Abstract
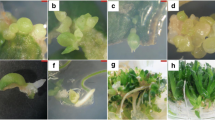
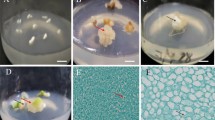
A highly efficient somatic embryo production and maturation procedure has been developed to regenerate plantlets from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). This procedure involves the acceleration of differentiation through manipulations of nutrient and microenvironment conditions. Embryogenic calli, initiated from hypocotyls or cotyledonary leaf sections on MS medium containing 0.1 mg/l 2,4 dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 0.5 mg/l kinetin, and 3% maltose produced globular-stage somatic embryos when transferred to hormone-free MS medium supplemented with high concentrations of nitrate. Subculture of globular embryos on hormone-free MS medium led to the development of torpedo- and cotyledonary-stage at a low frequency (two to four per plate) with the majority of embryos lacking further growth or entering into the dedifferentiation stage. Significant improvement in embryogenesis (two- to threefold) was achieved when calli were cultured on 1/5-strength MS medium irrespective of stress treatment. However, the frequency of globular embryos develo** into normal plantlets improved considerably (20–24 per plate) when cultured on filter paper placed on MS medium. In this procedure, about 33% of globular embryos not only developed into the cotyledonary stage but rooted simultaneously, eliminating a separate rooting step. More than 70% of cotyledonary embryos developed into normal plantlets when cultured on full- strength MS medium containing 0.05 mg/l gibberellic acid.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D :
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
- Fp :
-
Filter paper
- GA 3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- Kn :
-
Kinetin
- M :
-
Micropore sealing tape
- P :
-
Parafilm
References
Beasley CA, Ting IP (1973) The effects of plant growth substances on in vitro fiber development from fertilized cotton ovules. Am J Bot 60:130–139
Benedict JH, Altman DW (2001) Commercialization of transgenic cotton expressing insecticidal crystal protein. In: Jenkins JN, Saha S (eds) Genetic improvement of cotton. USDA- ARS, Oxford & IBH, New Delhi, pp 136–201
Cousins YL, Lyon BR, Llewellyn DJ (1991) Transformation of an Australian cotton cultivar: Prospects for cotton through genetic engineering. Aust J Plant Physiol 18:481–494
Davidonis GH, Hamilton RH (1983) Plant regeneration from callus tissue of Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Sci Lett 32:89–93
Finer JJ (1988) Plant regeneration from somatic embryogenic suspension cultures of cotton. Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Cell Rep 7:399–402
Firoozabady E, DeBoer DL (1993) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in many cultivars of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 29P:166–173
Firoozabady E, DeBoer DL, Merlo DJ, Halk EL, Amerson LN, Rashka KE, Murray EE (1987) Transformation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and regeneration of transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 10:105–116
Gawel NJ, Robacker CD (1990) Genetic control of somatic embryogenesis in cotton petiole callus cultures. Euphytica 49:249–253
Gawel NJ, Rao AP, Robacker CD (1986) Somatic embryogenesis from leaf and petiole callus cultures of Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Cell Rep 5:457–459
Ghosh-Biswas GC, Zapata FJ (1993) High frequency plant regeneration from protoplasts of indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) using maltose. J Plant Physiol 141:470–475
Gould J, Banister S, Hasegawa O, Fahima M, Smith RH (1991) Regeneration of Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbedense from shoot apex tissues for transformation. Plant Cell Rep 10:12–16
Kumar S, Pental D (1998) Regeneration of Indian cotton variety MCU-5 through somatic embryogenesis. Curr Sci 74:538–540
Merkle SA, Parrot WA, Flinn BS (1995) Morphogenic aspects of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 155–203
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:474–497
Price HJ, Smith RH (1979) Somatic embryogenesis in suspension cultures of Gossypium klotzschianum Anders. Planta 145:305–307
Rajasekaran K (1996) Regeneration of plants from cryopreserved embryogenic cell suspension and callus cultures of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Rep 15:859–864
Rangan TS (1993) Regeneration of cotton. USA patent no. 5,244,802
Rangan TS, Rajasekaran K (1996) Regeneration of cotton plant in suspension culture. USA patent no. 5,583,036
Saito T, Nishizawa S, Nishimura S (1991) Improved culture conditions for somatic embryogenesis from Asparagus officinalis L. using an aseptic ventilative filter. Plant Cell Rep 10:230–234
Shoemaker RC, Couche LJ, Galbraith DW (1986) Characterization of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Rep 3:178–181
Smith R, Price HJ, Thaxton JR (1977) Defined conditions for the initiation and growth of cotton callus in vitro. I. Gossypium arboreum. In vitro Cell Dev Biol 13:329–334
Trolinder NL, Goodin JR (1987) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Rep 6:231–234
Trolinder NL, Goodin JR (1988a) Somatic embryogenesis in cotton (Gossypium). I. Effects of source of explant and hormone regime. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 12:178–181
Trolinder NL, Goodin JR (1988b) Somatic embryogenesis in cotton (Gossypium). II. Requirements for embryo development and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 12:43–53
Trolinder NL, Xhixian C (1989) Genotype specificity of the somatic embryogenesis response in cotton. Plant Cell Rep 8:133–136
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the Maharashtra State Seed Corporation is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Uchimiya
RK and VGS contributed equally to this investigation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumria, R., Sunnichan, V.G., Das, D.K. et al. High-frequency somatic embryo production and maturation into normal plants in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) through metabolic stress. Plant Cell Rep 21, 635–639 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-002-0554-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-002-0554-9