Abstract
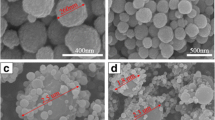
Oleic acid-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) encapsulated within poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) particles were prepared by the w/o/w emulsion technique using poly(vinyl alcohol) as a dispersant. The concentration of PLGA in the oil phase was varied (5, 15, 30, 45, and 60 mg/ml) at constant magnetite concentration in the oil phase (5 mg/ml) to study the properties of composite Fe3O4–PLGA nanoparticles. Even though PLGA concentration varied widely in the oil phase, the weight percent of 7–16 nm diameter magnetite in the particles varied only from 56 to 62 % (23–28 vol.%). The obtained composite nanoparticles were essentially spherical with magnetite spatially uniformly dispersed in individual PLGA particles, as measured by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Also, the magnetite concentration in each particle did not vary widely as determined qualitatively via microscopy. Hydrodynamic diameters of the composite nanoparticles as measured by dynamic light scattering increased by approximately 10 % with added magnetite, with a smaller relative increase in diameter measured by TEM. The zeta potential of the particles was about −26 mV, independent of Fe3O4 loading. Relatively high saturation magnetizations (36–45 emu/g) were measured for these highly loaded particles, with the latter value only 7 emu/g lower than the value measured for the oleic acid-coated particles alone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kluchova K, Zboril R, Tucek J, Pecova M, Zajoncova L, Safarik I, Mashlan M, Markova I, Jancik D, Sebela M, Bartonkova H, Bellesi V, Novak P, Petridis D (2009) Superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles from solid-state synthesis—their functionalization towards peroral MRI contrast agent and magnetic carrier for trypsin immobilization. Biomaterials 30(15):2855–2863. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.02.023
Hong RY, Pan TT, Li HZ (2006) Microwave synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as a precursor of nanocomposites and ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater 303(1):60–68. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.10.230
Chomoucka J, Drbohlavova J, Huska D, Adam V, Kizek R, Hubalek J (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharm Res 62(2):144–149. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2010.01.014
Lee SJ, Jeong JR, Shin SC, Kim JC, Chang YH, Chang YM, Kim JD (2004) Nanoparticles of magnetic ferric oxides encapsulated with poly(d,l latide-co-glycolide) and their applications to magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater 272:2432–2433. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.12.416
Sun C, Lee JSH, Zhang MQ (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Del Rev 60(11):1252–1265. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.018
Wassel RA, Grady B, Kopke RD, Dormer KJ (2007) Dispersion of super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles. Colloid Surf A 292(2–3):125–130. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.06.012
Gaihre B, Khil MS, Lee DR, Kim HY (2009) Gelatin-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as carrier system: drug loading and in vitro drug release study. Int J Pharm 365(1–2):180–189. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.08.020
Hans ML, Lowman AM (2002) Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery and targeting. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 6(4):319–327
Cheng FY, Wang SPH, Su CH, Tsai TL, Wu PC, Shieh DB, Chen JH, Hsieh PCH, Yeh CS (2008) Stabilizer-free poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for multimodal biomedical probes. Biomaterials 29(13):2104–2112. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.01.01
Arnold MM, Gonnan EM, Schieber LJ, Munson EJ, Berkland C (2007) NanoCipro encapsulation in monodisperse large porous PLGA microparticles. J Control Release 121(1–2):100–109. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.05.039
De Stefano D, De Rosa G, Maiuri MC, Ungaro F, Quaglia F, Iuvone T, Cinelli MP, La Rotonda MI, Carnuccio R (2009) Oligonucleotide decoy to NF-kappa B slowly released from PLGA microspheres reduces chronic inflammation in rat. Pharm Res 60(1):33–40. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2009.03.012
Blanco-Prieto MJ, Lecaroz C, Renedo MJ, Kunkova J, Gamazo C (2002) In vitro evaluation of gentamicin released from microparticles. Int J Pharm 242(1–2):203–206
Corrigan OI, Li X (2009) Quantifying drug release from PLGA nanoparticulates. Eur J Pharm Sci 37(3–4):477–485. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2009.04.004
Jain RA (2000) The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 21(23):2475–2490
Okassa LN, Marchais H, Douziech-Eyrolles L, Herve K, Cohen-Jonathan S, Munnier E, Souce M, Linassier C, Dubois P, Chourpa I (2007) Optimization of iron oxide nanoparticles encapsulation within poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) sub-micron particles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 67(1):31–38. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.12.020
Hamoudeh M, Al Faraj A, Canet-Soulas E, Bessueille F, Leonard D, Fessi H (2007) Elaboration of PLLA-based superparamagnetic nanoparticles: characterization, magnetic behaviour study and in vitro relaxivity evaluation. Int J Pharm 338(1–2):248–257. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.01.023
Zhang L, He R, Gu HC (2006) Oleic acid coating on the monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 253(5):2611–2617. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.05.023
Yang J, Park SB, Yoon HG, Huh YM, Haam S (2006) Preparation of poly epsilon-caprolactone nanoparticles containing magnetite for magnetic drug carrier. Int J Pharm 324(2):185–190. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.06.029
Liu ZL, Liu YJ, Yao KL, Ding ZH, Tao J, Wang X (2002) Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Synth Proc 10(2):83–87
Okassa LN, Marchais H, Douziech-Eyrolles L, Cohen-Jonathan S, Souce M, Dubois P, Chourpa I (2005) Development and characterization of sub-micron poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) particles loaded with magnetite/maghemite nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 302(1–2):187–196. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.06.024
Liu XQ, Kaminski MD, Guan YP, Chen HT, Liu HZ, Rosengart AJ (2006) Preparation and characterization of hydrophobic superparamagnetic magnetite gel. J Magn Magn Mater 306(2):248–253. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.03.049
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by National Center of Excellent for Petroleum, Petrochemicals, and Advance Materials, Chulalongkorn University. BPG contributed to this study partly supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grant no. R21-00357540) and the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (Grant no. AR082-009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bootdee, K., Nithitanakul, M. & Grady, B.P. Synthesis and encapsulation of magnetite nanoparticles in PLGA: effect of amount of PLGA on characteristics of encapsulated nanoparticles. Polym. Bull. 69, 795–806 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0773-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0773-3