Abstract
Purpose
To determine if 11C-l-methionine PET is a useful tool in the evaluation of the long-term effect of proton beam treatment in patients with meningioma remnant.
Methods
Included in the study were 19 patients (4 men, 15 women) with intracranial meningioma remnants who received hypofractionated high-energy proton beam treatment. Patients were examined with 11C-l-methionine PET and MRI prior to treatment and after 6 months, and 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 and 10 years. Temporal changes in methionine uptake ratio, meningioma volume, meningioma regrowth and clinical symptoms throughout the follow-up period were evaluated.
Results
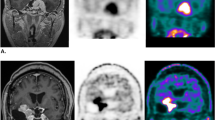
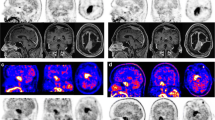
In 17 patients the tumour volume was unchanged throughout the follow-up. The methionine uptake ratio on PET decreased over the years in most patients. In two patients the tumour remnant showed progression on MRI. In these patients, prior to the volume increase on MRI, the methionine uptake ratio increased. One patient experienced transient clinical symptoms and showed radiological evidence of a radiation-induced reaction close to the irradiated field.
Conclusion
Proton beam treatment is a safe and effective treatment for achieving long-term growth arrest in meningioma remnants. Follow-up with 11C-l-methionine PET may be a valuable adjunct to, but not a replacement for, standard radiological follow-up.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Condra KS, Buatti JM, Mendenhall WM, Friedman WA, Marcus Jr RB, Rhoton AL. Benign meningiomas: primary treatment selection affects survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;39:427–36.
Ichinose T, Goto T, Ishibashi K, Takami T, Ohata K. The role of radical microsurgical resection in multimodal treatment for skull base meningioma. J Neurosurg. 2010;113:1072–8.
Mathiesen T, Lindquist C, Kihlström L, Karlsson B. Recurrence of cranial base meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1996;39:2–9.
DeMonte F, Smith HK, al-Mefty O. Outcome of aggressive removal of cavernous sinus meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 1994;81:245–51.
Desai R, Bruce J. Meningiomas of the cranial base. J Neurooncol. 1994;20:255–79.
Abdel-Aziz KM, Froelich SC, Dagnew E, Jean W, Breneman JC, Zuccarello M, et al. Large sphenoid wing meningiomas involving the cavernous sinus: conservative surgical strategies for better functional outcomes. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:1375–83. Discussion 1383–4.
Pichierri A, Santoro A, Raco A, Paolini S, Cantore G, Delfini R. Cavernous sinus meningiomas: retrospective analysis and proposal of a treatment algorithm. Neurosurgery. 2009;64:1090–101.
Misra BK. The paradigm of skull base meningiomas: what is optimal? World Neurosurg. 2012;78:220–1.
Bassiouni H, Asgari S, Sandalcioglu IE, Seifert V, Stolke D, Marquardt G. Anterior clinoidal meningiomas: functional outcome after microsurgical resection in a consecutive series of 106 patients. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2009;111:1078–90.
Seifert V. Clinical management of petroclival meningiomas and the eternal quest for preservation of quality of life: personal experiences over a period of 20 years. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010;152:1099–116.
O’Sullivan MG, van Loveren HR, Tew Jr JM. The surgical resectability of meningiomas of the cavernous sinus. Neurosurgery. 1997;40:238–44. Discussion 245–7.
De Monte F. Current management of meningiomas. Oncology (Williston Park). 1995;9:83–91, 96. Discussion 96, 99–101.
Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, Aranda D, Barani IJ, McDermott MW, Parsa AT. Factors affecting outcome following treatment of patients with cavernous sinus meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2010;113:1087–92.
McGregor JM, Sarkar A. Stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base meningiomas. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009;42:677–88.
Goldsmith B, Wara W, Wilson C, Larson D. Post-operative external beam irradiation for subtotally resected meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;24:126–7.
Nutting C, Brada M, Brazil L, Sibtain A, Saran F, Westbury C, et al. Radiotherapy in the treatment of benign meningioma of the skull base. J Neurosurg. 1999;90:823–7.
Rogers L, Barani I, Chamberlain M, Kaley TJ, McDermott M, Raizer J, et al. Meningiomas: knowledge base, treatment outcomes, and uncertainties. A RANO review. J Neurosurg. 2015;122:4–23.
Ohba S, Kobayashi M, Horiguchi T, Onozuka S, Yoshida K, Ohira T, et al. Long-term surgical outcome and biological prognostic factors in patients with skull base meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2011;114:1278–87.
Tanzler E, Morris CG, Kirwan JM, Amdur RJ, Mendenhall WM. Outcomes of WHO grade I meningiomas receiving definitive or postoperative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79:508–13.
Duma CM, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Harsh GRI, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery of cavernous sinus meningiomas as an addition or alternative to microsurgery. Neurosurgery. 1993;32:699–705.
Pollock BE, Stafford SL, Link MJ, Brown PD, Garces YI, Foote RL. Single-fraction radiosurgery of benign intracranial meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:604–13.
Starke RM, Williams BJ, Hiles C, Nguyen JH, Elsharkawy MY, Sheehan JP. Gamma knife surgery for skull base meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:588–97.
Santacroce A, Walier M, Regis J, Liscak R, Motti E, Lindquist C, et al. Long-term tumor control of benign intracranial meningiomas after radiosurgery in a series of 4565 patients. Neurosurgery. 2012;70:32–9. Discussion 39.
Kimball MM, Friedman WA, Foote KD, Bova FJ, Chi Y-Y. Linear accelerator radiosurgery for cavernous sinus meningiomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2009;87:120–7.
dos Santos MA, de Salcedo JB, Gutierrez Diaz JA, Calvo FA, Samblas J, Marsiglia H, et al. Long-term outcomes of stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of cavernous sinus meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:1436–41.
Haghighi N, Seely A, Paul E, Dally M. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign intracranial tumours of the cavernous sinus. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22:1450–5.
Gudjonsson O, Blomquist E, Nyberg G, Pellettieri L, Montelius A, Grusell E, et al. Stereotactic irradiation of skull base meningiomas with high energy protons. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1999;141:933–40.
Vernimmen FJ, Harris JK, Wilson JA, Melvill R, Smit BJ, Slabbert JP. Stereotactic proton beam therapy of skull base meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;49:99–105.
Weber DC, Lomax AJ, Peter Rutz H, Stadelmann O, Egger E, Timmermann B, et al. Spot-scanning proton radiation therapy for recurrent, residual or untreated intracranial meningiomas. Radiother Oncol. 2004;71:251–8.
Slater JD, Loredo LN, Chung A, Bush DA, Patyal B, Johnson WD, et al. Fractionated proton radiotherapy for benign cavernous sinus meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:e633–7.
Wenkel E, Thornton AF, Finkelstein D, Adams J, Lyons S, De La Monte S, et al. Benign meningioma: partially resected, biopsied, and recurrent intracranial tumors treated with combined proton and photon radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:1363–70.
Hug EB, DeVries A, Thornton AF, Munzenrider JE, Pardo FS, Hedley-Whyte ET, et al. Management of atypical and malignant meningiomas: role of high-dose, 3D-conformal radiation therapy. J Neurooncol. 2000;48:151–60.
Noël G, Habrand J-L, Mammar H, Haie-Meder C, Pontvert D, Dederke S, et al. Highly conformal therapy using proton component in the management of meningiomas. Strahlenther Onkol. 2002;178:480–5.
Noël G, Bollet MA, Calugaru V, Feuvret L, Haie-Meder C, Dhermain F, et al. Functional outcome of patients with benign meningioma treated by 3D conformal irradiation with a combination of photons and protons. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62:1412–22.
Boskos C, Feuvret L, Noel G, Habrand J-L, Pommier P, Alapetite C, et al. Combined proton and photon conformal radiotherapy for intracranial atypical and malignant meningioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75:399–406.
Simpson D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957;20:22–39.
Adegbite AB, Khan MI, Paine KWE, Tan LK. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurosurg. 1983;58:51–6.
Jääskeläinen J. Seemingly complete removal of histologically benign intracranial meningioma: late recurrence rate and factors predicting recurrence in 657 patients. A multivariate analysis. Surg Neurol. 1986;26:461–9.
Mirimanoff RO, Dosoretz DE, Linggood RM, Ojemann RG, Martuza RL. Meningioma: analysis of recurrence and progression following neurosurgical resection. J Neurosurg. 1985;62:18–24. doi:10.3171/jns.1985.62.1.0018.
Soyuer S, Chang EL, Selek U, Shi W, Maor MH, DeMonte F. Radiotherapy after surgery for benign cerebral meningioma. Radiother Oncol. 2004;71:85–90.
Yamashita J, Handa H, Iwaki K, Abe M. Recurrence of intracranial meningiomas, with special reference to radiotherapy. Surg Neurol. 1980;14:33–40.
Marks SM, Whitwell HL, Lye RH. Recurrence of meningiomas after operation. Surg Neurol. 1986;25:436–40.
Gudjonsson O, Blomquist E, Lilja A, Ericson H, Bergstrom M, Nyberg G. Evaluation of the effect of high-energy proton irradiation treatment on meningiomas by means of 11C-L-methionine PET. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000;27:1793–9.
Ikeda H, Tsuyuguchi N, Kunihiro N, Ishibashi K, Goto T, Ohata K. Analysis of progression and recurrence of meningioma using (11)C-methionine PET. Ann Nucl Med. 2013;27:772–80. doi:10.1007/s12149-013-0747-z.
Cornelius JF, Langen KJ, Stoffels G, Hanggi D, Sabel M, Jakob SH. Positron emission tomography imaging of meningioma in clinical practice: review of literature and future directions. Neurosurgery. 2012;70:1033–41. Discussion 1042.
Iuchi T, Iwadate Y, Namba H, Osato K, Saeki N, Yamaura A, et al. Glucose and methionine uptake and proliferative activity in meningiomas. Neurol Res. 1999;21:640–4.
Arita H, Kinoshita M, Okita Y, Hirayama R, Watabe T, Ishohashi K, et al. Clinical characteristics of meningiomas assessed by 11C-methionine and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography. J Neurooncol. 2012;107:379–86.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK. WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 4th ed. Lyon: IARC; 2007.
Grusell E, Montelius A, Russell KR, Blomquist E, Pellettieri L, Lilja A, et al. Patient positioning for fractionated precision radiation treatment of targets in the head using fiducial markers. Radiother Oncol. 1994;33:68–72.
Russell KR, Isacsson U, Saxner M, Ahnesjo A, Montelius A, Grusell E, et al. Implementation of pencil kernel and depth penetration algorithms for treatment planning of proton beams. Phys Med Biol. 2000;45:9–27.
ICRU. Prescribing, recording and reporting photon beam therapy (report 50). Bethesda: International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements; 1993.
Time, Dose and Fractionation in Radiotherapy. In: Hall EJ, Giaccia AJ, editors. Radiobiology for the radiologist. Philadelphia: Lippincott and Williams; 2012.
Alvernia JE, Sindou MP. Preoperative neuroimaging findings as a predictor of the surgical plane of cleavage: prospective study of 100 consecutive cases of intracranial meningioma. J Neurosurg. 2004;100:422–30.
Simis A, de Aguiar PH P, Leite CC, Santana Jr PA, Rosemberg S, Teixeira MJ. Peritumoral brain edema in benign meningiomas: correlation with clinical, radiologic, and surgical factors and possible role on recurrence. Surg Neurol. 2008;70:471–7. Discussion 477.
Lee JW, Kang KW, Park SH, Lee SM, Paeng JC, Chung JK, et al. 18F-FDG PET in the assessment of tumor grade and prediction of tumor recurrence in intracranial meningioma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36:1574–82.
Lippitz B, Cremerius U, Mayfrank L, Bertalanffy H, Raoofi R, Weis J, et al. PET-study of intracranial meningiomas: correlation with histopathology, cellularity and proliferation rate. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1996;65:108–11.
Wakai S, Yamakawa K, Manaka S, Takakura K. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage caused by brain tumor: its incidence and clinical significance. Neurosurgery. 1982;10:437–44.
Bosnjak R, Derham C, Popovic M, Ravnik J. Spontaneous intracranial meningioma bleeding: clinicopathological features and outcome. J Neurosurg. 2005;103:473–84.
Martinez-Lage JF, Poza M, Martinez M, Esteban JA, Antunez MC, Sola J. Meningiomas with haemorrhagic onset. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991;110:129–32.
Kwon Y, Ahn JS, Jeon SR, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Lee JK, et al. Intratumoral bleeding in meningioma after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:657–62.
Mangubat EZ, Byrne RW. Major intratumoral hemorrhage of a petroclival atypical meningioma: case report and review of literature. Skull Base. 2010;20:469–74.
Navarria P, Pessina F, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Villa E, Ascolese AM, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in skull base meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2015;124:283–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryttlefors, M., Danfors, T., Latini, F. et al. Long-term evaluation of the effect of hypofractionated high-energy proton treatment of benign meningiomas by means of 11C-l-methionine positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 1432–1443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3310-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3310-z