Abstract
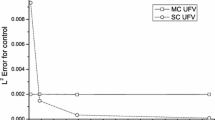
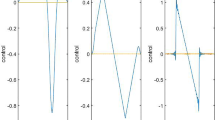
We consider the optimal control of a system governed by the Navier–Stokes equations with stochastic Dirichlet boundary conditions. Control conditions imposed only on the boundary are associated with reduced regularity of the system, as compared to distributed controls. To ensure the well-posedness of the solutions and the efficiency of numerical simulations, the stochastic boundary conditions and controls are required to belong almost surely to the Sobolev space of functions having first order weak derivative along the boundary. To simulate the system, numerical solutions are approximated using the stochastic collocation/finite element approach with sparse grid techniques and Monte Carlo methods which are applied to the boundary random field. An optimality system is derived for a matching-type cost functional. Error estimates are derived for the optimal state, the adjoint state and boundary control variables. Numerical examples for the deterministic cases are provided and compared in which the controls are applied on a part of or on the whole boundary. Simulations for the stochastic cases are also made with sparse grid and Monte Carlo methods to retrieve the statistical information of the optimal solution.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuška, I., Tempone, R., Zouraris, G.E.: Galerkin finite element approximations of stochastic elliptic partial differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(2), 800–825 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1137/S0036142902418680
Babuška, I., Nobile, F., Tempone, R.: A stochastic collocation method for elliptic partial differential equations with random input data. SIAM Rev. 52(2), 317–355 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1137/100786356
Balay, S., Abhyankar, S., Adams, M.F., Brown, J., Brune, P., Buschelman, K., Dalcin, L., Eijkhout, V., Gropp, W.D., Kaushik, D., Knepley, M.G., McInnes, L.C., Rupp, K., Smith, B.F., Zampini, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, H.: PETSc web page (2016). http://www.mcs.anl.gov/petsc
Das, S., Ghanem, R., Spall, J.C.: Asymptotic sampling distribution for polynomial chaos representation from data: a maximum entropy and Fisher information approach. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 30(5), 2207–2234 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1137/060652105
De los Reyes, J.C.: Numerical PDE-constrained optimization. In: Springer Briefs in Optimization. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13395-9
Desceliers, C., Ghanem, R., Soize, C.: Maximum likelihood estimation of stochastic chaos representations from experimental data. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 66(6), 978–1001 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1576
Eldred, M., Burkardt, J.: Comparison of non-intrusive polynomial chaos and stochastic collocation methods for uncertainty quantification. AIAA Pap. 976(2009), 1–20 (2009)
Flandoli, F., Gatarek, D.: Martingale and stationary solutions for stochastic Navier–Stokes equations. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 102(3), 367–391 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01192467
Fursikov, A., Gunzburger, M., Hou, L.S., Manservisi, S.: Optimal control problems for the Navier-Stokes equations. In: Lectures on Applied Mathematics (Munich, 1999), pp. 143–155. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Gerstner, T., Griebel, M.: Numerical integration using sparse grids. Numer. Algorithms 18(3–4), 209–232 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019129717644
Griebel, M., Schneider, M., Zenger, C.: A combination technique for the solution of sparse grid problems. In: Iterative Methods in Linear Algebra (Brussels, 1991), pp. 263–281. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1992)
Gunzburger, M.: Sensitivities in computational methods for optimal flow control. In: Computational Methods for Optimal Design and Control (Arlington, VA, 1997). Progress in Systems and Control Theory, vol. 24, pp. 197–236. Birkhäuser, Boston (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1780-0_12
Gunzburger, M.D.: Perspectives in flow control and optimization. In: Advances in Design and Control, vol. 5. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (2003)
Gunzburger, M.D., Hou, S.L.: Treating inhomogeneous essential boundary conditions in finite element methods and the calculation of boundary stresses. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(2), 390–424 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1137/0729024
Gunzburger, M.D., Manservisi, S.: The velocity tracking problem for Navier–Stokes flows with boundary control. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 39(2), 594–634 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1137/S0363012999353771
Gunzburger, M., Trenchea, C.: Analysis of an optimal control problem for the three-dimensional coupled modified Navier–Stokes and Maxwell equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 333(1), 295–310 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2006.10.053
Gunzburger, M.D., Hou, L.S., Svobodny, T.P.: Analysis and finite element approximation of optimal control problems for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations with Dirichlet controls. RAIRO Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. 25(6), 711–748 (1991)
Heroux, M.A., Bartlett, R.A., Howle, V.E., Hoekstra, R.J., Hu, J.J., Kolda, T.G., Lehoucq, R.B., Long, K.R., Pawlowski, R.P., Phipps, E.T., Salinger, A.G., Thornquist, H.K., Tuminaro, R.S., Willenbring, J.M., Williams, A., Stanley, K.S.: An overview of the Trilinos Project. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 31(3), 397–423 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1089014.1089021
Lions, J.L.: Optimal control of systems governed by partial differential equations. Translated from the French by S. K. Mitter. Die Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften, Band 170. Springer, New York (1971)
Mikulevicius, R., Rozovskii, B.L.: Global \(L_2\)-solutions of stochastic Navier–Stokes equations. Ann. Probab. 33(1), 137–176 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1214/009117904000000630
Nobile, F., Tempone, R., Webster, C.G.: A sparse grid stochastic collocation method for partial differential equations with random input data. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46(5), 2309–2345 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1137/060663660
Tröltzsch, F.: Optimal control of partial differential equations. In: Graduate Studies in Mathematics, vol. 112. American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI (2010). https://doi.org/10.1090/gsm/112. Theory, methods and applications, Translated from the 2005 German original by Jürgen Sprekels
Tröltzsch, F., Wachsmuth, D.: Second-order sufficient optimality conditions for the optimal control of Navier–Stokes equations. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 12(1), 93–119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1051/cocv:2005029
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Wenju Zhao was Supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. 12001325. Max Gunzburger was Supported in part by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research Grant FA9550-15-1-0001.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Gunzburger, M. Stochastic Collocation Method for Stochastic Optimal Boundary Control of the Navier–Stokes Equations. Appl Math Optim 87, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-022-09910-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-022-09910-y
Keywords
- Optimal control
- Stochastic Navier–Stokes equations
- Stochastic boundary condition
- Necessary condition for optimality