Abstract
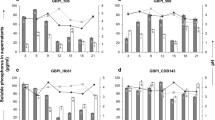
Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria have the ability of solubilizing mineral phosphate in soil and promoting growth of plants, but the activity of phosphate solubilization is influenced by exogenous soluble phosphate. In the present study, the effects of soluble phosphate on the activity of phosphate solubilization, acidification of media, growth, and organic acid secretion of phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2 were investigated under six levels of soluble phosphate conditions. The activity of phosphate solubilization decreased with the increase of soluble phosphate concentration, accompanying with the increase of media pH. However, the growth was promoted by adding soluble phosphate. Production of gluconic, tartaric, and oxalic acids by the strain was reduced with the increase of concentration of soluble phosphate, while acetic and pyruvic acids showed a remarkable increase. Gluconic acid predominantly produced by the strain at low levels of soluble phosphate showed that this acid was the most efficient organic acid in phosphate solubilization. Pyrroloquinoline quinone-glucose dehydrogenase gene gcd (pg5SD2) was cloned from the strain, and the expressions of pg5SD2 gene were repressed gradually with the increase of concentration of soluble phosphate. The soluble phosphate regulating the transcription of the gcd gene is speculated to underlie the regulation of the secretion of gluconic acid and subsequently the regulation of the activity of phosphate solubilization. Future research needs to consider a molecular engineering strategy to reduce the sensitivity of PSB strain to soluble phosphate via modification of the regulatory mechanism of gcd gene, which could improve the scope of PSB strains’ application.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames BN (1966) Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatase. Methods Enzymol 8(1):115–118
Antelmann H, Scharf C, Hecker M (2000) Phosphate starvation-inducible proteins of Bacillus subtilis: proteomics and transcriptional analysis. J Bacteriol 182(16):4478–4490
Arcand MM, Schneider KD (2006) Plant-and microbial-based mechanisms to improve the agronomic effectiveness of phosphate rock: a review. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 78(4):791–807
Barber S, Walker J, Vasey E (1963) Mechanisms for movement of plant nutrients from soil and fertilizer to plant root. J Agric Food Chem 11(3):204–207
Batjes N (1997) A world dataset of derived soil properties by FAO–UNESCO soil unit for global modelling. Soil Use Manag 13(1):9–16
Buch A, Archana G, Naresh Kumar G (2008) Metabolic channeling of glucose towards gluconate in phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas aeruginosa P4 under phosphorus deficiency. Res Microbiol 159(9):635–642
Chen Y, Rekha P, Arun A, Shen F, Lai W-A, Young C (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34(1):33–41
Chhonkar P, Subba-Rao N (1967) Phosphate solubilization by fungi associated with legume root nodules. Can J Microbiol 13(7):749–753
Farhat MB, Fourati A, Chouayekh H (2013) Coexpression of the pyrroloquinoline quinone and glucose dehydrogenase genes from Serratia marcescens CTM 50650 conferred high mineral phosphate-solubilizing ability to Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170(7):1738–1750
Fothergill-Gilmore LA (1986) The evolution of the glycolytic pathway. Trends Biochem Sci 11(1):47–51
Goldstein AH (1986) Bacterial solubilization of mineral phosphates: historical perspective and future prospects. Am J Altern Agric 1:51–57
Goldstein AH (1995) Recent progress in understanding the molecular genetics and biochemistry of calcium phosphate solubilization by Gram negative bacteria. Biol Agric Hortic 12(2):185–193
Goldstein AH (2000) Bioprocessing of rock phosphate ore: essential technical considerations for the development of a successful commercial technology. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Fertilizer Association Technical Conference, IFA, Paris
Goldstein AH, Liu S (1987) Molecular cloning and regulation of a mineral phosphate solubilizing gene from Erwinia herbicola. Nat Biotechnol 5(1):72–74
Huang C-T, Xu KD, McFeters GA, Stewart PS (1998) Spatial patterns of alkaline phosphatase expression within bacterial colonies and biofilms in response to phosphate starvation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(4):1526–1531
Illmer P, Schinner F (1992) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by microorganisms isolated from forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 24(4):389–395
Kang S, Denman SE, Morrison M, Yu Z, McSweeney CS (2009) An efficient RNA extraction method for estimating gut microbial diversity by polymerase chain reaction. Curr Microbiol 58(5):464–471
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2007) Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27(1):29–43
Kim CH, Han SH, Kim KY, Cho BH, Kim YH, Koo BS, Kim YC (2003) Cloning and expression of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) genes from a phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Enterobacter intermedium. Cur Microbiol 47(6):457–461. doi:10.1007/s00284-003-4068-7
Le Saux A, Houdebine LM, Jolivet G (2010) Chromosome integration of BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome): evidence of multiple rearrangements. Trans Res 19(5):923–931. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9368-7
Liu H, Wu XQ, Ren JH, Ye JR (2011) Isolation and identification of phosphobacteria in poplar rhizosphere from different regions of China. Pedosphere 21(1):90–97. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60083-5
Liu Y-G, Huang N (1998) Efficient amplification of insert end sequences from bacterial artificial chromosome clones by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant Mol Biol Rep 16(2):175
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \(2_{ }^{{ - \Delta \Delta C_{T} }}\) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Mander C, Wakelin S, Young S, Condron L, O’Callaghan M (2012) Incidence and diversity of phosphate-solubilising bacteria are linked to phosphorus status in grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 44(1):93–101. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.09.009
Mikanova O, Kubat J, Simon T, Vorisek K, Randova D (1997) Influence of soluble phosphate on P-solubilizing activity of bacteria. Rostlinna Vyroba 43:421–424
Mikanova O, Novakova J (2002) Evaluation of the P-solubilizing activity of soil microorganisms and its sensitivity to soluble phosphate. Rostlinna Vyroba 48(9):397–400
Neijssel OM, Tempest DW, Postma PW, Duine JA, Jzn JF (1983) Glucose metabolism by K+-limitedKlebsiella aerogenes: evidence for the involvement of a quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase. FEMS microbiol lett 20(1):35–39
Olijve W, Kok JJ (1979) Analysis of growth of Gluconobacter oxydans in glucose containing media. Arch Microbiol 121(3):283–290
Oubrie A, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Olsthoorn AJ, Duine JA, Dijkstra BW (1999) Structure and mechanism of soluble quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase. EMBO J 18(19):5187–5194
Parks EJ, Olson GJ, Brinckman FE, Baldi F (1990) Characterization by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of the solubilization of phosphorus in iron ore by a fungus. J Ind Microbiol 5(2–3):183–189
Patel DK, Archana G, Kumar GN (2008) Variation in the nature of organic acid secretion and mineral phosphate solubilization by Citrobacter sp. DHRSS in the presence of different sugars. Curr Microbiol 56(2):168–174
Prágai Z, Allenby NE, O’Connor N, Dubrac S, Rapoport G, Msadek T, Harwood CR (2004) Transcriptional regulation of the phoPR operon in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 186(4):1182–1190
Prágai Z, Harwood CR (2002) Regulatory interactions between the Pho and σB-dependent general stress regulons of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 148(5):1593–1602
Raghothama K (1999) Phosphate acquisition. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50(1):665–693
Trivedi P, Sa T (2008) Pseudomonas corrugata (NRRL B-30409) mutants increased phosphate solubilization, organic acid production, and plant growth at lower temperatures. Curr Microbiol 56(2):140–144
Vassilev N, Eichler-Lobermann B, Vassileva M (2012) Stress-tolerant P-solubilizing microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(4):851–859. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4224-8
Vassileva M, Serrano M, Bravo V, Jurado E, Nikolaeva I, Martos V, Vassilev N (2010) Multifunctional properties of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms grown on agro-industrial wastes in fermentation and soil conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(5):1287–1299
Vyas P, Gulati A (2009) Organic acid production in vitro and plant growth promotion in maize under controlled environment by phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent Pseudomonas. BMC Microbiol 9:174. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-174
Yamada M, Asaoka S, Saier M, Yamada Y (1993) Characterization of the gcd gene from Escherichia coli K-12 W3110 and regulation of its expression. J Bacteriol 175(2):568–571
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Chinese Special Research Program for Forestry Sectors Beneficial to Public (201004061), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and Innovation Plan for Graduate Students of Jiangsu, China (CXLX12_0544). The authors express their gratitude to Dr. De-Wei Li, The Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Wu, X. & Wen, X. Effects of Soluble Phosphate on Phosphate-Solubilizing Characteristics and Expression of gcd Gene in Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2. Curr Microbiol 72, 198–206 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0938-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0938-z