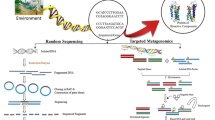
Abstract
Natural products isolated from sponges are an important source of new biologically active compounds. However, the development of these compounds into drugs has been held back by the difficulties in achieving a sustainable supply of these often-complex molecules for pre-clinical and clinical development. Increasing evidence implicates microbial symbionts as the source of many of these biologically active compounds, but the vast majority of the sponge microbial community remain uncultured. Metagenomics offers a biotechnological solution to this supply problem. Metagenomes of sponge microbial communities have been shown to contain genes and gene clusters typical for the biosynthesis of biologically active natural products. Heterologous expression approaches have also led to the isolation of secondary metabolism gene clusters from uncultured microbial symbionts of marine invertebrates and from soil metagenomic libraries. Combining a metagenomic approach with heterologous expression holds much promise for the sustainable exploitation of the chemical diversity present in the sponge microbial community.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Munro MH, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR (2006) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 23:26–78
Beer S, Ilan M (1998) In situ measurements of photosynthetic irradiance responses of two Red Sea sponges growing under dim light conditions. Mar Biol 131:613–617
Bewley CA, Holland ND, Faulkner DJ (1996) Two classes of metabolites from Theonella swinhoei are localized in distinct populations of bacterial symbionts. Experientia 52:716–722
Bode HB, Muller R (2005) The impact of bacterial genomics on natural product research. Angew Chem (Int Ed) 44:6828–6846
Brady SF, Chao CJ, Clardy J (2002) New natural product families from an environmental DNA (eDNA) gene cluster. J Am Chem Soc 124:9968–9969
Brady SF, Chao CJ, Handelsman J, Clardy J. (2001) Cloning and heterologous expression of a natural product biosynthetic gene cluster from eDNA. Org Lett 3:1981–1984
Crews P, Manes LV, Boehler M (1986) Jasplakinolide, a cyclodepsipeptide from the marine sponge, Jaspis sp. Tetrahedron Lett 27:2797–2800
Fieseler L, Horn M, Wagner M, Hentschel U (2004) Discovery of the novel candidate phylum “Poribacteria” in marine sponges. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3724–3732
Fieseler L, Quaiser A, Schleper C, Hentschel U (2006) Analysis of the first genome fragment from the marine sponge-associated, novel candidate phylum Poribacteria by environmental genomics. Environ Microbiol 8:612–624
Flowers AE, Garson MJ, Webb RI, Dumdei EJ, Charan RD (1998) Cellular origin of chlorinated diketopiperazines in the dictyoceratid sponge Dysidea herbacea (Keller). Cell Tissue Res 292:597–607
Friedrich AB, Fischer I, Proksch P, Hacker J, Hentschel U (2001) Temporal variation of the microbial community associated with the Mediterranean sponge Apylsina aerophoba. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:105–113
Gillespie DE, Brady SF, Bettermann AD, Cianciotto NP, Liles MR, Rondon MR, Clardy J, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (2002) Isolation of antibiotics turbomycin A and B from a metagenomic library of soil microbial DNA. Appl Environ Microbol 68:4301–4306
Gross F, Ring MW, Perlova O, Fu J, Schneider S, Gerth K, Kuhlmann S, Stewart AF, Zhang Y, Muller R (2006) Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for methylmalonyl-CoA biosynthesis to enable complex heterologous secondary metabolite formation. Chem Biol 13:1253–1264
Handelsman J (2004) Metagenomics: application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:669–685
Handelsman J, Rondon MR, Brady SF, Clardy J, Goodman RM (1998) Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: a new frontier for natural products. Chem Biol 5:245–249
Hentschel U, Schmid M, Wagner M, Fieseler L, Gernert C, Hacker J (2001) Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the Mediterranean sponges Aplysina aerophoba and Aplysina cavernicola. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:305–312
Hentschel U, Hopke J, Horn M, Friedrich AB, Wagner M, Hacker J, Moore BS (2002) Molecular evidence for a uniform microbial community in sponges from different oceans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4431–4440
Hentschel U, Usher KM, Taylor MW (2006) Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:167–177
Hildebrand M, Waggoner LE, Liu H, Sudek S, Allen S, Anderson C, Sherman DH, Haygood M (2004) bryA: an unusual modular polyketide synthase gene from the uncultivated bacterial symbiont of the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina. Chem Biol 11:1543–1552
Jansen R, Kunze B, Reichenbach H, Hofle G (1996) Chondramides A-D, new cytostatic and antifungal cyclodepsipeptides from Chondromyces crocatus (Myxobacteria): Isolation and structure elucidation. Liebigs Ann 2:285–290
Julien B, Shah S (2002) Heterologous expression of epothilone biosynthetic genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:2772–2778
Keller NP, Turner G, Bennett JW (2005) Fungal secondary metabolism—from biochemistry to genomics. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:937–947
Khosla C, Keasling JD (2003) Metabolic engineering for drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:1019–1025
Kim TK, Fuerst JA (2006) Diversity of polyketide synthase genes from bacteria associated with the marine sponge Pseudoceratina clavata: culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Environ Microbiol 8:1460–1470
Kim TK, Garson MJ, Fuerst JA (2005) Marine actinomycetes related to the “Salinospora” group from the Great Barrier Reef sponge Pseudoceratina clavata. Environ Microbiol 7:509–518
Kobayashi J, Ishibashi M (1993) Bioactive metabolites of symbiotic marine organisms. Chem Rev 93:1753–1770
Kuznetsov G, Towle MJ, Cheng H, Kawamura T, TenDyke K, Liu D, Kishi Y, Yu MJ, Littlefield BA (2004) Induction of morphological and biochemical apoptosis following prolonged mitotic blockage by halichondrin B macrocyclic ketone analog E7389. Cancer Res 64:5760–5766
Lam KS (2006) Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:245–251
Loganzo F, Discafani CM, Annable T, Beyer C, Musto S, Hari M, Tan X, Hardy C, Hernandez R, Baxter M, Singanallore T, Khafizova G, Poruchynsky MS, Fojo T, Nieman JA, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Zask A, Andersen RJ, Greenberger LM (2003) HTI-286, a synthetic analogue of the tripeptide hemiasterlin, is a potent antimicrotubule agent that circumvents P-glycoprotein-mediated resistance in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 63:1838–1845
Long PF, Dunlap WC, Battershill CN, Jaspars M (2005) Shotgun cloning and heterologous expression of the patellamide gene cluster as a strategy to achieving sustained metabolite production. ChemBioChem 6:1760–1765
MacNeil IA, Tiong CL, Minor C, August PR, Grossman TH, Loiacono KA, Lynch BA, Phillips T, Narula S, Sundaramoorthi R, Tyler A, Aldredge T, Long H, Gilman M, Holt D, Osburne MS. (2001) Expression and isolation of antimicrobial small molecules from soil DNA libraries. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3:301–308
Margot H, Acebal C, Toril E, Amils R, Fernandez Puentes JL (2002) Consistent association of crenarchael Archae with sponges of the genus Axinella. Mar Biol 140:739–745
Martinez A, Kolvek SJ, Yip CL, Hopke J, Brown KA, MacNeil IA, Osburne MS (2004) Genetically modified bacterial strains and novel bacterial artificial chromosome shuttle vectors for constructing environmental libraries and detecting heterologous natural products in multiple expression hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2452–2463
Mendola D (2003) Aquaculture of three phyla of marine invertebrates to yield bioactive metabolites: process developments and economics. Biomol Eng 20:441–458
Mickel SJ, Sedelmeier GH, Niederer D, Daeffler R, Osmani A, Schreiner K, Seeger-Weibel M, Berod B, Schaer K, Gamboni R, Chen S, Chen W, Jagoe CT, Kinder FR, Loo M, Prasad K, Repic O, Shieh WC, Wang RM, Waykole L, Xu DD, Xue S (2004a) Large-scale synthesis of the anti-cancer marine natural product (+)-discodermolide. Part 1: synthetic strategy and preparation of a common precursor. Org Process Res Dev 8:92–100
Mickel SJ, Sedelmeier GH, Niederer D, Schuerch F, Grimler D, Koch G, Daeffler R, Osmani A, Hirni A, Schaer K, Gamboni R, Bach A, Chaudhary A, Chen S, Chen W, Hu B, Jagoe CT, Kim HY, Kinder FR, Liu Y, Lu Y, McKenna J, Prashad M, Ramsey TM, Repic O, Rogers L, Shieh WC, Wang RM, Waykole L (2004b) Large-scale synthesis of the anti-cancer marine natural product (+)-discodermolide. Part 2: synthesis of fragments C1-6 and C9-14. Org Process Res Dev 8:101–106
Mickel SJ, Sedelmeier GH, Niederer D, Schuerch F, Koch G, Kuesters E, Daeffler R, Osmani A, Seeger-Weibel M, Schmid E, Hirni A, Schaer K, Gamboni R, Bach A, Chen S, Chen W, Geng P, Jagoe CT, Kinder FR, Lee GT, McKenna J, Ramsey TM, Repic O, Rogers L, Shieh WC, Wang RM, Waykole L (2004c) Large-scale synthesis of the anti-cancer marine natural product (+)-discodermolide. Part 3: synthesis of fragment C15-21. Org Process Res Dev 8:107–112
Mickel SJ, Sedelmeier GH, Niederer D, Schuerch F, Seger M, Schreiner K, Daeffler R, Osmani A, Bixel D, Loiseleur O, Cercus J, Stettler H, Schaer K, Gamboni R, Bach A, Chen GP, Chen W, Geng P, Lee GT, Loeser E, McKenna J, Kinder FR, Konigsberger K, Prasad K, Ramsey TM, Reel N, Repic O, Rogers L, ShiehWC, Wang RM, Waykole L, Xue S, Florence G, Paterson I (2004d) Large-scale synthesis of the anti-cancer marine natural product (+)-discodermolide. Part 4: preparation of fragment C7-24. Org Process Res Dev (Article) 8:113–121
Mickel SJ, Niederer D, Daeffler R, Osmani A, Kuesters E, Schmid E, Schaer K, Gamboni R, Chen W, Loeser E, Kinder FR, Konigsberger K, Prasad K, Ramsey TM, Repic O, Wang RM, Florence G, Lyothier I, Paterson I (2004e) Large-scale synthesis of the anti-cancer marine natural product (+)-discodermolide. Part 5: linkage of fragments C1-6 and C7-24 and finale. Org Process Res Dev 8:122–130
Mutka SC, Carney JR, Liu Y, Kennedy J (2006) Heterologous production of epothilone C and D in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 45:1321–1330
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM (2000) The influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep 17:215–234
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM (2003) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat Prod 66:1022–1037
Newman DJ, Hill RT (2006a) New drugs from marine microbes: the tide is turning. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 33:539–544
Newman JD, Marshall J, Chang M, Nowroozi F, Paradise E, Pitera D, Newman KL, Keasling JD (2006b) High-level production of amorpha-4,11-diene in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor of metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:684–691
Olson JB, Lord CC, McCarthy (2000) Improved recoverability of microbial colonies from marine sponge samples. Microb Ecol 40:139–147
Pfeifer BA, Khosla C (2001) Biosynthesis of polyketides in heterologous hosts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:106–118
Pfeifer BA, Admiraal SJ, Gramajo H, Cane DE, Khosla C (2001) Biosynthesis of complex polyketides in a metabolically engineered strain of E. coli. Science 291:1790–1792
Piel J (2004) Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat Prod Rep 21:519–538
Piel J (2006) Bacterial symbionts: prospects for the sustainable production of invertebrate-derived pharmaceuticals. Curr Med Chem 13:39–50
Piel J, Hui D, Wen G, Butzke D, Platzer M, Fusentani N, Matsunaga S (2004) Antitumor polyketide biosynthesis by an uncultivated bacterial sumbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16222–16227
Rachid S, Krug D, Kunze B, Kochems I, Scharfe M, Zabriskie TM, Blocker H, Muller R (2006) Molecular and biochemical studies of chondramide formation—highly cytotoxic natural products from Chondromyces crocatus Cm c5. Chem Biol 13:667–681
Ridley CP, Bergquist PR, Harper MK, Faulkner DJ, Hooper JNA, Haygood MG (2005) Speciation and biosynthetic variation in four dictoceratid sponges and their cyanobacterial symbiont, Oscaillatoria spongeliae. Chem Biol 12:397–406
Rutzler K (1985) Associations between Caribbean sponges and photosynthetic organisms. In: Rutzler K (ed) New perspectives in sponge biology. Smithsonian Institution, Washington, pp 455–466
Santavy DL, Willenz P, Colwell RR (1990) Phenotypic study of bacteria associated with the Caribbean sclerosponge Ceratoporella nicholsoni. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1750–1762
Selvin J, Joseph S, Asha KRT, Manjusha WA, Sangeetha VS, Jayaseema DM, Antony MC, Denslin Vinitha AJ (2004) Antibacterial potential of antagonistic Streptomyces sp. Isolated from marine spone Dendrilla nigra. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 50:117–122
Schirmer A, Gadkari R, Reeves CD, Ibrahim F, DeLong EF, Hutchinson CR (2005) Metagenomic analysis reveals diverse polyketide synthase gene clusters in microorganisms associated with the marine sponge Discodermia dissoluta. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4840–4849
Schmidt EW, Obraztsova AY, Davidson SK, Faulkner DJ, Haygood MG (2000) Identification of the antifungal peptide-containing symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei as a novel δ-proteobacterium, “CandidatusEntheonella palauensis”. Mar Biol 136:969–977
Schmidt EW, Nelson JT, Rasko DA, Sudek S, Eisen JA, Haygood MG, Ravel J (2005) Patellamide A and C biosynthesis by a microcin-like pathway in Prochloron didemni, the cyanobacterial symbiont of Lissoclinum patella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7315–7320
Sipkema D, Franssen MCR, Osinga R, Tramper J, Wijffels RH (2005) Marine sponges as pharmacy. Mar Biotechnol 7:142–162
Taylor MW, Schupp PJ, Dahllof I, Kjelleberg S, Steinberg PD (2004) Host specificity in marine-associated bacteria, and potential implications for marine microbial diversity. Environ Microbiol 6:121–130
Taylor MW, Schupp PJ, de Nys R, Kjelleberg S, Steinberg PD (2005) Biogeography of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Cymbastela concentrica. Environ Microbiol 7:419–433
Thoms C, Horn M, Wagner M, Hentschel U, Proksch P (2003) monitoring microbial diversity and natural product profiles of the sponge Aplysina cavernicola following transplantation. Mar Biol 142:685–692
Unson MD, Holland ND, Faulkner DJ (1994) A brominated secondary metabolite synthesized by the cyanobacterial symbiont of a marine sponge and accumulation of the crystalline metabolite in the sponge tissue. Mar Biol 119:1–11
Usher KM, Fromont J, Sutton DC, Toze S (2004) The biogeography and phylogeny of unicellular cyanobacterial symbionts in sponges from Australia and the Mediteranean. Microb Ecol 48:167–177
Vacelet J, Donadey C (1977) Electron microscope study of the association between some sponges and bacteria. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 30:301–314
Vacelet J, Fialamedioni A, Fisher CR, Bouryesnault N (1996) Symbiosis between methane-oxidizing bacteria and a deep-sea carnivorous cladorhizid sponge. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 145:77–85
Wang G (2006) Diversity and biotechnological potential of the sponge associated microbial consortia. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 33:545–551
Wang GY, Graziane E, Waters B, Pan W, Li X, McDermott J, Meurer G, Saxena G, Anderson RJ, Davies J (2000) Novel natural products from soil DNA libraries in a streptomycete host. Org Lett 2:2401–2404
Webster NS, Hill RT (2001) The culturable microbial community of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeidesodorabile is dominated by an alpha-proteobacterium. Mar Biol 138:843–851
Webster NS, Watts JEM, Hill RT (2001a) Detection and phylogenetic analysis of novel crenarchaeote and euryarchaeote 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences from a Great Barrier Reef sponge. Mar Biotechnol 3:600–608
Webster NS, Wilson KJ, Blackall LL, Hill RT (2001b) Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:434–444
Webster NS, Negri AP, Munro MMHG, Bettershill CN (2004) Diverse microbial communities inhabit Antartic sponges. Env Microbiol 6:288–300
Wenzel SC, Gross F, Zhang Y, Fu J, Stewart AF, Muller R (2005) Heterologous expression of a myxobacterial natural products assembly line in pseudomonads via red/ET recombineering. Chem Biol 12:349–356
Wilkinson CR, Nowak M, Austin B, Colwell RR (1981) Specificity of bacterial symbionts in Mediterranean and Great Barrier Reef Australia sponges. Microb Ecol 7:13–22
Yurkov VV, Beatty JT (1998) Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Bio Rev 62:695–724
Zhang H, Lee YK, Zhang W, Lee HK (2006) Culturable actinobacteria from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perleve: isolation and phylogenetic diversity by 16S rRNA gene–RFLP analysis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 90:159–169
Acknowledgements
JK is in receipt of a Marie Curie Transfer of Knowledge Host Fellowship (grant no. MTKD-CT-2006-042062). The authors acknowledge a receipt of funding from the Marine Institute in Ireland under the “Biodiscovery Programme” for work in this area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennedy, J., Marchesi, J.R. & Dobson, A.D.W. Metagenomic approaches to exploit the biotechnological potential of the microbial consortia of marine sponges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 11–20 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0875-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0875-2