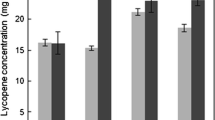
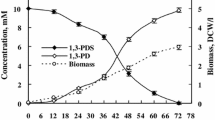
Abstract
Carvone has previously been found to highly inhibit its own production at concentrations above 50 mM during conversion of a diastereomeric mixture of (−)-carveol by whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis. Adaptation of the cells to the presence of increasing concentrations of carveol and carvone in n-dodecane prior to biotransformation proved successful in overcoming carvone inhibition. By adapting R. erythropolis cells for 197 h, an 8.3-fold increase in carvone production rate compared to non-adapted cells was achieved in an air-driven column reactor. After an incubation period of 268 h, a final carvone concentration of 1.03 M could be attained, together with high productivity [0.19 mg carvone h−1 (ml organic phase)−1] and high yield (0.96 g carvone g carveol−1).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth IR (2002) Stress and the single cell: intrapopulation diversity is a mechanism to ensure survival upon exposure to stress. Int J Food Microbiol 78:19–30
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2002a) Influence of reactor configuration on the production of carvone from carveol by whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. J Mol Catal B Enzym 19–20:377–387
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2002b) Maintenance of cell viability in the biotransformation of (−)-carveol with whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis. J Mol Catal B Enzym 19–20:389–398
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2003) A simple method to observe organic solvent drops with a standard optical microscope. Microsc Res Tech 60:465–466
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2004a) Solvent toxicity in organic-aqueous systems analysed by multivariate analysis. Bioprocess Biosyst 26:361–375
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2004b) Principal component analysis applied to bacterial cell behaviour in the presence of organic solvents. Biocatal Biotransform 22:203–214
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2005a) Degradation of hydrocarbons and alcohols at different temperatures and salinities by Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51:389–399
Carvalho CCCR de, da Fonseca MMR (2005b) Carvone: why and how should one bother to produce this terpene. Food Chem (in press) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.01.003
Carvalho CCCR de, van Keulen F, da Fonseca MMR (2000) Production and recovery of limonene-1,2-diol and simultaneous resolution of a diastereomeric mixture of limonene-1,2-epoxide with whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. Biocatal Biotransform 18:223–235
Carvalho CCCR de, van Keulen F, da Fonseca MMR (2002) Modelling the bio-kinetic resolution of diastereomers present in unequal initial amounts. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 13:1637–1643
Carvalho CCCR de, Cruz A, Pons MN, Pinheiro HM, Cabral JMS, da Fonseca MMR, Fernandes P, Ferreira BS (2004) Mycobacterium sp., Rhodococcus erythropolis and Pseudomonas putida behaviour in the presence of organic solvents. Microsc Res Tech 64:215–222
Carvalho CCCR de, Parreño-Marchante B, Neumann G, da Fonseca MMR, Heipieper HJ (2005) Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 to growth on n-alkanes, alcohols and terpenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (in press) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1750-z
Fichan I, Larroche G, Gros JB (1999) Water solubility, vapor pressure and activity coefficients of terpenes and terpenoids. J Chem Eng Data 44:56–62
Friedman M, Henika PR, Mandrell RE (2002) Bactericidal activities of plant essential oils and some of their isolated constituents against Campylobacter jejuni, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella enterica. J Food Prot 65:1545–1560
Genoni GP, Behra R, Montague CL, Güttinger H, Ternay-Aegerter R (2001) Complex dynamics of adaptation in a nonaxenic microcystis culture. 1. Effects of dinitrophenol on population growth. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:235–240
Gilbert P, Brown MRW (1995) Mechanisms of the protection of bacterial biofilms from antimicrobial agents. In: Lappin-Scott H, Costerton JW (eds) Microbial Biofilms. Cambridge University, Cambridge, UK, pp 118–130
Jirovetz L, Buchbauer G, Stoyanova AS, Georgiev EV, Damianova ST (2003) Composition, quality control, and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of long-time stored dill (Anethum graveolens L.) seeds from Bulgaria. J Agric Food Chem 51:3854–3857
Kieboom J, Dennis JJ, Zylstra GJ, de Bont JAM (1998) Active efflux of organic solvents by Pseudomonas putida S12 is induced by solvents. J Bacteriol 180:6769–6772
Ma JF, Hager PW, Howell ML, Phibbs PV, Hassett D (1998) Cloning and characterization of the Pseudomonas aeroginosa zwf gene encoding glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme important in tolerance to methyl viologen (paraquat). J Bacteriol 180:1741–1749
Montague CL, Behra R, Bosma TNP, Genoni GP, Güttinger H (2001) Complex dynamics of adaptation in a nonaxenic microcystis culture. 2. Computer simulation of dinitrophenol effects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:241–254
Mulvey M, Diamond SA (1991) Genetic factors and tolerance acquisition in populations exposed to metals and metalloids. In: Newman MC, McIntosh AW (eds) Metal Ecotoxicology. Lewis, Chelsea, Mich., pp 301–321
Pieper DH, Reineke W (2000) Engineering bacteria for bioremediation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:262–270
Sardessai Y, Bhosle S (2002) Tolerance of bacteria to organic solvents. Res Microbiol 153:263–268
Sonnleitner B (1998) Dynamic adaptation of microbes. J Biotechnol 65:47–60
Tecelão CSR, van Keulen F, da Fonseca MMR (2001) Development of a reaction system for the selective conversion of (−)-trans-carveol to (−)-carvone with whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. J Mol Catal B Enzym 11:725–731
Werf MJ van der, van der Ven C, Barbirato F, Eppink MHM, de Bont JAM, van Berkel JH (1999a) Stereoselective carveol dehydrogenase from Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14-A novel nicotinoprotein belonging to the short chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily. J Biol Chem 274:26296–26304
Werf MJ van der, Swarts HJ, de Bont JAM (1999b) Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 contains a novel degradation pathway for limonene. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2092–2102
Whyte LG, Slagman SJ, Pietrantonio F, Bourbonnière L, Koval SF, Lawrence JR, Inniss WE, Greer CW (1999) Physiological adaptations involved in alkane assimilation at a low temperature by Rhodococcus sp. strain Q15. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2961–2968
Wiegant WM, de Bont JAM (1980) A new route for ethylene glycol metabolism in Mycobacterium E44. J Gen Microbiol 120:325–331
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Ph.D. (PRAXIS XXI/BD/21574/99) and a post-doctoral grant (SFRH/BPD/14426/2003) awarded to Carla da C. C. R. de Carvalho by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal and by a SOCRATES- ERASMUS grant awarded to Alessandro Poretti.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Carvalho, C.C.C.R., Poretti, A. & da Fonseca, M.M.R. Cell adaptation to solvent, substrate and product: a successful strategy to overcome product inhibition in a bioconversion system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69, 268–275 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-1967-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-1967-5