Abstract
Background
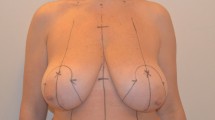
In mastopexy surgery, extra skin and a specific amount of breast tissue are resected. Resected breast tissue is not in a large amount as in reduction surgery. In this study, we have investigated the results of an auto-augmentation mastopexy technique involving use of a superior pedicled mastopexy with conic-shaped inferior butterfly flap for augmentation without implant or fat injection.
Methods
A total of 80 patients, 40 patients in each group, were included in the study. In the first group, double-pedicled auto-augmentation mastopexy with conic-shaped modified inferior butterfly flap technique was used. In the second group, conventional superior pedicled wise-pattern mastopexy was utilized. The results were evaluated from photographic measurements performed from standardized preoperative and postoperative lateral photographs.
Results
No major complications were seen such as partial or total areola necrosis or breast volume loss. None of our patients has made a return with request for revision surgery. Minor complication seen in several patients was resolved with early intervention. The preoperative and postoperative photographic measurements of breast projection, upper pole projection, nipple position and lower pole level from preoperative and postoperative standardized lateral photographs revealed no significant difference between the groups.
Conclusion
We obtained highly satisfactory results for our patients. Following the surgery, our patients protected the cup sizes of their bra. In spite of the fact that there was no real augmentation performed in this procedure, effective straightening and the compact breast structure patients that achieved were highly successful in creating an augmented breast image.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavigne B (2019) Mastopexy. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 64(5–6):562–568. (Mastopexie). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2019.07.011
Qureshi AA, Myckatyn TM, Tenenbaum MM (2018) Mastopexy and mastopexy-augmentation. Aesthetic Surg J 38(4):374–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx181
Ikander P, Sørensen JA, Thomsen JB (2020) Mastopexy with autologous augmentation in women after massive weight loss: a randomized clinical trial. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 45(1):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01642-0
Hidalgo DA, Spector JA (2013) Mastopexy. Plastic and Reconstr Surg 132(4):642e–656e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0b013e31829fe4b4
Sisti A, Tassinari J, Nisi G, Grimaldi L (2017) Superior pedicle mastopexy with the three fat-glandular flap support. Plastic Reconstr Surg 139(1):311e–312e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000002869
Aquinati A, Tuttolomondo A, Ruocco G, Riccio M (2019) Improvement of superomedial breast reduction and mastopexy with a new “Hammock” flap. Plastic Reconstr Surg Global Open 7(7):e2309. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000002309
Kotti B (2017) “The Chignon Mastopexy”: a double glandular suspended flaps for an auto-augmentation effect. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 42(1):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0985-x
Flowers RS, Smith EM (1998) “Flip-Flap” Mastopexy. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 22(6):425–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002669900228
Miotto GC, Eaves FF (2015) The circumrotational technique for mastopexy. Aesthetic Surg J 35(7):796–809. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjv093
De Benito J, Sánchez K (2010) Key points in mastopexy. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 34(6):711–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9527-5
Ship AG, Weiss PR, Engler AM (1989) Dual-pedicle dermoparenchymal mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(2):281–290. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198902000-00014
Austin RE, Saheb-Al-Zamani M, Lista F, Ahmad J (2019) Periareolar augmentation-mastopexy. Aesthetic Surg J 39(9):953–965. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz128
Daga G, Kumar R (2019) Donut mastopexy lumpectomy. Indian J Surg Oncol 10(2):372–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-018-0865-0
Peled IJ (1991) The concentric mastopexy and the purse-string suture. Plastic Reconstr Surg 87(2):385. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199102000-00040
Goes JC (2003) Periareolar mastopexy: double skin technique with mesh support. Aesthet Surg J 23(2):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1067/maj.2003.18
Graf RM, Closs Ono MC, Pace D, Balbinot P, Pazio ALB, de Paula DR (2019) Breast Auto-augmentation (Mastopexy and Lipofilling): an option for quitting breast implants. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 43(5):1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01387-5
Raafat SS, Ezzat SZ, Khachaba YA, Aboul-Nasr LA (2020) Autologous Mastopexy and Autoaugmention of the Breast. Plastic Reconstr Surg Global Open 8(10):e3126. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000003126
Calobrace MB, Gabriel A (2021) Mastopexy with autoaugmentation and fat transfer. Clin Plastic Surg 48(1):17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2020.09.008
Watfa W, Zaugg P, Baudoin J, Bramhall RJ, Raffoul W, di Summa PG (2019) Dermal triangular flaps to prevent pseudoptosis in mastopexy surgery. Plastic Reconstr Surg Global Open 7(11):e2473. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000002473
Walters J, Bourn L, Tessler O, Patterson C, Khoobehi K (2019) Single staged mastopexy with autologous fat grafting: an alternative to augmentation mastopexy with implants. Aesthetic Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz217
di Summa PG, Oranges CM, Watfa W et al (2019) Systematic review of outcomes and complications in nonimplant-based mastopexy surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 72(2):243–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2018.10.018
Swanson E (2020) A comparison of 28 published augmentation/mastopexy techniques using photographic measurements. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(9):e3092. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000003092
Gheita A, Moftah A (2010) Breast ptosis managed by mastopexy using the triple flaps procedure. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 35(1):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9545-3
Layt CWL (2021) Augmentation mastopexy. Clin Plastic Surg 48(1):45–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2020.09.002
Nahai F, Fisher J, Maxwell P, Millsii D (2007) Augmentation mastopexy: to stage or not. Aesthetic Surg J 27(3):297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2007.04.006
Khavanin N, Jordan SW, Rambachan A, Kim JYS (2014) A systematic review of single-stage augmentation-mastopexy. Plastic Reconstr Surg. 134(5):922–931. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000582
Mottura A (2007) Periareolar mastopexy and augmentation. Aesthetic Surg J 27(4):450–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2007.05.006
Efendioglu K, Aksam E, Aksam B, Tuzuner M, Gence H (2018) The tuck-in mastopexy. Ann Plastic Surg. 81(3):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0000000000001535
Kelemen N, Kannan RY, Offer GJ (2013) A stacked technique of mastopexy: volume redistribution mastopexy with inferior flap and superomedially based pedicle. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 37(2):349–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0079-3
Hammond DC, O’Connor EA (2014) The lower island flap transposition (LIFT) technique for control of the upper pole in circumvertical mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(4):655–660. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000521
Foustanos A, Zavrides H (2007) A double-flap technique: an alternative mastopexy approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(1):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000263320.57385.a2
Yilmaz KB (2021) A modified superior pedicle mastopexy technique with an inferolateral-based auto augmentation flap. Aesthetic Plastic Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02127-4
Hönig JF, Frey HP, Hasse FM, Hasselberg J (2009) Autoaugmentation mastopexy with an inferior-based pedicle. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 33(3):302–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-009-9310-7
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MOV 69971 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MOV 90892 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altınel, D., Serin, M. & Toplu, G. Comparison of Classic Mastopexy Method with Double-Pedicled Auto-augmentation Mastopexy with Conic-Shaped Modified Inferior Butterfly Flap. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 1641–1649 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02816-8