Abstract
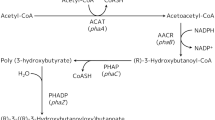
Haloferax mediterranei is capable of producing large amounts of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) from many kinds of carbon sources, with exopolysaccharide (EPS) as a by-product. In this study, we identified a gene cluster involved in EPS biosynthesis in H. mediterranei. Knocking out the genes in this cluster encoding the putative UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 6-dehydrogenase (HFX_2145), glycosyltransferases (HFX_2146 and HFX_2147) and polysaccharide transporter (HFX_2148) eliminated EPS synthesis. The deficiency in EPS biosynthesis in the mutant strain remarkably decreased the viscosity of culture broth, and hence increased the dissolved oxygen content and decreased the foaming propensity. Compared with the wild-type (WT) strain, the PHBV production of the EPS-mutant strain was significantly enhanced (approximately 20 %), whereas the cell growth rate remained similar under the same culture conditions. These results indicated that the carbon sources used for synthesizing EPS were shifted to PHBV production. Thus, a novel engineered H. mediterranei strain was developed, which would be favorable for future industrial production of PHBV.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton J, Meseguer I, Rodriguez-Valera F (1988) Production of an extracellular polysaccharide by Haloferax mediterranei. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(10):2381–2386
Bauer H, Owen AJ (1988) Some structural and mechanical-properties of bacterially production poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate-co-beta-hydroxyvalerate. Colloid Polym Sci 266(3):241–247. doi:10.1007/bf01452586
Boan IF, Garcia-Quesada JC, Anton J, Rodriguez-Valera F, Marcilla A (1998) Flow properties of haloarchaeal polysaccharides in aqueous solutions. Polymer 39(26):6945–6950
Booth SC, Workentine ML, Wen J, Shaykhutdinov R, Vogel HJ, Ceri H, Turner RJ, Weljie AM (2011) Differences in metabolism between the biofilm and planktonic response to metal stress. J Proteome Res 10(7):3190–3199. doi:10.1021/pr2002353
Brandt U, Raberg M, Voigt B, Hecker M, Steinbuechel A (2012) Elevated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis in mutants of Ralstonia eutropha H16 defective in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(2):471–483. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-3909-3
Cai S, Cai L, Liu H, Liu X, Han J, Zhou J, **ang H (2012) Identification of the haloarchaeal phasin (PhaP) that functions in polyhydroxyalkanoate accumulation and granule formation in Haloferax mediterranei. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(6):1946–1952. doi:10.1128/aem.07114-11
Chen G-Q (2009) A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem Soc Rev 38(8):2434–2446. doi:10.1039/b812677c
Chen G-Q (2010) Industrial production of PHA. In: Chen GQ (ed) Plastics from bacteria: natural functions and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–132
Chen CW, Don TM, Yen HF (2006) Enzymatic extruded starch as a carbon source for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) by Haloferax mediterranei. Process Biochem 41(11):2289–2296. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.05.026
Don TM, Chen CW, Chan TH (2006) Preparation and characterization of poly(hydroxyalkanoate) from the fermentation of Haloferax mediterranei. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 17(12):1425–1438
Escalona AM, Varela FR, Gomis AM (1996) Procedure for extraction of polyhydroxyalkanoates from halophilic bacteria which contain them. US 5536419
Falb M, Mueller K, Koenigsmaier L, Oberwinkler T, Horn P, von Gronau S, Gonzalez O, Pfeiffer F, Bornberg-Bauer E, Oesterhelt D (2008) Metabolism of halophilic archaea. Extremophiles 12(2):177–196. doi:10.1007/s00792-008-0138-x
Fialho AM, Moreira LM, Granja AT, Popescu AO, Hoffmann K, Sa-Correia I (2008) Occurrence, production, and applications of gellan: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(6):889–900. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1496-0
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):95–108. doi:10.1038/nrmicro821
Han J, Zhang F, Hou J, Liu X, Li M, Liu H, Cai L, Zhang B, Chen Y, Zhou J, Hu S, **ang H (2012) Complete genome sequence of the metabolically versatile halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei, a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) producer. J Bacteriol 194(16):4463–4464. doi:10.1128/JB.00880-12
Holmes ML, Nuttall SD, Dyallsmith ML (1991) Construction and use of halobacterial shuttle vectors and further-studies on haloferax DNA gyrase. J Bacteriol 173(12):3807–3813
Huang TY, Duan KJ, Huang SY, Chen CW (2006) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from inexpensive extruded rice bran and starch by Haloferax mediterranei. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33(8):701–706. doi:10.1007/s10295-006-0098-z
Jung YM, Lee YH (2000) Utilization of oxidative pressure for enhanced production of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) in Ralstonia eutropha. J Biosci Bioeng 90(3):266–270
Kadouri D, Burdman S, Jurkevitch E, Okon Y (2002) Identification and isolation of genes involved in poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthesis in Azospirillum brasilense and characterization of a phbC mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(6):2943–2949. doi:10.1128/aem.68.6.2943-2949.2002
Keshavarz T, Roy I (2010) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: bioplastics with a green agenda. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(3):321–326. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2010.02.006
Koller M, Hesse P, Bona R, Kutschera C, Atlic A, Braunegg G (2007) Potential of various archae- and eubacterial strains as industrial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers from whey. Macromol Biosci 7(2):218–226. doi:10.1002/mabi.200600211
Lillo JG, Rodriguez-Valera F (1990) Effects of culture conditions on poly(beta-hydroxybutyric acid) production by Haloferax mediterranei. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(8):2517–2521
Liu H, Han J, Liu X, Zhou J, **ang H (2011) Development of pyrF-based gene knockout systems for genome-wide manipulation of the archaea Haloferax mediterranei and Haloarcula hispanica. J Genet Genomics 38(6):261–269. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2011.05.003
Lu Q, Han J, Zhou L, Zhou J, **ang H (2008) Genetic and biochemical characterization of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) synthase in Haloferax mediterranei. J Bacteriol 190(12):4173–4180. doi:10.1128/jb.00134-08
Mishra P, Srivastava P, Kundu S (2005) A comparative evaluation of oxygen mass transfer and broth viscosity using Cephalosporin-C production as a case strategy. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21(4):525–530. doi:10.1007/s11274-004-3489-1
Nagorska K, Ostrowski A, Hine K, Holland IB, Obuchowski M (2010) Importance of eps genes from Bacillus subtilis in biofilm formation and swarming. J Appl Genet 51(3):369–381. doi:10.1007/bf03208867
Namboori SC, Graham DE (2008) Acetamido sugar biosynthesis in the euryarchaea. J Bacteriol 190(8):2987–2996. doi:10.1128/jb.01970-07
Palmer BR, Marinus MG (1994) The dam and dcm strains of Escherichia coli — a review. Gene 143(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90597-5
Parolis H, Parolis LAS, Boan IF, Rodriguez-Valera F, Widmalm G, Manca MC, Jansson PE, Sutherland IW (1996) The structure of the exopolysaccharide produced by the halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei strain R4 (ATCC 33500). Carbohydr Res 295:147–156
Rodriguez-Valera F, Lillo JAG (1992) Halobacteria as producers of polyhydroxyalkanoates. FEMS Microbiol Rev 103(2–4):181–186. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05836.x
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schügerl K (1981) Oxygen transfer into highly viscous media. Reactors and reactions. Springer, Berlin, pp 71–174
Trevelyan WE, Forrest RS, Harrison JS (1952) Determination of yeast carbohydrates with the anthrone reagent. Nature 170(4328):626–627. doi:10.1038/170626a0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2010AA09Z401), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 30621005, 30830004, and 30925001) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCXZ- EW-G-2-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Cai, L., Wu, J. et al. Improving polyhydroxyalkanoate production by knocking out the genes involved in exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Haloferax mediterranei . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3027–3036 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4415-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4415-3