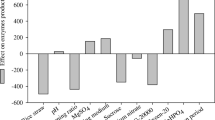
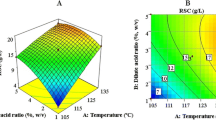
Abstract
Cellulase, Tween 80, and β-glucosidase loading were studied and optimized by response surface methodology to improve saccharification. Microwave alkali-pretreated rice straw used as substrate for onsite enzyme production by Aspergillus heteromorphus and Trichoderma reesei. The highest enzymatic hydrolysis (84%) was obtained from rice straw at crude enzyme loading of 10 FPU/gds of cellulase, 0.15% Tween 80, and 100 international unit/g dry solids of β-glucosidase activities. Enzymatic hydrolyzate of pretreated rice straw was used for ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Scheffersomyces stipitis, and by co-culture of both. The yield of ethanol was 0.50, 0.47, and 0.48 gp/gs by S. cerevisiae, S. stipitis, and by co-culture, respectively, using pretreated rice straw hydrolyzate. The co-culture of S. cerevisiae and S. stipitis produced 25% more ethanol than S. cerevisiae alone and 31% more ethanol than S. stipitis alone. During anaerobic fermentation 65.08, 36.45, and 50.31 μmol/ml CO2 released by S. cerevisiae, S. stipitis, and by co-culture, respectively. The data indicated that saccharification efficiency using optimized crude enzyme cocktail was good, and enzymatic hydrolyzate could be fermented to produce ethanol.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed A, Vermette P (2008) Enhanced enzyme production from mixed cultures of Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 and Aspergillus niger LMA grown as fed batch in a stirred tank bioreactor. Biochem Eng J 42:41–46
Aswathy US, Sukumaran RK, Devi GL, Rajasree KP, Singhania RR, Pandey A (2009) Bio-ethanol from water hyacinth biomass: an evaluation of enzymatic saccharification strategy. Bioresour Technol 101:925–930
Balat M, Balat H, Oz C (2008) Progress in bioethanol processing. Prog Energy Combust Sci 34:551–573
Banerjee S, Mudliar S, Giri B, Satpute D, Chakrabarti T, Pandey RA (2010) Commercializing lignocellulosic bioethanol: technology bottlenecks and possible remedies. Biofuels Bioprod Bior 4:77–93
Binod P, Sindhu R, Singhania RR, Vikram S, Devi L, Nagalakshmi S, Kurien N, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2010) Bioethanol production from rice straw: an overview. Bioresour Technol 101:4767–4774
Caputi AJ, Ueda M, Brown T (1968) Spectrophotometric determination of ethanol in wine. American J Enol Vitti 19:160–165
Chen Y (2011) Development and application of co-culture for ethanol production by co-fermentation of glucose and xylose: a systematic review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:581–597
Chen M, **a L, Xue P (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob and ethanol production from cellulosic hydrolyzate. Int Biodeter Biodeg 59:85–89
Chen M, Zhao J, **a L (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of maize straw polysaccharides for the production of reducing sugars. Carbohyd Polymers 71:411–415
Cheng YS, Zheng Y, Yu CW, Dooley TM, Jenkins BM, VanderGheynst JS (2010) Evaluation of high solids alkaline pretreatment of rice straw. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1768–1784
Dehkhoda A, Tomas B, Mohammad MJ (2008) Comparison of vacuum and high pressure evaporated wood hydrolyzate for ethanol production by repeated fed batch using flocculating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BioResources 4(1):309–320
Dhillon GS, Oberoi HS, Kaur S, Bansal S, Brar SK (2011) Value-addition of agricultural wastes for augmented cellulase and xylanase production through solid-state tray fermentation employing mixed-culture of fungi. Ind Crop Prod 34:1160–1167
du Preez JC, Bosch M, Prior BA (1986) The fermentation of hexose and pentose sugars by Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:228–233
El-Zawawy WK, Ibrahima MM, Abdel-Fattahb YR, Soliman NA, Mahmoud MM (2011) Acid and enzyme hydrolysis to convert pretreated lignocellulosic materials into glucose for ethanol production. Carbohyd Polymers 84:865–871
Fang H, Zhao C, Song XY (2010) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-exploded corn stover by two approaches: Response surface methodology or using cellulase from mixed cultures of Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 and Aspergillus niger NL02. Bioresour Technol 101:4111–4119
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Goering HK, Van Soest PJ (1970) Forage fiber analysis (apparatus, reagent, procedures, and some applications). Agricultural handbook no. 379. Agriculture Research Service-United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, pp 1–20
Gottschalk LMF, Oliveira RO, Bon EPS (2010) Cellulases, xylanases, β-glucosidase and ferulic acid esterase produced by Trichoderma and Aspergillus act synergistically in the hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Biochem Eng J 51:72–78
Gupta R, Sharma KK, Kuhad RC (2009) Separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) of Prosopis juliflora, a woody substrate, for the production of cellulosic ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis-NCIM 3498. Bioresour Technol 100:1214–1220
Hamidimotlagh R, Iraj N, Giti E, Sorah A (2007) Mixed sugar fermentation by Pichia stipitis, Sacharomyces cerevisiaea, and an isolated xylose fermenting Kluyveromyces marxianus and their cocultures. African J Biotechnol 6(9):1110–1114
Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aerts A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, ** YS, Passoth V, Richardson PM (2007) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nature Biotechnol 25:319–326
Kapoor M, Nair LM, Kuhad RC (2008) Cost-effective xylanase production from free and immobilized Bacillus pumilus strain MK001 and its application in saccharification of Prosopis juliflora. Biochem Eng J 38:88–97
Kurtzman CP, Suzuki M (2010) In: Kurtzman CP, Fell J, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, volume 2, 5th edn. Elsevier, New York, pp 773–777
Maeda RN, Serpa VI, Rocha VAL, Mesquita RAA, Anna, LMMS, Castro AM, Driemeier CE, Pereira N, Polikarpov I (2011) Enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated sugarcane bagasse using Penicillium funiculosum and Trichoderma harzianum cellulases. Process Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2011.01.022
Mamma D, Christakopoulos P, Koullas D, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Koukios E (1995) An alternative approach to the bioconversion of sweet sorghum carbohydrates to ethanol. Biomass Bioenerg 8:99–103
Manonmani HK, Sreekanitah KR (1987) Saccharification of sugar-cane bagasse with enzymes from Aspergillus ustus and Trichoderma viride. Enzyme Microb Technol 9:484–488
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Pereira FB, Guimarães PMR, Teixeira JA, Domingues L (2010) Optimization of low-cost medium for very high gravity ethanol fermentations by Saccharomyces cerevisiae using statistical experimental designs. Bioresour Technol 101:7856–7863
Saha BC, Nichols NN, Qureshi N, Cotta MA (2011) Comparison of separate hydrolysis and fermentation and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation processes for ethanol production from wheat straw by recombinant Escherichia coli strain FBR5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:865–874
Silverstein RA, Chen Y, Sharma-Shivappa RR, Boyette MD, Osborne J (2007) A comparison of chemical pretreatment methods for improving saccharification of cotton stalks. Bioresour Technol 98:3000–3011
Singh A, Tuteja S, Singh N, Bishnoi NR (2011) Enhanced saccharification of rice straw and hulls by microwave-alkali pretreatment and lignocellulolytic enzyme production. Bioresour Technol 102:1773–1782
Sukumaran RK, Singhania RR, Mathew GM, Pandey A (2009) Cellulase production using biomass feed stock and its application in lignocellulose saccharification for bio-ethanol production. Renew Energy 34:421–424
Taniguchi M, Tohma T, Itaya T, Fuji M (1997) Ethanol production from a mixture of glucose and xylose by co-culture of Pichia stipitis sand a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Fermen Bioengg 83:364–370
Xu Y, Isom L, Hanna MA (2010) Adding value to carbon dioxide from ethanol fermentations. Bioresour Technol 101:3311–3319
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial assistance to Ms. Anita Singh by CSIR, New Delhi in the form of Senior Research Fellowship and University Grant Commission, New Delhi for providing financial support under the Major Research Project scheme F-33-144/2007(SR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Bishnoi, N.R. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated rice straw and ethanol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 1785–1793 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3870-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3870-1