Abstract
Background
The aim of the present study was to identify a panel of microRNAs (miRNAs) that can predict overall survival (OS) in non micro-dissected cancer tissues from patients operated for pancreatic cancer (PC).
Methods
MiRNAs were purified from formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) cancer tissue from 225 patients operated for PC. Only a few of those patients received adjuvant chemotherapy. Expressions of miRNAs were determined with the TaqMan MicroRNA Array v2.0. Two statistical methods, univariate selection and the Lasso (Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator) method, were applied in conjunction with the Cox proportional hazard model to relate miRNAs to OS.
Results
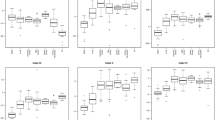
High expression of miR-212 and miR-675 and low expression of miR-148a*, miR-187, and let-7g* predicted short OS independent of age, gender, calendar year of operation, KRAS mutation status, tumor stage, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, localization (not miR-148a*), and differentiation of tumor. A prognostic index (PI) based on these five miRNAs was calculated for each patient. The median survival was 1.09 years (Confidence Interval [CI] 0.98–1.43) for PI > median PI compared to 2.23 years (CI 1.84–4.36) for PI < median. MiR-212, miR-675, miR-187, miR-205, miR-944, miR-431, miR-194*, miR-148a*, and miR-769-5p showed the strongest prediction ability by the Lasso method. Thus miR-212, miR-675, miR-187, and miR-148a* were predictors for OS in both statistical methods.
Conclusions
The combination of five miRNAs expression in non micro-dissected FFPE PC tissue can identify patients with short OS after radical surgery. The results are independent of chemotherapy treatment. Patients with a prognostic index > median had a very short median OS of only 1 year.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Hildago M (2010) Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 362:1605–1612
Wagner M, Redaelli C, Lietz M et al (2004) Curative resection is the single most important factor determining outcome in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg 91:586–594
Beger HG, Thorab FC, Liu Z et al (2004) Pathogenesis and treatment of neoplastic diseases of the papilla of Vater: Kausch-Whipple procedure with lymph node dissection in cancer of the papilla of Vater. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 11:232–238
Bettschart V, Rahman MQ, Engelken FJ et al (2004) Presentation, treatment and outcome in patients with ampullary tumours. Br J Surg 91:1600–1607
Locker GY, Hamilton S, Harris J et al (2006) 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:5313–5327
Nelson KM, Weiss GJ (2008) MicroRNAs and cancer: past, present and potential future. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3655–3660
Bartels CL, Tsongalis GJ (2009) MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem 55:623–631
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2009) MicroRNAs in cancer: small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol 27:5848–5856
Visone R, Croce CM (2009) MiRNAs and cancer. Am J Pathol 174:1131–1138
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P et al (2011) MiRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol 223:102–115
Li J, Smyth P, Flavin R et al (2007) Comparison of miRNA expression patterns using total RNA extracted from matched samples of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cells and snap frozen cells. BMC Biotechnol 7:36
Zhang X, Chen J, Radcliffe T et al (2008) An array-based analysis of microRNA expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. J Mol Diagn 10:513–519
Rachagani S, Kumar S, Batra SK (2010) MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer: pathological, diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cancer Lett 292:8–16
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F et al (2007) MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 297:1901–1908
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J et al (2007) MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 26:4442–4452
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg 12:2171–2176
Szafranska AE, Doleshal M, Edmunds HS et al (2008) Analysis of microRNAs in pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant tissues. Clin Chem 54:1716–1724
Habbe N, Koorstra JB, Mendell JT et al (2009) miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther 8:340–346
Seux M, Iovanna J, Dagorn J-C et al (2009) MicroRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: new diagnostic and therapeutic clues. Pancreatology 9:66–72
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P et al (2009) MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res 2:807–813
Zhang Y, Li M, Wang H et al (2009) Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World J Surg 33:698–709. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9833-0
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A et al (2010) Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int J Cancer 126:73–80
Hwang JH, Voortman J, Giovannetti E et al (2010) Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 5:e10630
Ikenaga N, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K et al (2010) MicroRNA-203 expression as a new prognostic marker of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 17:3120–3128
Ali S, Almhanna K, Chen W et al (2011) Differential expressed miRNAs in the plasma may provide a molecular signature for aggressive pancreatic cancer. Am J Transl Res 3:28–47
Kong X, Du Y, Wang G et al (2011) Detection of differentially expressed microRNAs in serum of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients: miR-196a could be a potential marker for poor prognosis. Dig Dis Sci 56:602–609
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Kayashima T et al (2011) MicroRNA expression as a predictive marker for gemcitabine response after surgical resection of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18:2381–2387
Schultz NA, Werner J, Willenbrock H et al (2012) MicroRNA expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and ampullary adenocarcinoma. Modern Pathol (in press)
Preis M, Gardner TB, Gordon SR et al (2011) MicroRNA-10b expression correlates with response to neoadjuvant therapy and survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:5812–5821
Jamieson NB, Morran DC, Morton JP et al (2012) MicroRNA profiles associated with diagnosis, clinicopathological criteria and overall survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 18:534–545
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W et al (2006) Reporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:229–235
WHO Classification of Tumours (2000) Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Digestive System. IARC Press, Lyon
Mar JC, Kimura Y, Schroder K et al (2009) Data-driven normalization strategies for high-throughput quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Bioinformatics 10:110
Bovelstad HM, Nygard S, Storvold HL et al (2007) Predicting survival from microarray data—a comparative study. Bioinformatics 23:2080–2087
Tibshirani R (1997) The LASSO method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med 16:385–395
Grambsch P, Therneau T (1994) Proportional hazards tests and diagnostics based on weighted residuals. Biometrika 81:515–526
R Development Core Team (2007) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Hanoun N, Delpu Y, Suriawinata AA et al (2010) The silencing of microRNA 148a production by DNA hypermethylation is an early event in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin Chem 56:1107–1118
Grutzmann R, Foerder M, Alldinger I et al (2003) Gene expression profiles of microdissected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch 443:508–517
Buchholz M, Braun M, Heidenblut A et al (2005) Transcriptome analysis of microdissected pancreatic intraepithelial neoplastic lesions. Oncogene 24:6626–6636
Schultz NA, Roslind A, Christensen IJ et al (2011) Frequencies and prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF mutations in patients with localized pancreatic and ampullary adenocarcinomas. Pancreas 41:759–766
Torrisani J, Bournet B, du Rieu MC et al (2009) Let-7 microRNA transfer in pancreatic cancer derived cells inhibits in vitro cell proliferation but fails to alter tumor progression. Hum Gen Ther 20:831–844
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Ragusa M, Majorana A, Statello L et al (2010) Specific alterations of microRNA transcriptome and global network structure in colorectal carcinoma after cetuximab treatment. Mol Cancer Ther 9:3396–3409
Ferrone CR, Finkelstein DM, Thayer SP et al (2006) Perioperative CA 19–9 levels can predict stage and survival in patients with respectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:2897–2902
Smith RA, Bosonnet L, Ghaneh P et al (2008) Preoperative CA 19–9 levels and lymph node ratio are independent predictors of survival in patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Surg 25:226–232
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D et al (2008) MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid tumors: biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1600–1608
Hatakeyama H, Cheng H, Wirth P et al (2010) Regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by miR-212 and acquired cetuximab-resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 5:e12702
Tsang WP, Ng EK, Ng SS et al (2010) Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 31:350–358
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the Research Council at Herlev Hospital and two private funds: the “Augustinus Fonden” and the “Læge Sofus Carl Emil Friis og hustru Olga Doris Friis’ Legat.” The funding organizations had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript. The authors are grateful to molecular biologist Mel Herein and technicians Krisztina Faludi and Eileen Wong of Herlev Hospital, Copenhagen University Hospital, for help with the sectioning of the samples, and to Mogens Kruhøffer from AROS, Applied Biotechnology A/S, Aarhus, Denmark, who provided excellent technical assistance with the microRNA array analysis.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
CONSORT diagram. (JPG 119kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Nomogram for the multivariate survival model predicting OS in patients operated for PC. To estimate risk, calculate points for each miRNA expression in PC tissue by drawing a straight line from patients miRNA to the axis labeled “points.” Sum all points and draw a straight line from the total point axis to the 3-month, 1-year, and 10-year survival probability axes. (DOC 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schultz, N.A., Andersen, K.K., Roslind, A. et al. Prognostic MicroRNAs in Cancer Tissue from Patients Operated for Pancreatic Cancer—Five MicroRNAs in a Prognostic Index. World J Surg 36, 2699–2707 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1705-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1705-y