Abstract
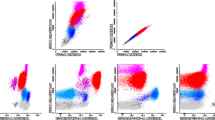
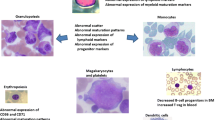
Flow cytometry (FCM) is being increasingly evaluated for the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). We employed multiple FCM approaches to assess MDS. Five-color FCM, morphology blind, was done on bone marrow aspirates of 57 suspected MDS and 31 normal controls. Maturation pattern, quantitative FCM for low-grade MDS that awards FCM score, and expression of selected antigens on erythroid cells and CD34+ blasts were evaluated. FCM results were correlated with clinical and laboratory workup. Patients (n = 57) included proven MDS (n = 14), suspected MDS (n = 13), and non-MDS (n = 30). By pattern-based approach, all proven cases were FCM positive. In suspected MDS, 11 (84.61 %) were positive including morphology-negative cases, and two (15.38 %) were intermediate. In non-MDS cases, 27 of 30 (90 %) were FCM negative, 2 of 30 (6.67 %) intermediate, and 1 of 30 (3.33 %) a hematinic-responsive case, positive. Quantitative parameters that characterized MDS included FCM score of >3, percentage CD34+ B cells, and expression of CD11b, CD15, and CD56 on myeloblasts. CD71 MFI on CD235a+ erythroblasts and CD38 MFI on myeloblasts were significantly lower in MDS. The former was present in FCM-intermediate suspected MDS but not FCM-intermediate non-MDS cases. Used in the overall clinical context, both maturation pattern recognition and quantitative approaches, the latter for low-grade MDS, are sensitive methods of diagnosing MDS, including cases negative by morphology and cytogenetics, especially if combined with evaluation of selected antigens, CD71 on CD235a+ cells and CD38 on CD34+ cells. The value of FCM in morphology-negative cases needs better definition of specificity through more extensive evaluation of secondary dyspoiesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida Y, Stephenson J, Mufti GJ (1993) Myelodysplastic syndromes: from morphology to molecular biology. Part I. Classification, natural history and cell biology of myelodysplasia. Int J Hematol 57:87–97
Ogata K (2006) Myelodysplastic syndromes: recent progress in diagnosis and understanding of their pathophysiology. J Nippon Med Sch 73:300–307
Valent P, Horny HP, Bennett JM, Fonatsch C, Germing U, Greenberg P, Haferlach T, Haase D, Kolb HJ, Krieger O, Loken M, van de Loosdrecht A, Ogata K, Orfao A, Pfeilstöcker M, Rüter B, Sperr WR, Stauder R, Wells DA (2007) Definitions and standards in the diagnosis and treatment of the myelodysplastic syndromes: consensus statements and report from a working conference. Leuk Res 31:727–736
Stetler-Stevenson M, Yuan CM (2009) Myelodysplastic syndromes: the role of flow cytometry in diagnosis and prognosis. Int J Lab Hematol 31:479–483
Olney HJ, Le Beau MM (2001) The cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 14:479–495
Ogata K (2008) Diagnostic utility of flow cytometry for low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol Oncol 26:193–198
Griffing GT, Melby JC (1982) Enalapril (MK-421) and the white cell count and haematocrit. Lancet 1:1361
Sica DA, Mannino R (2007) Antihypertensive medications and anemia. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 9:723–727
Elghetany MT (1998) Surface marker abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 83:1104–1115
Bianco T, Farmer BJ, Sage RE, Dobrovic A (2001) Loss of red cell A, B and H antigens is frequent in myeloid malignancies. Blood 97:3633–3639
Izumi M, Takeshita A, Shinjo K, Naito K, Matsui H, Shibata K, Ohnishi K, Kanno T, Ohno R (2001) Decreased amount of mpl and reduced expression of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa and glycoprotein Ib on platelets from patients with refractory anemia: analysis by a non-isotopic quantitative ligand binding assay and immunofluorescence. Eur J Haematol 66:245–252
Cherian S, Moore J, Bantly A, Vergilio JA, Klein P, Luger S, Bagg A (2005) Flow-cytometric analysis of peripheral blood neutrophils: a simple, objective, independent and potentially clinically useful assay to facilitate the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Hematol 79:243–245
Hansen I, Meyer K, Hokland P (1998) Flow cytometric identification of myeloid disorders by asynchronous expression of the CD14 and CD66 antigens. Eur J Haematol 61:339–346
Chang CC, Cleveland RP (2000) Decreased CD10-positive mature granulocytes in bone marrow from patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124:1152–1156
Ohsaka A, Saionji K, Igari J, Watanabe N, Iwabuchi K, Nagaoka I (1997) Altered surface expression of effector cell molecules on neutrophils in myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 98:108–113
Otawa M, Kawanishi Y, Iwase O, Shoji N, Miyazawa K, Ohyashiki K (2000) Comparative multi-color flow cytometric analysis of cell surface antigens in bone marrow hematopoietic progenitors between refractory anemia and aplastic anemia. Leuk Res 24:359–366
Mann KP, DeCastro CM, Liu J, Moore JO, Bigner SH, Traweek ST (1997) Neural cell adhesion molecule (CD56)-positive acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative syndromes. Am J Clin Pathol 107:653–660
Schlesinger M, Silverman LR, Jiang JD, Yagi MJ, Holland JF, Bekesi JG (1996) Analysis of myeloid and lymphoid markers on the surface and in the cytoplasm of mononuclear bone marrow cells in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Lab Immunol 48:149–166
Xu D, Schultz C, Akker Y, Cannizzaro L, Ramesh KH, Du J, Ratech H (2003) Evidence for expression of early myeloid antigens in mature, non-blast myeloid cells in myelodysplasia. Am J Hematol 74:9–16
Cherian S, Moore J, Bantly A, Vergilio JA, Klein P, Luger S, Bagg A (2005) Peripheral blood MDS score: a new flow cytometric tool for the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 64:9–17
Del Cnizo MC, Fernandez ME, Lopez A, Vidriales B, Villarón E, Arroyo JL, Ortuño F, Orfao A, San Miguel JF (2003) Immunophenotypic analysis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematologica 88:402–407
Wells DA, Benesch M, Loken MR, Vallejo C, Myerson D, Leisenring WM, Deeg HJ (2003) Myeloid and monocytic dyspoiesis as determined by flow cytometric scoring in myelodysplastic syndrome correlates with the IPSS and with outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 102:394–403
Stetler-Stevenson M, Arthur DC, Jabbour N, ** in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 98:979–987
Kussick SJ, Wood BL (2003) Using 4-color flow cytometry to identify abnormal myeloid populations. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:1140–1147
Kussick SJ, Fromm JR, Rossini A, Li Y, Chang A, Norwood TH, Wood BL (2005) Four-color flow cytometry shows strong concordance with bone marrow morphology and cytogenetics in the evaluation for myelodysplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 124:170–181
Stachurski D, Smith BR, Pozdnyakova O, Andersen M, **ao Z, Raza A, Woda BA, Wang SA (2008) Flow cytometric analysis of myelomonocytic cells by a pattern recognition approach is sensitive and specific in diagnosing myelodysplastic syndrome and related marrow diseases: emphasis on a global evaluation and recognition of diagnostic pitfalls. Leuk Res 32:215–224
Truong F, Smith BR, Stachurski D, Cerny J, Medeiros LJ, Woda BA, Wang SA (2009) The utility of flow cytometric immunophenoty** in cytopenic patients with a non-diagnostic bone marrow: a prospective study. Leuk Res 33:1039–1046
Elghetany MT (2002) Diagnostic utility of flow cytometric immunophenoty** in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 99:391–392
Ogata K, Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Picone C, Yokose N, Matsuda A, Yamashita T, Tamura H, Tsukada J, Dan K (2009) Diagnostic utility of flow cytometry in low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes: a prospective validation study. Haematologica 94:1066–1074
Malcovati L, Della Porta MG, Lunghi M, Pascutto C, Vanelli L, Travaglino E, Maffioli M, Bernasconi P, Lazzarino M, Invernizzi R, Cazzola M (2005) Flow cytometry evaluation of erythroid and myeloid dysplasia in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 19:776–783
Ogata K, Nakamura K, Yokose N, Tamura H, Tachibana M, Taniguchi O, Iwakiri R, Hayashi T, Sakamaki H, Murai Y, Tohyama K, Tomoyasu S, Nonaka Y, Mori M, Dan K, Yoshida Y (2002) Clinical significance of phenotypic features of blasts in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 100:3887–3896
Ogata K, Yoshida Y (2005) Clinical implications of blast immunophenotypes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma 46:1269–1274
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, Bloomfield CD (2009) The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 114:937–951
Ogata K (2011) Flow cytometry will be a routine tool in clinical practice in myelodysplastic syndromes: a real story. Leuk Res 35:848–849
Goardon N, Nikolousis E, Sternberg A, Chu WK, Craddock C, Richardson P, Benson R, Drayson M, Standen G, Vyas P, Freeman S (2009) Reduced CD38 expression on CD34+ cells as a diagnostic test in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 94:1160–1163
Brunning RD, Orazi A, Germing U, Le Beau MM, Porwi A, Baumann I, Vardiman JW, Hellstrom-Lindberg E (2008) Myelodysplastic syndromes/neopasms, overview. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th edn. IARC, Lyon, pp 88–97
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Amit Kumar and Mr. Zubair Abdullah for technical and secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, A., Pati, H., Mahapatra, M. et al. Flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndrome: analysis of diagnostic utility using maturation pattern-based and quantitative approaches. Ann Hematol 91, 1351–1362 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1461-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1461-y