Abstract
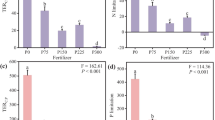
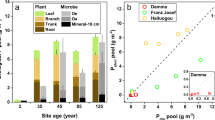
Despite that organic phosphorus (Po) is a source of bioavailable P during the early stage of soil development, it remains unclear whether P availability or organic carbon (C) mineralization is the main regulator of Po mineralization. In this study, the P availability (labile inorganic P, Pi) and the potential organic C mineralization (β-glucosidase activity) were investigated at the Hailuogou Chronosequence and a reference site (35–125 and ∼1400 years after glacier retreat, respectively) to decipher their relationships with the potential Po mineralization (acid and alkaline phosphomonoesterase activities). Labile Pi displayed no trend in the soil profile, whereas it was significantly higher at the reference site than the young sites. Enzyme activities decreased down the soil profile, but this trend weakened for specific activities (enzyme activity per microbial biomass C). Enzyme activities and specific activities displayed no trend with the succession stage. Potential Po mineralization was more related to potential organic C mineralization (R 2 = 0.41–0.69, p < 0.0001) than P availability (R 2 = 0.05–0.09, p ≤ 0.05). By increasing the specific activity of β-glucosidase, the microbial biomass C:P ratio decreased to reach the value of 8:1. Probably, the phosphate in the excess of microbial demand was released as the by-product of C mineralization. At the young sites of the chronosequence, the significant correlation between Po and C concentrations in the surface mineral horizon (R 2 = 0.85, p < 0.0001) suggested that the mineralizations of Po and organic C were linked to each other. The results suggested that the demand for C may drive the microbial mineralization of soil Po during the early stage of soil development, and the phosphate released by the Po mineralization may serve as a potential source of labile Pi for plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achat DL, Bakker MR, Zeller B, Pellerin S, Bienaime S, Morel C (2010) Long-term organic phosphorus mineralization in Spodosols under forests and its relation to carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1479–1490
Allison SD, Vitousek PM (2005) Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol Biochem 37:937–944
Allison V, Condron L, Peltzer D, Richardson S, Turner B (2007) Changes in enzyme activities and soil microbial community composition along carbon and nutrient gradients at the Franz Josef chronosequence, New Zealand. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1770–1781
Beauchemin S, Simard R (1999) Soil phosphorus saturation degree: review of some indices and their suitability for P management in Quebec, Canada. Can J Soil Sci 79:615–625
Bing H, Wu Y, Zhou J, Ming L, Sun S, Li X (2014) Atmospheric deposition of lead in remote high mountain of eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Atmos Environ 99:425–435
Bowman WD, Bahn L, Damm M (2003) Alpine landscape variation in foliar nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations and the relation to soil nitrogen and phosphorus availability. Arct Antarct Alp Res 35:144–149
Brookes P, Powlson D, Jenkinson D (1982) Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 14:319–329
Burns RG, DeForest JL, Marxsen J, Sinsabaugh RL, Stromberger ME, Wallenstein MD, Weintraub MN, Zoppini A (2013) Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 58:216–234
Clarholm M (1993) Microbial biomass P, labile P, and acid phosphatase activity in the humus layer of a spruce forest, after repeated additions of fertilizers. Biol Fertil Soils 16:287–292
Clemmensen KE, Bahr A, Ovaskainen O, Dahlberg A, Ekblad A, Wallander H, Stenlid J, Finlay RD, Wardle DA, Lindahl BD (2013) Roots and associated fungi drive long-term carbon sequestration in boreal forest. Science 339:1615–1618
Cleveland CC, Liptzin D (2007) C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 85:235–252
Colman AS, Blake RE, Karl DM, Fogel ML, Turekian KK (2005) Marine phosphate oxygen isotopes and organic matter remineralization in the oceans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:13023–13028
Colvan SR, Syers JK, O’Donnell AG (2001) Effect of long-term fertiliser use on acid and alkaline phosphomonoesterase and phosphodiesterase activities in managed grassland. Biol Fertil Soils 34:258–263
Condron LM, Turner BL, Cade-Menun BJ, Sims J, Sharpley A (2005) Chemistry and dynamics of soil organic phosphorus. In: Sims JT, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 87–121
Cotrufo MF, Wallenstein MD, Boot CM, Denef K, Paul E (2013) The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob Chang Biol 19:988–995
Cotrufo MF, Soong JL, Horton AJ, Campbell EE, Haddix ML, Wall DH, Parton WJ (2015) Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat Geosci 8:776–779
Courchesne F, Turmel M (2006) Extractable Al, Fe, Mn, and Si. In: Cartery MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. Canadian Society of Soil Science, Boca Raton, pp 307–316
Crews TE, Kitayama K, Fownes JH, Riley RH, Herbert DA, Muellerdombois D, Vitousek PM (1995) Changes in soil-phosphorus fractions and ecosystem dynamics across a long chronosequence in Hawaii. Ecology 76:1407–1424
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
García C, Hernández T, Costa C, Ceccanti B, Masciandaro G, Ciardi C (1993) A study of biochemical parameters of composted and fresh municipal wastes. Bioresour Technol 44:17–23
Göransson H, Olde Venterink H, Bååth E (2011) Soil bacterial growth and nutrient limitation along a chronosequence from a glacier forefield. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1333–1340
Gressel N, McColl JG, Preston CM, Newman RH, Powers RF (1996) Linkages between phosphorus transformations and carbon decomposition in a forest soil. Biogeochemistry 33:97–123
Gross A, Angert A (2015) What processes control the oxygen isotopes of soil bio-available phosphate? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 159:100–111
Heuck C, Weig A, Spohn M (2015) Soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 85:119–129
Hoppe H-G, Ullrich S (1999) Profiles of ectoenzymes in the Indian Ocean: phenomena of phosphatase activity in the mesopelagic zone. Aquat Microb Ecol 19:139–148
Iwg W (2006) World reference base for soil resources 2006—a framework for international classification, correlation and communication. World soil resources reports food and agriculture organization of the United Nations, Rome, p 128
Jenkinson DS, Brookes PC, Powlson DS (2004) Measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 36:5–7
Johnson AH, Frizano J, Vann DR (2003) Biogeochemical implications of labile phosphorus in forest soils determined by the Hedley fractionation procedure. Oecologia 135:487–499
Juma N, Tabatabai M (1978) Distribution of phosphomonoesterases in soils. Soil Sci 126:101–108
Kirkby CA, Kirkegaard JA, Richardson AE, Wade LJ, Blanchard C, Batten G (2011) Stable soil organic matter: a comparison of C:N:P:S ratios in Australian and other world soils. Geoderma 163:197–208
Kirkby CA, Richardson AE, Wade LJ, BattenB GD, Blanchard C, Kirkegaard JA (2013) Carbon-nutrient stoichiometry to increase soil carbon sequestration. Soil Biol Biochem 60:77–86
Landi L, Renella G, Moreno J, Falchini L, Nannipieri P (2000) Influence of cadmium on the metabolic quotient, L-:D-glutamic acid respiration ratio and enzyme activity: microbial biomass ratio under laboratory conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 32:8–16
Li X, **ong S (1995) Vegetation primary succession on glacier foreland in Hailuogou, Mt. Gongga. Mount Res 12:109–115 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Z, He Y, Yang X, Theakstone WH, Jia W, Pu T, Liu Q, He X, Song B, Zhang N, Wang S, Du J (2010) Changes of the Hailuogou glacier, Mt. Gongga, China, against the background of climate change during the Holocene. Quat Int 218:166–175
Li L, Liang X, Ye Y, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, ** Y, Yuan J, Chen Y (2015) Effects of repeated swine manure applications on legacy phosphorus and phosphomonoesterase activities in a paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 51:167–181
Liebisch F, Keller F, Huguenin-Elie O, Frossard E, Oberson A, Bünemann E (2014) Seasonal dynamics and turnover of microbial phosphorusin a permanent grassland. Biol Fertil Soils 50:465–475
Liu E, Shen J, Zhang E, Wu Y, Yang L (2010) A geochemical record of recent anthropogenic nutrient loading and enhanced productivity in Lake Nansihu, China. J Paleolimnol 44:15–24
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193:696–704
Maynard DG, Curran MP (2006) Soil density measurement in forest soils. In: Cartery MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. Canadian Society of Soil Science, Boca Raton, pp 863–869
McGill WB, Cole CV (1981) Comparative aspects of cycling of organic C, N, S and P through soil organic matter. Geoderma 26:267–286
Mori T, Ohta S, Ishizuka S, Konda R, Wicaksono A, Heriyanto J (2014) Phosphorus application reduces N2O emissions from tropical leguminous plantation soil when phosphorus uptake is occurring. Biol Fertil Soils 50:45–51
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nannipieri P, Johnson RL, Paul EA (1978) Criteria for measurement of microbial growth and activity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 10:223–229
Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Landi L, Renella G (2011) Role of phosphatase enzymes in soil. In: Bünemann E, Oberson A, Frossard E (eds) Phosphorus in action: biological processes in soil phosphorus cycling. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–243
Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Renella G, Puglisi E, Ceccanti B, Masciandaro G, Fornasier F, Moscatelli MC, Marinari S (2012) Soil enzymology: classical and molecular approaches. Biol Fertil Soils 48:743–762
Olander LP, Vitousek PM (2000) Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability. Biogeochemistry 49:175–191
Prietzel J, Dümig A, Wu YH, Zhou J, Klysubun W (2013) Synchrotron-based P K-edge XANES spectroscopy reveals rapid changes of phosphorus speciation in the topsoil of two glacier foreland chronosequences. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 108:154–171
Ratliff TJ, Fisk MC (2016) Phosphatase activity is related to N availability but not P availability across hardwood forests in the northeastern United States. Soil Biol Biochem 94:61–69
Šantrůčková H, Vrba J, Picek T, Kopáček J (2004) Soil biochemical activity and phosphorus transformations and losses from acidified forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1569–1576
Schütz K, Nagel P, Vetter W, Kandeler E, Ruess L (2009) Flooding forested groundwater recharge areas modifies microbial communities from top soil to groundwater table. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:171–182
Sinsabaugh RL, Shah JJF (2012) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 43:313–343
Sinsabaugh RL, Hill BH, Shah JJF (2009) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 462:795–798
Šnajdr J, Valášková V, Merhautová V, Herinková J, Cajthaml T, Baldrian P (2008) Spatial variability of enzyme activities and microbial biomass in the upper layers of Quercus petraea forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2068–2075
Spohn M, Kuzyakov Y (2013) Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol Biochem 61:69–75
Spohn M, Novák TJ, Incze J, Giani L (2015a) Dynamics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in calcareous soils after land-use abandonment—a chronosequence study. Plant Soil:1-12
Spohn M, Treichel NS, Cormann M, Schloter M, Fischer D (2015a) Distribution of phosphatase activity and various bacterial phyla in the rhizosphere of Hordeum vulgare L. depending on P availability. Soil Biol Biochem 89:44–51
Stone M, DeForest J, Plante A (2014) Changes in extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community structure with soil depth at the Luquillo Critical Zone Observatory. Soil Biol Biochem 75:237–247
Tabatabai M (1994) Soil enzymes. In: Hart SC, Stark JM, Davidson EA, Firestone MK (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2: microbiological and biochemical properties. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 775–833
Tiessen H, Moir J (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. Canadian Society of Soil Science, Boca Raton, pp 293–305
Turner BL, Wright SJ (2014) The response of microbial biomass and hydrolytic enzymes to a decade of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium addition in a lowland tropical rain forest. Biogeochemistry 117:115–130
Turner BL, Condron LM, Richardson SJ, Peltzer DA, Allison VJ (2007) Soil organic phosphorus transformations during pedogenesis. Ecosystems 10:1166–1181
Vincent AG, Schleucher J, Grobner G, Vestergren J, Persson P, Jansson M, Giesler R (2012) Changes in organic phosphorus composition in boreal forest humus soils: the role of iron and aluminium. Biogeochemistry 108:485–499
Waldrop MP, Balser TC, Firestone MK (2000) Linking microbial community composition to function in a tropical soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1837–1846
Walker T, Syers J (1976) The fate of phosphorus during pedogenesis. Geoderma 15:1–19
Wang S, Ye J, Gong D (1998) Climate in China during the Little Ice Age. Quat Sci 18:54–64 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang J, Pan B, Zhang G, Cui H, Cao B, Geng H (2013a) Late Quaternary glacial chronology on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain, eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Sci China Earth Sci 56:354–365
Wang S, Fan J, Song M, Yu G, Zhou L, Liu J, Zhong H, Gao L, Hu Z, Wu W, Song T (2013b) Patterns of SOC and soil 13C and their relations to climatic factors and soil characteristics on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 363:243–255
Wardle D (1992) A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biol Rev 67:321–358
Wardle DA, Walker LR, Bardgett RD (2004) Ecosystem properties and forest decline in contrasting long-term chronosequences. Science 305:509–513
Wood T, Bormann F, Voigt G (1984) Phosphorus cycling in a northern hardwood forest: biological and chemical control. Science 223:391–393
Wu J, He Z, Wei W, O’Donnell AG, Syers JK (2000) Quantifying microbial biomass phosphorus in acid soils. Biol Fertil Soils 32:500–507
Wu Y, Ding N, Wang G, Xu J, Wu J, Brookes PC (2009) Effects of different soil weights, storage times and extraction methods on soil phospholipid fatty acid analyses. Geoderma 150:171–178
Wu Y, Li W, Zhou J, Cao Y (2013) Temperature and precipitation variations at two meteorological stations on eastern slope of Gongga Mountain, SW China in the past two decades. J Mount Sci 10:370–377
Wynn JG, Harden JW, Fries TL (2006) Stable carbon isotope depth profiles and soil organic carbon dynamics in the lower Mississippi Basin. Geoderma 131:89–109
Yang X, Post WM (2011) Phosphorus transformations as a function of pedogenesis: a synthesis of soil phosphorus data using Hedley fractionation method. Biogeosciences 8:2907–2916
Yang Y, Wang G, Shen H, Yang Y, Cui H, Liu Q (2014) Dynamics of carbon and nitrogen accumulation and C:N stoichiometry in a deciduous broadleaf forest of deglaciated terrain in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. For Ecol Manag 312:10–18
Yang Z, Bing H, Zhou J, Wu Y, Sun H, Luo J, Sun S, Wang J (2015) Variation of mineral composition along the soil chronosequence at the Hailuogou glacier foreland of Gongga Mountain. Acta Pedol Sin 52:39–48
Yoshitake S, Uchida M, Koizumi H, Nakatsubo T (2007) Carbon and nitrogen limitation of soil microbial respiration in a High Arctic successional glacier foreland near Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Polar Res 26:22–30
Zhang H, Shi L, Wen D, Yu K (2016) Soil potential labile but not occluded phosphorus forms increase with forest succession. Biol Fertil Soils 52:41–51
Zhou J, Wu Y, Prietzel J, Bing H, Yu D, Sun S, Luo J, Sun H (2013) Changes of soil phosphorus speciation along a 120-year soil chronosequence in the Hailuogou Glacier retreat area (Gongga Mountain, SW China). Geoderma 195:251–259
Acknowledgments
This research was co-funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41272200 and 41401253).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1231 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wu, Y., Zhou, J. et al. Carbon demand drives microbial mineralization of organic phosphorus during the early stage of soil development. Biol Fertil Soils 52, 825–839 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1123-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1123-7