Abstract
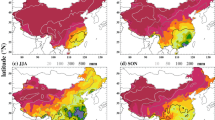
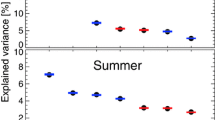
Using the latest daily observational rainfall datasets for the period 1961–2008, the present study investigates the interannual variability of June–September (JJAS) mean rainfall in northern China. The regional characteristics of JJAS mean rainfall are revealed by a rotated empirical orthogonal function (REOF) analysis. The analysis identifies three regions of large interannual variability of JJAS rainfall: North China (NC), Northeast China (NEC), and the Taklimakan Desert in Northwest China (TDNWC). Summer rainfall over NC is shown to have displayed a remarkable dry period from the late 1990s; while over NEC, decadal-scale variation with a significant decreasing trend in the last two decades is found, and over TDNWC, evidence of large interannual variability is revealed. Results also show that the interannual variability of JJAS rainfall in northern China is closely associated with the Northern Hemisphere circumglobal teleconnection (CGT). Correlation coefficients between the CGT index and regional-averaged JJAS mean rainfall over NC and NEC were calculated, revealing values of up to 0.50 and 0.53, respectively, both of which exceeded the 99% confidence level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrizzi, T., B. Hoskins, and H. Hsu, 1995: Rossby wave propagation and teleconnection patterns in the austral winter. J. Atmos. Sci, 52, 3661–3672.
Chen, L., M. Dong, and Y. Shao, 1992: The characteristics of interannual variations on the East Asian monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 397–421.
Chen, W., D. Zhu, H. Liu, and S. Sun, 2009: Land-air interaction over arid/semi-arid areas in China and its impact on the east Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Calibration of the land surface model (BATS) using multicriteria methods. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 1088–1098, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-8187-3.
Ding, Q., and B. Wang, 2005: Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer. J. Climate, 18, 3483–3505.
Ding, Y., Z. Wang, and Y. Sun, 2008: Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol, 28, 1139–1161.
Endo, N., B. Ailikun, and T. Yasunari, 2005: Trends in precipitation amounts and the number of rainy days and heavy rainfall events during summer in China from 1961 to 2000. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 83, 621–631.
Enomoto, T., 2004: Interannual variability of the Bonin high associated with the propagation of rossby waves along the Asian jet. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 1019–1034.
Enomoto, T., B. Hoskins, and Y. Matsuda, 2003: The formation mechanism of the Bonin high in August. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc, 129, 157–178.
Gong, D., P. Shi, and J. Wang, 2004: Daily precipitation changes in the semi-arid region over northern China. Journal of Arid Environments, 59, 771–784.
Huang, G., 2006: Global climate change phenomenon associated with the droughts in North China. Climatic and Environmental Research, 11, 270–279. (in Chinese)
Huang, R. H., Y. H. Xu, and L. T. Zhou, 1999: The interdecadal variation of summer precipitations in China and the drought trend in North China. Plateau Meteorology, 18, 465–476. (in Chinese)
Huang, R. H., L. Gu, J. L. Chen, and G. Huang, 2008: Recent progresses in studies of the temporal-spatial variations of the east asian monsoon system and their impacts on climate anomalies in China. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 32, 691–719. (in Chinese)
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Krishnan, R., and M. Sugi, 2001: Baiu rainfall variability and associated monsoon teleconnections. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 79, 851–860.
Li, X., Y. Zhu, and W. Qian, 2002: Spatiotemporal variations of summer rainfall over eastern China during 1880–1999. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 19, 1055–1068.
Liu, Z., and S. Yu, 1993: The upper tropospheric lowfrequency waveguides in summer. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 9, 142–149. (in Chinese)
Lu, R., J. Oh, and B. Kim, 2002: A teleconnection pattern in upper-level meridional wind over the North African and Eurasian continent in summer. Tellus A, 54, 44–55.
Ma, Z., and C. Fu, 2006: Some evidences of drying trend over North China from 1951 to 2004. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 2913–2925.
Murata, A., 1990: Regionality and periodicity observed in rainfall variations of the Baiu season over Japan. Int. J. Climatol., 10, 627–646.
Nitta, T., and Z. Hu, 1996: Summer climate variability in China and its association with 500 hPa height and tropical convection. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 425–445.
Richman, M., 1986: Rotation of principal components. Int. J. Climatol., 6, 293–335.
Rodwell, M., and B. Hoskins, 1996: Monsoons and the dynamics of deserts. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc, 122, 1385–1404.
Sato, N., and M. Takahashi, 2006: Dynamical processes related to the appearance of quasi-stationary waves on the subtropical jet in the midsummer northern hemisphere. J. Climate, 19, 1531–1544.
Shi, S. F., and R. Y. Lu, 2010: Teleconnection patterns along the Asian jet associated with different combinations of convetion oscillation over the Indian continent and western North Pacific during summer. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 3, 14–18.
Shi, Y., Y. Shen, E. Kang, D. Li, Y. Ding, G. Zhang, and R. Hu, 2007: Recent and future climate change in northwest China. Climatic Change, 80, 379–393.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and K. Lau, 2001: Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific-East Asian monsoons. J. Climate, 14, 4073–4090.
Wang, W., and K. Li, 1990: Precipitation fluctuation over semiarid region in northern China and the relationship with El Niño/Southern Oscillation. J. Climate, 3, 769–783.
Wang, Z., C. Chang, B. Wang, and F. **, 2005: Teleconnections from Tropics to northern extratropics through a southerly conveyor. J. Atmos. Sci, 62, 4057–4070.
Wu, R., and B. Wang, 2002: A contrast of the east Asian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship between 1962–77 and 1978–93. J. Climate, 15, 3266–3279.
Xu, G., X. Yang, and X. Sun, 2005: Interdecadal and interannual variation characteristics of rainfall in North China and its relation with the northern hemisphere atmospheric circulations. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 48, 511–518. (in Chinese)
Xue, Y., 1996: The impact of desertification in the Mongolian and the inner Mongolian grassland on the regional climate. J. Climate, 9, 2173–2189.
Yang, L., and Q. Zhang, 2008: Interannual variation of summer precipitation in **njiang and Asian subtropical westerly jet stream. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 19, 171–179. (in Chinese)
Yatagai, A., and T. Yasunari, 1994: Trends and decadalscale fluctuations of surface air temperature and precipitation over China and Mongolia during the recent 40 year period(1951–1990). J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 72, 937–957.
Yatagai, A., and T. Yasunari, 1995: Interranual variations of summer precipitation in the arid/semi-arid regions in China andMongolia: Their regionality and relation to the Asian summer monsoon: Special edition on HEIFE. I. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 73, 909–923.
Zhang, J., W. Dong, and C. Fu, 2005: Impact of land surface degradation in northern China and southern Mongolia on regional climate. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50, 75–81.
Zhou, L., and R. Huang, 2009: Interdecadal variability of summer rainfall in Northwest China and its possible causes. Int. J. Climatol., 30, 549–557.
Zhou, L. T., and R. H. Huang, 2006: Characteristics of interdecadal variability of the difference between surface temperature and surface air temperature in spring in arid and semi-arid region of Northwest China and its impact on summer precipitation in North China. Climatic and Environmental Research, 11, 1–13. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, G., Liu, Y. & Huang, R. The interannual variability of summer rainfall in the arid and semiarid regions of Northern China and its association with the northern hemisphere circumglobal teleconnection. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 28, 257–268 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-9225-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-9225-x