Abstract
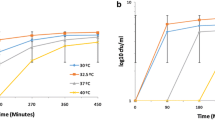
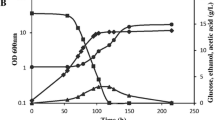
Metabolically active cells produce a wide array of metabolites that can inhibit their growth. Acetate is a widely known preservative, and it is also produced by yeast cells during their growth. Kluyveromyces marxianus DSM 5422 is a promising yeast strain that could be employed in biotechnological processes, but the knowledge of its stress physiology is scarce. Here, we investigate the effects of acetate on growth and changes in cell population structure during adaptation to elevated concentrations of acetate in K. marxianus DSM 5422. Our results indicate that acetate inhibits growth in a pH-dependent manner and has pronounced effects if yeast is grown on lactose or galactose. When challenged with acetate, culture extends lag phase, during which cells adapt to elevated acetate concentrations, and growth reoccurs, albeit at a slower rate, when majority of the population is acetate resistant. Acetate resistance is maintained only if acetate is present in the media or if the culture has reached end of active growth phase. This study shows possible caveats in lactose fermentation with K. marxianus and gives a further perspective in non-conventional yeast applications in biotechnology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arneborg N, Jespersen L, Jakobsen M (2000) Individual cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zygosaccharomyces bailii exhibit different short-term intracellular pH responses to acetic acid. Arch Microbiol 174(1–2):125–128
Banat IM, Nigam P, Marchant R (1992) Isolation of thermotolerant, fermentative yeasts growing at 52 °C and producing ethanol at 45 °C and 50 °C. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8(3):259–263
Bellaver LH, de Carvalho NMB, Abrahão-Neto J, Gombert AK (2004) Ethanol formation and enzyme activities around glucose-6-phosphate in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS 6556 exposed to glucose or lactose excess. FEMS Yeast Res 4(7):691–698
Bianchi MM, Brambilla L, Protani F, Liu CL, Lievense J, Porro D (2001) Efficient homolactic fermentation by Kluyveromyces lactis strains defective in pyruvate utilization and transformed with the heterologous LDH gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(12):5621–5625
Cabral MG, Viegas CA, Sa-Correia I (2001) Mechanisms underlying the acquisition of resistance to octanoic-acid-induced-death following exposure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to mild stress imposed by octanoic acid or ethanol. Arch Microbiol 175:301–307
Carmelo V, Santos H, Sa’-Correira I (1997) Effect of extracellular acidification on the activity of plasma membrane ATPase and on the cytosolic and vacuolar pH of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1325:63–70
Carvalho-Silva M, Spencer-Martins I (1990) Modes of lactose uptake in the yeast species Kluyveromyces marxianus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 57:77–81
De Bruijne AW, Schuddemat J, Van den Broek PJ, Van Steveninck J (1988) Regulation of sugar transport systems of Kluyveromyces marxianus: the role of carbohydrates and their catabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 939(3):569–576
Ding J, Bierma J, Smith MR, Poliner E, Wolfe C, Hadduck AN, Zara S, Jirikovic M, Zee K, Penner MH, Patton-Vogt J, Bakalinsky AT (2013) Acetic acid inhibits nutrient uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: auxotrophy confounds the use of yeast deletion libraries for strain improvement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(16):7405–7416
Fonseca GG, Gombert AK, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2007) Physiology of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus during batch and chemostat cultures with glucose as the sole carbon source. FEMS Yeast Res 7:422–435
Fonseca GG, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Gombert AK (2008) The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and its biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(3):339–354
Fonseca GG, De Carvalho NMB, Gombert AK (2013) Growth of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS 6556 on different sugar combinations as sole carbon and energy source. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(11):5055–5067
Gasnier B (1987) Characterization of low- and high-affinity glucose transport in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochim Biophys Acta 903:425–433
Goncalves JA, Castillo FJ (1982) Partial purification and characterization of β-D-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Diary Sci 65(11):2088–2094
Hermann R, Lehmann M, Buchs J (2003) Characterization of gas–liquid mass transfer phenomena in microtiter plates. Biotechnol Bioeng 81(2):178–186
Klosinska MM, Crutchfield CA, Bradley PH, Rabinowitz JD, Broach JR (2011) Yeast cells can access distinct quiescent states. Genes Dev 25(4):336–349
Koynov A, Tryggvason G, Khinast JG (2007) Characterization of the localized hydrodynamic shear forces and dissolved oxygen distribution in sparged bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 97(2):317–331
Lane MM, Morrissey JP (2010) Kluyveromyces marxianus: a yeast emerging from its sister’s shadow. Fungal Biol Rev 24(1–2):17–26
Löser C, Urit T, Keil P, Bley T (2015) Studies on the mechanism of synthesis of ethyl acetate in Kluyveromyces marxianus DSM 5422. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1131–1144
Mira NP, Teixeira MC, Sá-Correia I (2010) Adaptive response and tolerance to weak acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a genome-wide view. Omics: J Integr Biol 14(5):525–540
Orij R, Urbanus ML, Vizeacoumar FJ, Giaever G, Boone C, Nislow C, Brul S, Smits GJ (2012) Genome-wide analysis of intracellular pH reveals quantitative control of cell division rate by pHc in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biology 13(9):R80
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hagerdal B (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. I: inhibition and detoxification. Bioresour Technol 74:17–24
Piper P, Calderon CO, Hatzixanthis K, Mollapour M (2001) Weak acid adaptation: the stress response that confers yeasts with resistance to organic acid food preservatives. Microbiology 147:2635–2642
Remize F, Andrieu E, Dequin S (2000) Engineering of the pyruvate dehydrogenase bypass in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: role of the cytosolic Mg2+ and mitochondrial K+ acetaldehyde dehydrogenases Ald6p and Ald4p in acetate formation during alcoholic fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(8):3151–3159
Rosa MF, Sá-Correia I (1992) Ethanol tolerance and activity of plasma membrane ATPase in Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzym Microb Technol 14:23–27
Rouwenhorst RJ, Visser LE, van der Baan AA, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1988) Production, distribution, and kinetic properties of inulinase in continuous culture of Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS 6556. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1131–1137
Rouwenhorst RJ, Ritmeester WS, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1990) Localization of inulinase and invertase in Kluyveromyces species. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(11):3329–3336
Rugthaworn P, Murata Y, Machida M, Apiwatanapiwat W, Hirooka A, Thanapase W, Dangjarean H, Ushiwaka S, Morimitsu K, Kosugi A, Arai T, Vaithanomsat P (2014) Growth inhibition of thermotolerant yeast, Kluyveromyces marxianus, in hydrolysates from cassava pulp. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173(5):1197–1208
Sansonetti S, Hobley TJ, Curcio S, Villadsen J, Sin G (2013) Use of continuous lactose fermentation for ethanol production by Kluveromyces marxianus for verification and extension of a biochemically structured model. Bioresour Technol 130:703–709
Schuller C, Mamnun YM, Mollapour M, Krapf G, Schuster M, Bauer BE, Piper PW, Kuchler K (2004) Global phenotypic analysis and transcriptional profiling defines the weak acid stress response regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 15:706–720
Sellick CA, RN C, RJ R (2008) Galactose metabolism in yeast-structure and regulation of the Leloir pathway enzymes and the genes encoding them. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 269:111–150
Signori L, Passolunghi S, Ruohonen L, Porro D, Branduardi P (2014) Effect of oxygenation and temperature on glucose-xylose fermentation in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS712 strain. Microb Cell Factories 13(1):51
Stratford M, Steels H, Nebe-von-Caron G, Novodvorska M, Hayer K, Archer DB (2013) Extreme resistance to weak-acid preservatives in the spoilage yeast Zygosaccharomyces bailii. Int J Food Microbiol 166(1):126–134
Teixeira MC, Sa ‘-Correia I (2002) Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistance to chlorinated phenoxyacetic acid herbicides involves Pdr1p-mediated transcriptional activation of TPO1 and PDR5 genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:530–537
Thomas KC, Hynes SH, Ingledew WM (2002) Influence of medium buffering capacity on inhibition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth by acetic and lactic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1616–1623
Toussaint M, Levasseur G, Gervais-Bird J, Wellinger RJ, Elela SA, Conconi A (2006) A high-throughput method to measure the sensitivity of yeast cells to genotoxic agents in liquid cultures. Mutat Res 606(1–2):92–105
van Heerden JH, Wortel MT, Bruggeman FJ, Heijnen JJ, Bollen YJM, Planqué R, Teusink B (2014) Lost in transition: startup of glycolysis yields subpopulations of nongrowing cells. Science 343:1245114–1245114
Viegas CA, Almeida PF, Cavaco M, Sa ‘-Correia I (1998) The H(+)-ATPase in the plasma membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is activated during growth latency in octanoic acid-supplemented medium accompanying the decrease in intracellular pH and cell viability. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:779–783
Wilkins MR, Mueller M, Eichling S, Banat IM (2008) Fermentation of xylose by the thermotolerant yeast strains Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB2, IMB4, and IMB5 under anaerobic conditions. Process Biochem 43:346–350
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by European Regional Development Fund project Nr. 2DP/2.1.1.1.0/14/APIA/VIAA/043.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 662 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynova, J., Kokina, A., Kibilds, J. et al. Effects of acetate on Kluyveromyces marxianus DSM 5422 growth and metabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 4585–4594 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7392-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7392-0