Abstract
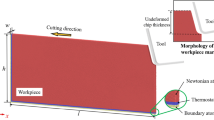
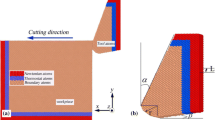
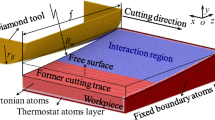
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of nanometric-cutting copper are conducted to study the critical rake angle during the cutting process. A new approach based on the maximum displacement of atoms in cutting direction is proposed to estimate the chip formation in MD simulation. It is found that the minimum rake angle for chip formation is −65∘–(−70∘) and the subsurface deformations of copper are mostly the dislocation and stacking faults. Three-dimensional simulation results show that the effective rake angle of stagnation region is constant with the same depth of cut. According to the limited depth of cut of copper can be achieved, the available minimum tool edge radius is suggested to be not less than 10 nm.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.J. Yuan, M. Zhou, S. Dong, Effect of diamond tool sharpness on minimum cutting thickness and cutting surface integrity in ultraprecision machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 62, 327 (1996)
M. Malekian, M.G. Mostofa, S.S. Park, M.B. Jun, Modeling of minimum uncut chip thickness in micro machining of aluminum. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 553 (2012)
X. Liu, R.E. Devor, S.G. Kapoor, An analytical model for the prediction of minimum chip thickness in micromachining. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 128, 474 (2006)
S.M. Son, H.S. Lim, J.H. Ahn, Effects of the friction on the minimum cutting thickness in micro cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 45, 529 (2005)
X.M. Lai, H.T. Li, C.F. Lin, Z.Q. Lin, J. Ni, Modeling and analysis of micro scale milling considering size effect micro cutter edge radius and minimum chip thickness. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 48, 1 (2007)
S. Shimada, N. Ikawa, H. Tanaka, G. Ohmori, J. Uchikoshi, Feasibility study on ultimate accuracy in microcutting using molecular dynamics simulation. CIRP Ann. 42(1), 117 (1993)
R. Komanduri, Some aspects of machining with negative rake tools simulating grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tool Des. Res. 11, 223 (1971)
R. Komanduri, N. Chandrasekaran, L.M. Raff, Effect of tool geometry in nanometric cutting: A molecular dynamics simulation approach. Wear 219, 97 (1998)
R. Komanduri, N. Chandrasekaran, L.M. Raff, Some aspects of machining with negative-rake tools simulating grinding a molecular dynamics simulation approach. Philos. Mag., B 79(7), 955 (1999)
F.Z. Fang, V.C. Venkatesh, Diamond cutting of silicon with nanometric finish. CIRP Ann. 47, 45 (1998)
F.Z. Fang, G.X. Zhang, An experimental study of edge radius effect on cutting single crystal silicon. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 22, 703 (2003)
F.Z. Fang, H. Wu, Y.C. Liu, Modeling and experimental investigation on nanometric cutting of monocrystalline silicon. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 45, 1681 (2005)
F.Z. Fang, H. Wu, W. Zhou, X.T. Hu, A study on mechanism of nano-cutting single crystal silicon. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 184, 407 (2007)
Q.X. Pei, C. Lu, H.P. Lee, Large scale molecular dynamics study of nanometric machining of copper. Comput. Mater. Sci. 41, 177 (2007)
C.L. Kelchner, S.J. Plimpton, J.C. Hamilton, Dislocation nucleation and defect structure during surface indentation. Phys. Rev. B 58(17), 11085 (1998)
Z.G. Zhang, F.Z. Fang, X.T. Hu, Three-dimensional molecular dynamics modeling of nanocutting. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 27(3), 1340 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the support of the State Key Development Program of Basic Research of China (“973” Project Grant No. 2011CB706703), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 90923038 and 90923024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, M., Zhang, X.D. & Fang, F.Z. Study on critical rake angle in nanometric cutting. Appl. Phys. A 108, 809–818 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6973-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6973-8