Abstract
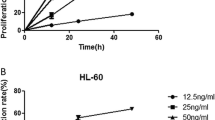
Tanshinone I (Tan I), a diterpene quinone extracted from herbal medicine Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, has recently been reported to have antitumor effects. As the mechanism of its proapoptotic effects on human myeloid leukemia cells has not been extensively studied, we performed an in-depth evaluation of the effects of Tan I on apoptosis in human K562 and HL-60 cells. The results revealed that Tan I could inhibit the growth of leukemia cells and cause apoptosis in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Apoptosis was observed clearly by flow cytometry and Hoechst 33258 staining, as well as DNA fragmentation analysis. After treatment by Tan I for 48 h, the percentage of disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) was increased in a dose-dependent manner. Western blotting analysis demonstrated the cleavage of caspase-3 zymogen protein and a dose-dependent cleavage of poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Tan I-induced apoptosis was accompanied by a significant decrease in survivin and an increase in Bax. Moreover, Tan I treatment remarkably downregulated the phosphorylation of both P85/PI3K and Akt in a time-dependent manner, and the PI3K/AKT-specific inhibitor (LY294002) mimicked the apoptosis-inducing effects of Tan I. We therefore conclude that the induction of apoptosis by Tan I in these leukemia cells is mainly related to the disruption of Δψm, the upregulation of Bax expression, and the activation of caspase-3. This process is highly correlated with the inactivation of PI3K/Akt/survivin signaling pathways. The results indicate that Tan I may serve as an effective adjunctive reagent in the treatment of leukemia.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon H, Wong J (2004) Botanical medicine and cancer: a review of the safety and efficacy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5:2485–2501
Zhou L, Zuo Z, Chow MS (2005) Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol 45:1345–1359
Wang AM, Sha SH, Lesniak W, Schacht J (2003) Tanshinone (Salviae miltiorrhizae extract) preparations attenuate aminoglycoside-induced free radical formation in vitro and ototoxicity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1836–1841
Choi HS, Cho DI, Choi HK, Im SY, Ryu SY, Kim KM (2004) Molecular mechanisms of inhibitory activities of tanshinones on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide generation in RAW 264.7 cells. Arch Pharm Res 27:1233–1237
Wang X, Wei Y, Yuan S, Liu G, Lu Y, Zhang J, Wang W (2005) Potential anticancer activity of tanshinone IIA against human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 116:799–807
Yuan SL, Wei YQ, Wang XJ, **ao F, Li SF, Zhang J (2004) Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of tanshinone II-A on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 10:2024–2028
Su CC, Chen GW, Lin JG (2008) Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction by tanshinone I in human colon cancer Colo 205 cells. Int J Mol Med 22:613–618
Lee CY, Sher HF, Chen HW, Liu CC, Chen CH, Lin CS, Yang PC, Tsay HS, Chen JJ (2008) Anticancer effects of tanshinone I in human non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3527–3538
Nizamutdinova IT, Lee GW, Lee JS, Cho MK, Son KH, Jeon SJ, Kang SS, Kim YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Chang KC, Kim HJ (2008) Tanshinone I suppresses growth and invasion of human breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231, through regulation of adhesion molecules. Carcinogenesis 29:1885–1892
Carlo-Stella C, Lavazza C, Locatelli A, Viganò L, Gianni AM, Gianni L (2007) Targeting TRAIL agonistic receptors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:2313–2317
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Dall’Aglio PP, Ridolo E, Carlo-Stella C, Pelicci PG, Bonati A (2003) Downmodulation of ERK activity inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of primary acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Leukemia 17:1783–1793
Carlo-Stella C, Lavazza C, Di Nicola M, Cleris L, Longoni P, Milanesi M, Magni M, Morelli D, Gloghini A, Carbone A, Gianni AM (2006) Antitumor activity of human CD34+ cells expressing membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Hum Gene Ther 17:1225–1240
Carlo-Stella C, Di Nicola M, Turco MC, Cleris L, Lavazza C, Longoni P, Milanesi M, Magni M, Ammirante M, Leone A, Nagy Z, Gioffrè WR, Formelli F, Gianni AM (2006) The anti-human leukocyte antigen-DR monoclonal antibody 1D09C3 activates the mitochondrial cell death pathway and exerts a potent antitumor activity in lymphoma-bearing nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res 66:1799–1808
Garcia-Echeverria C, Sellers WR (2008) Drug discovery approaches targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer. Oncogene 27:5511–5526
Seol DW (2008) Up-regulation of IAPs by PI-3K: a cell survival signal-mediated anti-apoptotic mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377:508–511
Lindsley CW, Barnett SF, Layton ME, Bilodeau MT (2008) The PI3K/Akt pathway: recent progress in the development of ATP-competitive and allosteric Akt kinase inhibitors. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8:7–18
Downward J (2004) PI 3-kinase, Akt and cell survival. Semin Cell Dev Biol 15:177–182
Maddika S, Ande SR, Panigrahi S, Paranjothy T, Weglarczyk K, Zuse A, Eshraghi M, Manda KD, Wiechec E, Los M (2007) Cell survival, cell death and cell cycle pathways are interconnected: implications for cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat 10:13–29
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Koutsilieris M (2004) The Akt pathway: molecular targets for anti-cancer drug development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4:235–256
Michl P, Downward J (2005) Mechanisms of disease: PI3K/AKT signaling in gastrointestinal cancers. Z Gastroenterol 43:1133–1139
De Santis G, Miotti S, Mazzi M, Canevari S, Tomassetti A (2009) E-cadherin directly contributes to PI3K/AKT activation by engaging the PI3K-p85 regulatory subunit to adherens junctions of ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncogene 28:1206–1217
Morgan TM, Koreckij TD, Corey E (2009) Targeted therapy for advanced prostate cancer: inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:237–249
Qian J, Zou Y, Rahman JS, Lu B, Massion PP (2009) Synergy between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and Bcl-xL in the control of apoptosis in adenocarcinoma cells of the lung. Mol Cancer Ther 8:101–109
Shen JK, Du HP, Yang M, Wang YG, ** J (2009) Casticin induces leukemic cell death through apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe. Ann Hematol 88:743–752
Liu H, Mihara K, Song G, Tanaka H, Kimura A (2007) Interferon-gamma attenuates the survival activity of G-CSF through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in mouse multipotent progenitor cells. Ann Hematol 86:547–555
Zhang QY, Mao JH, Liu P, Huang QH, Lu J, **e YY, Weng L, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Chen SJ, Chen Z (2009) A systems biology understanding of the synergistic effects of arsenic sulfide and imatinib in BCR/ABL-associated leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3378–3383
Brown VI, Seif AE, Reid GS, Teachey DT, Grupp SA (2008) Novel molecular and cellular therapeutic targets in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoproliferative disease. Immunol Res 42:84–105
Zhang QL, Wang L, Zhang YW, Jiang XX, Yang F, Wu WL, Janin A, Chen Z, Shen ZX, Chen SJ, Zhao WL (2009) The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid to induce T-leukemia/lymphoma cells apoptosis. Leukemia 23:1507–1514
Guan L, Han B, Li J, Li Z, Huang F, Yang Y, Xu C (2009) Exposure of human leukemia NB4 cells to increasing concentrations of selenite switches the signaling from pro-survival to pro-apoptosis. Ann Hematol 88:733–742
Karp JE, Lancet JE (2004) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) in myeloid malignancies. Ann Hematol 83(1):S87–88
Zhang M, Ling Y, Yang CY, Liu H, Wang R, Wu X, Ding K, Zhu F, Griffith BN, Mohammad RM, Wang S, Yang D (2007) A novel Bcl-2 small molecule inhibitor 4-(3-methoxy-phenylsulfannyl)-7-nitro-benzofurazan-3-oxide (MNB)-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Ann Hematol 86:471–481
Jung JT, Kim DH, Kwak EK, Kim JG, Park TI, Sohn SK, Do YR, Kwon KY, Song HS, Park EH, Lee KB (2006) Clinical role of Bcl-2, Bax, or p53 overexpression in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Ann Hematol 85:575–581
Bogner C, Sandherr M, Perker M, Weick K, Ringshausen I, Peschel C, Decker T (2006) Cyclin E but not bcl-2, bax or mcl-1 is differentially expressed in ZAP 70-positive and ZAP 70-negative B-CLL cells. Ann Hematol 85:458–462
Kang MH, Reynolds CP (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15:1126–32
Debatin KM (2004) Apoptosis pathways in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:153–197
Gianelli U, Fracchiolla NS, Cortelezzi A, Pellegrini C, Savi F, Moro A, Grimoldi MG, Deliliers GL, Coggi G, Bosari S (2007) Survivin expression in "low-risk" and "high-risk" myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Hematol 86:185–189
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ (2008) Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 5:5000–5005
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y, Yan XJ, Xu F, Wang BS, Mao JH, Shen ZX, Chen SJ, Chen Z (2008) Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4826–4831
Zhou GB, Kang H, Wang L, Gao L, Liu P, **e J, Zhang FX, Weng XQ, Shen ZX, Chen J, Gu LJ, Yan M, Zhang DE, Chen SJ, Wang ZY, Chen Z (2007) Oridonin, a diterpenoid extracted from medicinal herbs, targets AML1-ETO fusion protein and shows potent antitumor activity with low adverse effects on t(8;21) leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Blood 109:3441–3450
Han JY, Fan JY, Horie Y, Miura S, Cui DH, Ishii H, Hibi T, Tsuneki H, Kimura I (2008) Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion. Pharmacol Ther 117:280–295
Fu J, Huang H, Liu J, Pi R, Chen J, Liu P (2007) Tanshinone IIA protects cardiac myocytes against oxidative stress-triggered damage and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 568:213–221
Pérez-Quintanilla D, Gómez-Ruiz S, Zizak Z, Sierra I, Prashar S, del Hierro I, Fajardo M, Juranić ZD, Kaluderović GN (2009) A new generation of anticancer drugs: mesoporous materials modified with titanocene complexes. Chemistry 15:5588–5597
Darzynkiewicz Z, Xuan H, Masaki O (2006) Detection of DNA strand breaks by flow and laser scanning cytometry in studies of apoptosis and cell proliferation (DNA replication). Meth Mol Biol 314:81–93
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of our laboratories for their insight and technical support. This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Foundation of China (no. 30570786, no. 30770782) and Guangdong Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 8151008901000128) as well as the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (no. NCET-06-0721).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jia-Jun Liu, Wen-Da Liu, Hong-Zhi Yang, Yong Zhang, and Pei-Qing Liu equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JJ., Liu, WD., Yang, HZ. et al. Inactivation of PI3k/Akt signaling pathway and activation of caspase-3 are involved in tanshinone I-induced apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells in vitro. Ann Hematol 89, 1089–1097 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0996-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0996-z