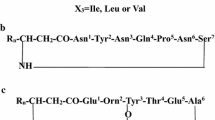Abstract
A soil microorganism identified as Bacillum megaterium was found to produce several antibiotics substances after growth for 20 h at 37°C in a mineral culture medium. Analysis both by electron spray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization—time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) identified these substances as lipopeptides. Predominant peaks at m/z 1,041 and m/z 1,065 revealed ions which are compatible with surfactins and lichenysins, respectively. Two other ions m/z 1,057 and m/z 1,464 were further studied by collision-induced dissociation (CID) unveiling an iturin A at the first and fengycins A and B at the second m/z peaks. The CID spectrum of the m/z 1,464 ion also suggests the existence of fengycins A and B variants in which Ile was changed to Val in the position 10 of the peptide moiety. Raw mixtures of all these compounds were also assayed for antibiotic features. The data enlighten the unusual diversity of the lipopeptide mixture produced by a sole Bacillus species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, synthesis and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56:845–857
González-Pastor JE, Hobbs EC, Losick R (2003) Cannibalism by sporulating bacteria. Science 301:510–513
Kakinuma A, Sugino H, Isono M, Tamura G, Arima K (1969) Determination of fatty acid in surfactin and elucidation of the total structure of surfactin. Agric Biol Chem 33:973–976
Isogai A, Takayama S, Murakoshi S, Suzuki A (1982) Structures of α-amino acids in antibiotic iturin A. Tetrahedron Lett 23:3065–3068
Peypoux F, Guinand M, Michel G, Delcambe L, Das BC, Lederer E (1978) Structure of iturin A, a peptidolipid antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry 17:3992–3996
Jenny K, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1991) Biosurfactants from Bacillus licheniformis: structural analysis and characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:5–13
Yakimov MM, Abraham W-R, Meyer H, Giuliano L, Golyshin PN (1999) Structural characterization of lichenysin A components by fast atom bombardment tandem mass spectrometry. Biochim Biophys Acta 1438:273–280
Grangemard I, Bonmartin J-M, Bernillon J, Das BC, Peypoux F (1999) Lichenysins G, a novel family of lipopeptide biosurfactants from Bacillus licheniformis IM 1307: production, isolation and structural evaluation by NMR and mass spectrometry. J Antibiotics 52:363–373
Vanittanakom N, Loeffler W, Koch U, Jung G (1986) Fengycin, a novel antifungal lipopeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis F-29–3. J Antibiot 39:888–901
Schneider J, Taraz K, Budzikiewicz H, Deleu M, Thonart P, Jacques P (1999) The structure of two fengycins from Bacillus subtilis S499. Z Naturforsch 54:859–866
Naruse N, Tenmyo O, Kobaru S, Kamei H, Miyaki T, Konishi M, Oki T (1990) Pumilacidin, a complex of new antiviral antibiotics. J Antibiot 43:267–280
Hasumi K, Takizawa K, Takahashi F, Park JJ, Endo A (1995) Inhibition of acyl-CoA: cholesterol acytransferase by isohalobacillin, a complex o novel cyclic acypeptides produced by Bacillus sp. A1238. J Antibiot 48:1419–1425
Besson F, Peypoux F, Quentin MJ, Michel G (1984) Action of antifungal peptidolipids from Bacillus subtilis on the cell membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisae. J Antibiot 37:172–177
Latoud C, Peypoux F, Michel G (1987) Action of iturin A, an antifungal antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae. Modifications of membrane permeability and lipid composition. J Antibiot 40:1588–1595
Mikkola R, Kolari M, Andersson MA, Helin J, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2000) Toxic lactonic lipopeptide from food poisoning isolates of Bacillus licheniformis. Eur J Biochem 267:4068–4074
Vaara M (1992) Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol Rev 56:395–411
Hancock REW (1997) The bacterial outer membrane as drug barrier. Trends Microbiol 5:37–42
Poole K (2000) Efflux mediated resistance to fluoroquinolones in Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:2233–2241
Poole K (2001) Multidrug efflux pumps and antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related organisms. J Mol Microbiol Biotech 3:255–264
Hagelin G, Oulie I, Raknes A, Udheim K, Clausen OG (2004) Preparative high-performance liquid chromatographic separation and analysis of the Maltacin complex—a family of cyclic peptide antibiotics from Bacillus subtilis. J Chromatogr B 811:243–251
Hagelin G (2005a) Structure investigation of maltacine B1a, B1b, B2a and B2b: cyclic peptide lactones of the maltacine complex from Bacillus subtilis. J Mass Spectrom 40:527–538
Hagelin G (2005b) Structure investigation of maltacine C1a, C1b, C2a and C2b—cyclic peptide lactones of the maltacine complex from Bacillus subtilis. J Mass Spectrom 40:1276–1286
Hagelin G (2005c) Structure investigation of maltacine D1a, D1b and D1c—cyclic peptide lactones of the maltacine complex from Bacillus subtilis. J Mass Spectrom 40:1287–1299
Thimon L, Peypoux F, Maget-Dana R, Roux B, Michel G (1992) Interactions of bioactive lipopeptides, iturin A and surfactin from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 16:144–151
Koumoutsi A, Chen X-H, Henne A, Liesegang H, Hitzeroth G, Franke P, Vater J, Borriss R (2004) Structural and functional characterization of gene clusters directing nonribosomal synthesis of bioactive cyclic lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FZB42. J Bacteriol 186:1084–1096
Rouser G, Fleischer S, Yamamoto A (1970) Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorous analysis of spots. Lipids 5:494–496
Maget-Dana R, Peypoux F (1994) Iturins, a special class of pore-forming lipopeptides: biological and physicochemical properties. Toxicology 87:151–174
Lichtemberg D, Robson RJ, Dennis EA (1983) Solubilization of phospholipid detergents. Structural and kinetic aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta 737:285–304
Smith R, Tanford C (1972) The critical micelle concentration of L-α-palmitoylphosphatidylcholine in water and in water/methanol. J Mol Biol 67:75–83
Williams BH, Hathout Y, Fenselau C (2002) Structural characterization of lipopeptide biomarkers isolated from Bacillus globigii. J Mass Spectrom 37:259–264
Bode HB, Bethe B, Höfs R, Zeek A (2002) Big effects from small changes: possible ways to explore nature’s chemical diversity. Chem Bio Chem 3:619–627
Wessjohann LA, Ruijter E, Garcia-Rivera D, Brandt W (2005) What can a chemist learn from nature’s macrocycles? A brief conceptual view. Mol Divers 3:171–186
Biemann K (1990) Nomenclature for peptide fragment ions (positive ions). Methods Enzymol 193:886–887
Madonna AJ, Voorhees KJ, Taranenko NI, Laiko VV, Doroshenko VM (2003) Detection of cyclic lipopeptide biomarkers from Bacillus species using atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorbtion/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75:1628–1637
Pabel CT, Vater J, Wilde C, Franke P, Hofemeister J, Adler, Bringmann G, Hacker J, Hentschel U (2003) Antimicrobial activities and mass-assisted laser desorbtion/ionization mass spectrometry of Bacillus isolates from the marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Mar Biotechnol 5:424–434
Wang J, Liu J, Wang X, Yao J, Yu Z (2004) Application of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in rapid ty** of fengycin homologues produced by Bacillus subtilis. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:98–102
Akpa E, Jacques P, Wathelet B, Paquot M, Fuchs R, Budzikiewicz H, Thonart P (2001) Influence of culture conditions on lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 91–93:551–561
Frank G, Torsten HS, Barvel K, Peter F, Joachim V (1999) Rapid ty** of Bacillus subtilis strains by the secondary metabolites using matrix—assisted laser desorbtion/ionization mass spectrometry of intact cells. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 13:943–949
Opsteen JA, Cornelissen J, van Hest JCM (2004) Block copolymer vesicles. Pure Appl Chem 76:1309–1319
Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Babin J, Zappone B, Lecommandoux S (2005) Preparation of shell cross-linked nano-objects from hybrid peptide block copolymers. Biomacromolecules 6:2213–2220
Discher DE, Eisenberg A (2002) Polymer vesicles. Science 297:967–973
Vary PS (1994) Prime time for Bacillus megaterium. Microbiology 140:1001–1013
Vary PS, Biedendieck R, Fuerch T, Meinhardt F, Rohde M, Deckwer W-D, Jahn D (2007) Bacillus megaterium—from simple soil bacterium to industrial protein production host. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:957–967
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Fernanda Manso Prado, Izaura Nobuko Toma, and Sirlei Mendes de Oliveira for technical assistance. Financial support was from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP, grant No 98/11480-1) and from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, grant No 473145/2006-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pueyo, M.T., Bloch, C., Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. et al. Lipopeptides Produced by a Soil Bacillus Megaterium Strain. Microb Ecol 57, 367–378 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9464-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9464-x