Abstract
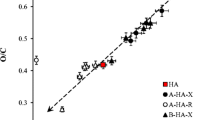
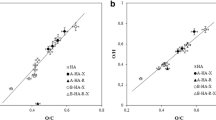
Changes in molecular size distributions of four different humic materials were evaluated through high performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC), before and after treating humic solutions with naturally occurring dicarboxylic (oxalic, malonic, succinic and glutaric) acids. Chromatograms of dissolved humic substances showed a decrease in peak absorbance as well as an increase in peak elution volume when the solution pH was lowered from 7 to 3.5 by addition of dicarboxylic acids before HPSEC analysis. The resulting reduction in molecular size is explained by the disruption of unstable humic superstructures into smaller-sized associations stabilized by the formation of strong intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds among humic molecules. The extent of humic size variation was in the order: oxalic<malonic<succinic<glutaric acid. Dicarboxylic acids with an increasing number of C atoms and pKas, had progressively larger degrees of protonation which increasingly reduced the electrostatic repulsion from humic molecules. The less dissociated dicarboxylic acids enabled a closer contact with the hydrophobic domains of weakly bound humic superstructures and produced more extensive conformational rearrangements. Recognition of a process controlling the conformational structure of humic molecules by organic acids exuded in the soil solution by either plant roots or soil microbes may be important in understanding the role of humus in soil-plant interactions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Yosef B (1991) Root excretions and their environmental effects. Influence on availability of phosphorous. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant roots. The hidden half. Dekker, New York, pp 529–557
Conte P, Piccolo A (1999) Conformational arrangement of dissolved humic substances. Influence of solution composition on association of humic molecules. Environ Sci Technol 33:1682–1690
Conte P, Piccolo A, van Lagen B, Buurman P, Hemminga MA (2002) Elemental quantitation of natural organic matter by CPMAS 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 21:158–170
Cozzolino A, Conte P, Piccolo A (2001) Conformational changes of humic substances induced by some hydroxy-, keto-, and sulfonic acids. Soil Biol Biochem 33:563–571
Junk AO (1991) Dynamics of nutrient movement at the soil-root interface. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (eds) Plant roots. The hidden half. Dekker, New York, pp 455–481
Müller MB, Schmitt D, Frimmel FH (2000) Fractionation of natural organic matter by size-exclusion chromatography. Properties and stability of fractions. Environ Sci Technol 34:4867–4872
Nardi S, Panuccio MR, Abenavoli MR, Muscolo A (1994) Auxin-like effect of humic substances extracted from faeces of Allolobophora caliginosa and Antennaria rosea. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1341–1346
Nardi S, Concheri G, Dell'Agnola G (1996) Biological activity of humus. In: Piccolo A (ed) Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 361–406
O'Donnell RW (1973) The auxin-like effect of humic preparations from leonardite. Soil Sci 116:106–112
Ohwaki Y, Hirata H (1992) Differences in carboxylic acid exudation among P-starved leguminous crops in relation to carboxylic acid contents in plant tissues and phospholipid level in roots. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 38:235–243
Piccolo A (2001) The supramolecular structure of humic substances. Soil Sci 166:810–832
Piccolo A (2002) The supramolecular structure of humic substances. A novel understanding of humus chemistry and implications in soil science. Adv Agron 75:57–134
Piccolo A, Nardi S, Concheri G (1992) Structural characteristics of humic substances as related to nitrate uptake and growth regulation in plant systems. Soil Biol Biochem 24:373–380
Piccolo A, Conte P, Cozzolino A (1999) Conformational association of dissolved humic substances as affected by interactions with mineral and monocarboxylic acids. Eur J Soil Sci 50:687–694
Piccolo A, Conte P, Cozzolino A (2001a) Differences in high performance size-exclusion chromatography between humic substances and macromolecular polymers. In: Gabbhour EA, Davies G (eds) Humic substances. Versatile components of plant, soils and water. Royal Society of Chemistry, special publication no. 259. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 111–124
Piccolo A, Conte P, Cozzolino A (2001b) A chromatographic and spectrophotometric study of dissolved humic substances as compared to macromolecular polymers. Soil Sci 166:174–185
Piccolo A, Conte P, Cozzolino A, Spaccini R (2001c) Molecular sizes and association forces of humic substances in solution. In: Clapp CE, Hayes MHB, Senesi N, Bloom P, Jardine PM (eds) Humic substances and chemical contaminants. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wis., pp 89–118
Piccolo A, Conte P, Trivellone E, van Lagen B, Buurman P (2002) Reduced heterogeneity of a lignite humic acid by preparative HPSEC following interaction with an organic acid. Characterization of size separates by PYR-GC-MS and 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36:76–84
Pinton R, Varanin Z, Nannipieri P (2001) The rhizosphere as a site of biochemical interactions among soil components, plants, and microorganisms. In: Pinton R, Varanini Z, Nannipieri P (eds) The rhizosphere at the soil-plant interface. Dekker, New York, pp 1–17
Schwarzenbach RP, Gschwend PM, Imboden DM (1993) Environmental Organic Chemistry. Wiley, New York
Smeulders DE, Wilson MA, Kamali Kannagara GS (2001) Host-guest interactions in humic materials. Org Geochem 32:1357–1371
Smidova M (1960) The Influence of humic acid on the respiration of plant roots. Biol Plants 2:152–164
Tanford C (1991) The hydrophobic effect: formation of micelles and biological membranes. Krieger, Malabar, Fla.
Tyler M, Ström C (1995) Differing organic acid exudation pattern explains calcifuge and acidfuge behaviour of plants. Ann Bot 75:75–78
Varanini Z, Pinton R (2001) Direct versus indirect effects of soil humic substances on plant growth and nutrition. In: Pinton R, Varanini Z, Nannipieri P (eds) The rhizosphere at the soil-plant interface. Dekker, New York, pp 141–157
Vaughan D, Linehan DJ (1976) The growth of wheat plants in humic acid solution under axenic conditions. Plant Soil 44:445–449
Vaughan D, Malcolm RE (1985) Soil organic matter and biological activity. Nijhoff, Dordrecht
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MIUR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piccolo, A., Conte, P., Spaccini, R. et al. Effects of some dicarboxylic acids on the association of dissolved humic substances. Biol Fertil Soils 37, 255–259 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0583-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0583-8