarke BF (1980) The nature history of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Q J Med 49:95–108
Ewing DJ, Campbell IW, Clarke BF (1981) Heart rate variability in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1:183–186
Kardelen F, Akcurin G, Ertug H, Akcurin S, Bircan I (2006) Heart rate variability and circadian variations in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes 7:45–50
Macor F, Fagard R, Amery A (1996) Power spectral-analysis of RR interval and blood- pressure short-term variability at rest and during dynamic exercise: comparison between cyclists and controls. Int J Sports Med 17:175–181
Mandigout S, Melin A, Fauchier L, N’Guyen LD, Courteix D, Obert P (2002) Physical training increases heart rate variability in healthy prepubertal children. Eur J Clin Investig 32:479–487
Melanson EL (2000) Resting heart rate variability in men varying in habitual physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1894–1901
Monahan KD, Dinenno FA, Tanaka H, Clevenger CM, DeSouza CA, Seals DR (2000) Regular aerobic exercise modulates age-associated declines in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in healthy men. J Physiol 529:263–271
Nagai N, Hamada T, Kimura T, Moritani T (2004) Moderate physical exercise increases cardiac autonomic nervous system activity in children with low heart rate variability. Childs Nerv Syst 20:209–214
O’Brien IA, McFafffen JP, Corrall RJM (1991) The influence of autonomic neuropathy on mortality insulin-dependent diabetes. Q J Med 79:495–502
Ram Z, Sadeh M, Walden R, Adar R (1991) Vascular insufficiency quantitatively aggravates diabetic neuropathy. Arch Neurol 48:1239–1242
Rennie KL, Hemingway H, Kumari M, Brunner E, Malik M, Marmot M (2003) Effects of moderate and vigorous physical activity on heart rate variability in a British study of civil servants. Am J Epidemiol 158:135–143
Salvatoni A, Cardani R, Biasoli R, Salmaso M, De Paoli A, Nespoli L (2005) Physical activity and diabetes. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense 76:85–88
Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Wasserman DH, Castaneda-Sceppa C, White RD (2006) Physical activity/exercise and type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 29:1433–1438
Sochett E, Daneman D (1999) Early diabetes related complications in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: implications for screening and intervention. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 28:865–882
Stella P, Ellis D, Maser RE, Orchard TJ (2000) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (expiration and inspiration ratio) in type 1 diabetes. Incidence and predictors. J Diabetes Its Complicat 14:1–6
Sztajzel J (2004) Heart rate variability: a noninvasive electrocardiographic method to measure the autonomic nervous system. Swiss Med Wkly 134:514–522
Takase B, Kitamura H, Noritake M, Nagase T, Kurita, Ohsuza F (2002) Assessment of diabetic autonomic neuropathy using twenty-four-hour spectral analysis of heart rate variability: a comparison with the findings of the Ewing battery. Jpn Heart J 43:127–135
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (2003) Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26:3160–3167
Vanelli M, Corchia M, Iovane B, Bernardini A, Mele A, Chiari G (2006) Self-monitoring adherence to physical activity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense 77(Suppl 1):47–50
Vinik AI, Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Freeman R (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26:1553–1579
Walsh MG, Zgibor J, Borch-Johnsen K, Orchard TJ; DiaMond Investigators (2004) A multinational comparison of complications assessment in type 1 diabetes: the DiaMond substudy of complications (DiaComp) level 2. Diabetes Care 27:1610–1617
Weston PJ, James MA, Panerai RB, McNally PG, Potter JF, Thurston H (1998) Evidence of defective cardiovascular regulation in insulin-dependent diabetic patients without clinical autonomic dysfunction. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 42:141–148
Wheeler SG, Ahroni JH, Boyko EJ (2002) Prospective study of autonomic neuropathy as a predictor of mortality in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 58:131–138
Yabe-Nishimura C (1998) Aldose reductase in glucose toxicity: a potential target for the prevention of diabetic complications. Pharmacol Rev 50:21–33
Yoshiharu Y, Hughson RL, Peterson JC (1991) Autonomic control of heart rate during exercise studied by heart rate variability spectral analysis. J Appl Physiol 71:1136–1142
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend sincere appreciation to the children who participated in the study. In addition, we are thankful to Mackay Memorial Hospital (94MMH-TMU-04) who funded this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SR., Lee, YJ., Chiu, HW. et al. Impact of physical activity on heart rate variability in children with type 1 diabetes. Childs Nerv Syst 24, 741–747 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0499-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0499-y