Abstract
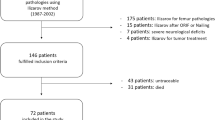
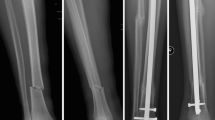
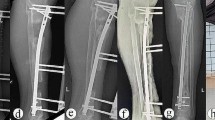
Bone transport can be performed with an external fixator alone or with the monorail technique which entails the combination of a fixator and an intramedullary nail. The purpose of this study was to compare the complication rates and long-term outcomes of these methods. Two groups of patients, the external fixator (n = 21) and the monorail group (n = 18), were compared. The average follow-up period was 7.9 ± 5.6 years and the mean defect length 8.3 ± 3.1 cm. Healing was achieved in 19 (90%) and 13 (72%) of the fixator and monorail patients, respectively. Six patients underwent amputations because of persistent infections (two in the fixator and four in the monorail group). The rate of deformities was significantly higher in the fixator group (p = 0.049). No statistically significant difference was found when comparing categories of the SF-36 test or the ability to work or do sports. The main advantages of the monorail method are reduction of the external fixation time and the lower rate of deformities. However, the authors recommend segmental transport with external fixator in patients with chronic infections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cierny G 3rd, Zorn KE (1994) Segmental tibial defects. Comparing conventional and Ilizarov methodologies. Clin Orthop Relat Res 301:118–123
Mankin HJ, Doppelt S, Tomford W (1983) Clinical experience with allograft implantation. The first ten years. Clin Orthop Relat Res 174:69–86
Mekhail AO, Abraham E, Gruber B, Gonzalez M (2004) Bone transport in the management of posttraumatic bone defects in the lower extremity. J Trauma 56(2):368–378
Doi K, Kawakami F, Hiura Y, Oda T, Sakai K, Kawai S (1995) One-stage treatment of infected bone defects of the tibia with skin loss by free vascularized osteocutaneous grafts. Microsurgery 16(10):704–712
El-Gammal TA, El-Sayed A, Kotb MM (2002) Microsurgical reconstruction of lower limb bone defects following tumor resection using vascularized fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap. Microsurgery 22(5):193–198
El-Alfy B, El-Mowafi H, El-Moghazy N (2010) Distraction osteogenesis in management of composite bone and soft tissue defects. Int Orthop 34(1):115–118
Benacquista T, Kasabian AK, Karp NS (1996) The fate of lower extremities with failed free flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 98(5):834–840
Chew WY, Low CK, Tan SK (1995) Long-term results of free vascularized fibular graft. A clinical and radiographic evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 311:258–261
El-Gammal TA, Shiha AE, El-Deen MA, El-Sayed A, Kotb MM, Addosooki AI, Ragheb YF, Saleh WR (2008) Management of traumatic tibial defects using free vascularized fibula or ilizarov bone transport: A comparative study. Microsurgery 28(5):339–346
Minami A, Kimura T, Matsumoto O, Kutsumi K (1993) Fracture through united vascularized bone grafts. J Reconstr Microsurg 9(3):227–232
Green SA (1994) Skeletal defects. A comparison of bone grafting and bone transport for segmental skeletal defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res 301:111–117
Marsh JL, Prokuski L, Biermann JS (1994) Chronic infected tibial nonunions with bone loss. Conventional techniques versus bone transport. Clin Orthop Relat Res 301:139–146
Song HR, Cho SH, Koo KH, Jeong ST, Park YJ, Ko JH (1998) Tibial bone defects treated by internal bone transport using the Ilizarov method. Int Orthop 22(5):293–297
Wani N, Baba A, Kangoo K, Mir M (2010) Role of early Ilizarov ring fixator in the definitive management of type II, IIIA and IIIB open tibial shaft fractures. Int Orthop. [Epub ahead of print]
Lovisetti G, Sala F, Thabet AM, Catagni MA, Singh S (2010) Osteocutaneous thermal necrosis of the leg salvaged by TSF/Ilizarov reconstruction. Report of 7 patients. Int Orthop. [Epub ahead of print]
Raschke MJ, Mann JW, Oedekoven G, Claudi BF (1992) Segmental transport after unreamed intramedullary nailing. Preliminary report of a "Monorail" system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 282:233–240
Paley D (1990) Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res 250:81–104
Liodakis E, Kenawey M, Krettek C, Ettinger M, Jagodzinski M, Hankemeier S (2010) Segmental transports for posttraumatic lower extremity bone defects: are femoral bone transports safer than tibial? Arch Orthop Trauma. [Epub ahead of print]
Kocaoglu M, Eralp L, Rashid HU, Sen C, Bilsel K (2006) Reconstruction of segmental bone defects due to chronic osteomyelitis with use of an external fixator and an intramedullary nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(10):2137–2145
Kenawey M, Krettek C, Liodakis E, Meller R, Hankemeier S (2010) Insufficient bone regenerate after intramedullary femoral lengthening: risk factors and classification system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. [Epub ahead of print]
Oh CW, Song HR, Roh JY, Oh JK, Min WK, Kyung HS, Kim JW, Kim PT, Ihn JC (2008) Bone transport over an intramedullary nail for reconstruction of long bone defects in tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(8):801–808
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Paremain G, Bhave A (1997) Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail. A matched-case comparison with Ilizarov femoral lengthening. J Bone Jt Surg Am 79(10):1464–1480
Gopal S, Giannoudis PV, Murray A, Matthews SJ, Smith RM (2004) The functional outcome of severe, open tibial fractures managed with early fixation and flap coverage. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(6):861–867
Watanabe K, Tsuchiya H, Sakurakichi K, Yamamoto N, Kabata T, Tomita K (2005) Tibial lengthening over an intramedullary nail. J Orthop Sci 10(5):480–485
Conflict of interest statement
There was no financial support for this study. None of the authors have received or will receive benefits for professional or personal use from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Ethical Board Review approval was obtained for this study (#644 – 05/01/2010).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liodakis, E., Kenawey, M., Krettek, C. et al. Comparison of 39 post-traumatic tibia bone transports performed with and without the use of an intramedullary rod: the long-term outcomes. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 35, 1397–1402 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-010-1094-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-010-1094-5