Abstract
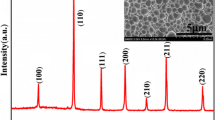
Complex impedance analysis of perovskite structured polycrystalline, [Bi0.5(Na1−x−y K x Li y )0.5]TiO3, at x=0.2, y=0.1 ceramic was synthesized by a mixed oxide method. The formation of single-phase material was confirmed by X-ray studies, and it was found to be rhombohedral structure at room temperature. Under scanning electron microscope, grains separated by well-defined boundaries are visible, which is in good agreement with impedance analysis. The BNKLT ceramic shows excellent piezoelectric properties and the optimum properties measured are: d 33=251 pC/N, g 33=24×10−3 mV/N, k p =30.5% and k t =28.1%. A complex impedance spectroscopy (CIS) study has been carried out to investigate the electrical properties. Impedance and modulus plots helped to separate the grain and grain boundary to the overall polarization or electrical behavior. CIS analysis suggests the presence of temperature-dependent relaxation process in the material. A possible hop** mechanism for electrical transport processes in the studied material is evident from the modulus analysis. The modulus mechanism indicates the non-Debye type of conductivity relaxation in the materials, which is supported by impedance data. The activation energies have been calculated from impedance (E τ =0.58 eV) and electric modulus (E τ =0.40 eV) studies, which suggests that the conduction is ionic in nature. The variation in width of the curves, \(M''/M''_{\max}\) and \(Z''/Z''_{\max}\) at FWHM, allows to conform that the relaxation process involved is of non-Debye type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.D. Megaw, Ferroelectricity in Crystals (Methun, London, 1957)
W.G. Cady, Piezoelectricity (Dover Publication, New York, 1962)
J.C. Burfoot, Ferroelectrics (Van Nostrand, New York, 1967)
M. Deri, Ferroelectric Ceramics (Gordon & Breach, New York, 1969)
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook Jr., H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics (Academic Press, London, 1971)
S.B. Lang, Sourcebook of Pyroelectricity (Gordon and Breach, New York, 1974)
R.E. Newnham, Structure–Property Relations (Springer, New York, 1975)
T. Mitsui, I. Tatsuzaki, E. Nakamura, An Introduction to the Physics of Ferroelectrics (Gordon & Breach, London, 1976)
M.E. Lines, A.M. Glass, Principles and Applications of Ferroelectric and Related Materials (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1977)
J.M. Herbert, Ferroelectric Transducers and Sensors (Gordon & Breach, London, 1982)
R.C. Buchanan (ed.), Ceramic Materials for Electronics-Processing, Properties and Applications (Dekker, New York, 1986)
L.M. Levinson (ed.), Electronic Ceramics-Properties, Devices and Applications (Dekker, New York, 1987)
A.J. Moulson, J.M. Herbert, Electroceramics, Materials, Properties and Applications (Chapman & Hall, London, 1990)
J.F. Nye, Physical Properties of Crystals (Clarendon, Oxford, 1990)
Y. Xu, Ferroelectric Materials and their Applications (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991)
G.H. Haertling, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(4), 797 (1999)
J. Ravez, Solid State Chem. Cryst. Chem. 3, 267 (2000)
J.F. Scott, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57(10), 1439 (1996)
T. Takennaka, K. Maruyama, K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. I 30, 2236 (1991)
J. Yoo, D. Oh, Y. Jeong, J. Hong, M. Jung, Mater. Lett. 58, 3821 (2004)
H. Ishii, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 5660 (2001)
T. Takenaka, T. Okuda, K. Takegahara, Ferroelectrics 196, 175 (1997)
H. Nagata, N. Koizumi, T. Takenaka, Key Eng. Mater. 37, 169 (1999)
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya, E. Otsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5564 (1999)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978)
J. Suchanicz, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 55, 114–118 (1998)
J. Plocharski, W. Wieczoreck, Solid State Ion. 28, 979–982 (1988)
S.P. Singh, A.K. Singh, D. Pandey, J. Mater. Res. 18, 1 (2003)
M.A.L. Nobtre, S. Lanfredi, Matter. Lett. 47, 362 (2001)
M.A.L. Nobtre, S. Lanfredi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 451 (2002)
S. Sen, P. Pramanik, R.N.P. Choudhary, Appl. Phys. A 82, 549 (2006)
M.M. Kumar, Z.G. Ze, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 934 (2001)
M.A.L. Nobtre, S. Lanfredi, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 2457 (2003)
P.L. Bonora, F. Deflorian, L. Fedrizzi, Electrochim. Acta 41, 1073 (1996)
S. Dutta, R.N.P. Choudhary, R.K. Sinha, Ceram. Int. 33, 13 (2007)
K. Prasad, K.L. Kumari, K.P. Chandra, K.L. Yadav, S. Sen, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 88, 377 (2007)
K. Sambasiva Rao, P. Murali Krishna, D. Madhava Prasad, J.H. Lee, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 1231 (2009)
I.M. Hogde, M.D. Ingram, A.R. West, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 58, 429 (1975)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850 (1989)
S.K. Barik, R.N.P. Choudhary, P.K. Mahapatra, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 88, 217–222 (2007)
G. Williams, D.C. Watts, Trans. Faraday Soc. 66, 80 (1970)
C.T. Moynihan, L.P. Boesch, N.L. Laberge, J. Phys. Chem. 78, 122 (1974)
M.M. Kumar, Z.G. Ze, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 934 (2001)
K.S. Cole, R.H. Cole, J. Chem. Phys. 9, 341 (1941)
S. Dundarakannan, K. Kakimoto, H. Ohsato, J. Appl. Phys. 9, 5182 (2003)
S. Bu, D. Chun, G. Park, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 31, 223 (1997)
R. Gerhardt, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 55(12), 1491 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varada Rajulu, K.C., Tilak, B. & Sambasiva Rao, K. Impedance spectroscopy study of BNKLT polycrystalline ceramic. Appl. Phys. A 106, 533–543 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6631-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6631-6