Abstract
Purpose
Among the signaling pathways implicated in the tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, a downstream target of which is a family of serine/threonine kinases known as the 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinases (RSKs). This study aims to investigate the role of BI-D1870, a specific inhibitor of p90 RSKs, in a panel of OSCC cell lines.
Methods
The antitumor effects and mechanisms of BI-D1870 were assessed by MTT assays, flow cytometry, Western blotting, transfection, and confocal microscopy.
Results
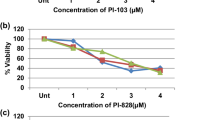
BI-D1870 exhibited a dose-responsive antiproliferative effect on OSCC cells with relative sparing of normal human oral keratinocytes. The compound inhibited the downstream RSK target YB-1 and caused apoptosis as evidenced by PARP cleavage, activation of the caspase cascade, and the presence of pyknotic nuclei in the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole assay. In addition, BI-D1870 also induced G2/M arrest by modulating the expression of p21 and other cell cycle regulators. Other newly discovered anticancer attributes of BI-D1870 included the generation of reactive oxygen species and increases in endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy.
Conclusions
Together, these results suggest the translational value of BI-D1870 in oral squamous cell carcinoma therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C, Gorlia T, Mesia R, Degardin M, Stewart JS, Jelic S, Betka J, Preiss JH, van den Weyngaert D, Awada A, Cupissol D, Kienzer HR, Rey A, Desaunois I, Bernier J, Lefebvre JL (2007) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357:1695–1704
Anjum R, Blenis J (2008) The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:747–758
Frodin M, Gammeltoft S (1999) Role and regulation of 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in signal transduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol 151:65–77
Chen RH, Sarnecki C, Blenis J (1992) Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol 12:915–927
Kang S, Elf S, Lythgoe K, Hitosugi T, Taunton J, Zhou W, **ong L, Wang D, Muller S, Fan S, Sun SY, Marcus AI, Gu TL, Polakiewicz RD, Chen ZG, Khuri FR, Shin DM, Chen J (2010) p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 2 promotes invasion and metastasis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Clin Invest 120:1165–1177
Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M, Shpiro N, Hastie CJ, McLauchlan H, Klevernic I, Arthur JS, Alessi DR, Cohen P (2007) The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J 408:297–315
Sapkota GP, Cummings L, Newell FS, Armstrong C, Bain J, Frodin M, Grauert M, Hoffmann M, Schnapp G, Steegmaier M, Cohen P, Alessi DR (2007) BI-D1870 is a specific inhibitor of the p90 RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) isoforms in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J 401:29–38
Nguyen TL (2008) Targeting RSK: an overview of small molecule inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 8:710–716
Chambard JC, Lefloch R, Pouyssegur J, Lenormand P (2007) ERK implication in cell cycle regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1299–1310
Stratford AL, Fry CJ, Desilets C, Davies AH, Cho YY, Li Y, Dong Z, Berquin IM, Roux PP, Dunn SE (2008) Y-box binding protein-1 serine 102 is a downstream target of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in basal-like breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 10:R99
Fang J, Seki T, Maeda H (2009) Therapeutic strategies by modulating oxygen stress in cancer and inflammation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:290–302
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC (2008) Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1013–1030
Lin Y, Wang Z, Liu L, Chen L (2011) Akt is the downstream target of GRP78 in mediating cisplatin resistance in ER stress-tolerant human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 71:291–297
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V, White E (2007) Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:961–967
Scherz-Shouval R, Elazar Z (2011) Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 36:30–38
Tanimura S, Hashizume J, Kurosaki Y, Sei K, Gotoh A, Ohtake R, Kawano M, Watanabe K, Kohno M (2011) SH3P2 is a negative regulator of cell motility whose function is inhibited by ribosomal S6 kinase-mediated phosphorylation. Genes Cells 16:514–526
Petrella BL, Armstrong DA, Vincenti MP (2011) CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein beta activation of MMP-1 gene expression in SW1353 cells: independent roles of extracellular signal-regulated and p90/ribosomal S6 kinases. J Cell Physiol 226:3349–3354
Chen S, Mackintosh C (2009) Differential regulation of NHE1 phosphorylation and glucose uptake by inhibitors of the ERK pathway and p90RSK in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Cell Signal 21:1984–1993
Mishima K, Yamada E, Masui K, Shimokawara T, Takayama K, Sugimura M, Ichijima K (1998) Overexpression of the ERK/MAP kinases in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 11:886–891
Johnson GL, Lapadat R (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298:1911–1912
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA (2007) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1263–1284
Das N, Majumder J, DasGupta UB (2000) ras gene mutations in oral cancer in eastern India. Oral Oncol 36:76–80
Chang SE, Bhatia P, Johnson NW, Morgan PR, McCormick F, Young B, Hiorns L (1991) Ras mutations in United Kingdom examples of oral malignancies are infrequent. Int J Cancer 48:409–412
Mishima K, Inoue K, Hayashi Y (2002) Overexpression of extracellular-signal regulated kinases on oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 38:468–474
Partridge M, Gullick WJ, Langdon JD, Sherriff M (1988) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor on oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 26:381–389
Werkmeister R, Brandt B, Joos U (2000) Clinical relevance of erbB-1 and -2 oncogenes in oral carcinomas. Oral Oncol 36:100–105
Yu T, Wu Y, Helman JI, Wen Y, Wang C, Li L (2011) CXCR4 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma migration and invasion through inducing expression of MMP-9 and MMP-13 via the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res 9:161–172
Yang LC, Yang SH, Tai KW, Chou MY, Yang JJ (2004) MEK inhibition enhances bleomycin A5-induced apoptosis in an oral cancer cell line: signaling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Oral Pathol Med 33:37–45
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Exton JH (2004) Critical role of endogenous Akt/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 279:49420–49429
Zhang LJ, Chen S, Wu P, Hu CS, Thorne RF, Luo CM, Hersey P, Zhang XD (2009) Inhibition of MEK blocks GRP78 up-regulation and enhances apoptosis induced by ER stress in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett 274:40–46
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Taiwan Department of Health, China Medical University Hospital Cancer Research of Excellence (DOH102-TD-C-111-005), National Science Council Grant (NSC 101-2320-B-039-029-MY2), China Medical University (CMU98-S52), and China Medical University Hospital (DMR-99-304, DMR-101-008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chang-Fang Chiu and Li-Yuan Bai have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, CF., Bai, LY., Kapuriya, N. et al. Antitumor effects of BI-D1870 on human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 237–247 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2349-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2349-9