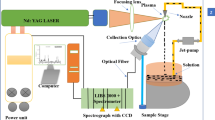
Abstract
In order to prove the feasibility of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) in measuring toxic metals Cr in water solution, a series of potassium bichromate standard solutions were prepared in the lab. The characteristic line intensity of Cromium (Cr) element at 357.87, 359.35, 360.53, 425.43, 427.48, and 428.97 nm was taken to build up the correlation with concentration. The indexes of relative standard deviation, intercept, slope, R 2 (coefficient of determination), and root mean square error of calibration were selected to verify the precision and accuracy of models. The comprehensive results showed that the 425.43 nm line had better superiority than other lines. And the detection limit of 6 ug/ml and repeatability of 3 % are reported. To improve the model accuracy further, the intensity ratio of single 425.43 nm line to the whole spectrum was extracted. And a linear relationship between the intensity ratio and the element Cr concentration was constructed. The results demonstrated the intensity ratio calibration had better accuracy than single line calibration, especially after smoothing. To verify the accuracy of prediction, the 100 ug/ml concentration sample was used as prediction sample. The relative error values are 13.2, 11.7, and 10.8 % for single line calibration, intensity ratio calibration with raw data, and by use of smooth processing data, respectively. The results further indicated that the intensity ratio calibration improved the accuracy of measurement than single line calibration. It is worth mentioning that the application of LIBS aiming the direct analysis of heavy metals in water is a great challenge that still needs efforts for its development and validation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.N. Husaini, J.H. Zaidi, Matiullah, M. Akram, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 289, 203 (2011)
A.N. Anthemidis, K.I.G. Ioannou, Talanta 79, 86 (2009)
D. Chen, H. Bin, C. Huang, Talanta 78, 491 (2009)
Z. Wang, L. Li, L. West, Z. Li, Spectrochim. Acta. Part B 68, 58 (2012)
T. Hussain, M.A. Gondal, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 80, 561 (2008)
S. Christopher, P. **ao Fang, Appl. Phys. A 103, 1131 (2011)
M. Sadegh Cheri, S.H. Tavassoli, Appl. Opt. 50, 1227 (2011)
F.A. Barreda, F. Trichard, S. Barbier, N. Gilon, L.S. Jalmes, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00216-012-6019-2
M.E. Sadat, A.F.M.Y. Haider, J. Bangladesh Acad. Sci. 34, 123 (2010)
S. Koch, W. Garen, Appl. Phys. A 79, 1071 (2004)
N.K. Rai, A.K. Rai, J. Hazard. Mater. 150, 835 (2008)
N.K. Rai, A.K. Rai, Appl. Opt. 47, 105 (2008)
X. Fang, S.R. Ahmad, Appl. Phys. B 106, 453 (2012)
R. Kumar, A.K. Rai, Environ. Monit. Assess. (2012). doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2541-0
Z. Chen, H. Li, M. Liu, R. Li, Spectrochim. Acta. Part B 63, 64 (2008)
F. Zhao, Z. Chen, F. Zhang, R. Li, J. Zhou, Anal. Methods 2, 408 (2010)
D.M. Díaz Pace, C.A. D’Angelo, Spectrochim. Acta. Part B 61, 929 (2006)
J.O. Cáceres, J. Tornero López, Spectrochim. Acta. Part B 56, 831 (2001)
M. Yao, J. Lin, M. Liu, Y. Xu, Appl. Opt. 51, 1552 (2012)
Y. Xu, M. Yao, L. Muhua, L. Zejian, P. Qiumei, X. Zhang, T. Chen, Acta. Optica. Sinica. 31, 282 (2011)
L. Li, Z. Wang, T. Yuan, Z. Hou, Z. Li, W. Ni, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 26, 2274 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank National Natural Science Foundation of China for their supports on this paper (No. 30972052). This work was partially supported by the Jiangxi Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2010BSA19600). Additional support was provided by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. 090168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Yao, M., Xu, Y. et al. Determination of Cr in water solution by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with different univariate calibration models. Appl. Phys. B 111, 45–51 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5305-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5305-1