Abstract
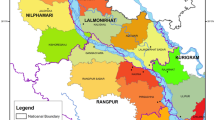
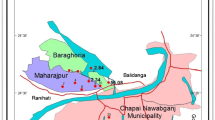
Arsenic is present in groundwater at Siliguri–Jalpaiguri area, West Bengal, India. This is the place where Tista river descending from the Himalayas meets the alluvial plain. The area represents alluvial fan and floodplains of Tista, Mahananda-Balasan, Jaladhaka and its tributaries. In the river sediment samples, para- and ferro-magnetic minerals within 0.3–0.05 mm fraction contain 9–80 ppm of arsenic. The study indicates that iron bearing minerals viz. biotite, hornblende as well as iron coated grains of the sediment are major contributors towards arsenic budget. Though magnetite as a mineral shows maximum arsenic content (22 ppm), it is volumetrically not of much significance. Measurement of groundwater collected from tube wells shows up to 0.05 ppm of arsenic. These arsenic contaminated tube wells occur in a linear fashion along the course of the rivers. Moreover, localization of contaminated tube wells coincides with the change of channel gradient as observed in longitudinal section. The study enumerates a cause–effect relationship of arsenic occurrence with river gradient and fluvial sedimentation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya SK, Lahiri S, Raymahashay BC, Bhowmik A (2000) Arsenic toxicity of groundwater in parts of the Bengal basin in India and Bangladesh: the role of Quarternary stratigraphy and Holocene sea-level fluctuation. Environ Geol 39:1127–1137
BGS (1999) Groundwater studies for arsenic ontamination in Bangladesh. Main Report, London, UK. British Geological Survey, Mott MacDonald Ltd, UK
Bhattacharya P, Chatterjee D, Jacks G (1997) Occurrence of As-contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from the delta plains, eastern India: options for safe drinking water supply. Water Resour Dev 13:76–92
CGWB (1999) High incidence of arsenic in groundwater in West Bengal. Central Ground Water Board, India, Ministry of Water resource, Government of India
Dowling CB, Poreda RJ, Basu AR, Peters SL (2002) Geochemical study of arsenic release mechanisms in the Bengal basin groundwater. Water Resour Res 38(9):1173
Mukherjee PK, Taraknath Pal, Sengupta S, Shome S (2001) Arsenic rich phases in aquifer sediments from southern West Bengal. J Geol Soc India 58:173–176
Mukhopadhyay B, Mukherjee PK, Debkumar Bhattacharyya, Sengupta S (2006) Delineation of arsenic-contaminated zones in Bengal Delta, India: a Geographic Information System and fractal approach. Environ Geol 49:1009–1020
PHED (1991) Arsenic pollution in groundwater in West Bengal, Report of Arsenic investigation project to the National Drinking water Mission, New Delhi, India
Sengupta S, Mukherjee PK, Pal T, Shome S (2004) Nature and origin of arsenic carriers in shallow aquifer sediments of Bengal Delta, India. Environ Geol 45(8):1071–1081
WHO (1996) Guidelines of drinking water-recommendation, vol 2, 2nd edn. World Health Organisation, Geneva
Yan X-P, Kerrich R, Hendry MJ (2000) Distribution of arsenic(3), arsenic(5) and total inorganic arsenic in porewaters from a thick till and clay rich aquitard sequence, Saskatchewan, Canada. Geochem Cosmochem Acta 62:2637–2648
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Director General, Geological Survey of India for according permission to publish the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, D., Mukherjee, P.K. Contamination of shallow aquifers by arsenic in upper reaches of Tista river at Siliguri–Jalpaiguri area of West Bengal, India. Environ Geol 57, 1687–1692 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1450-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1450-6